Castile or Castille is a territory of imprecise limits located in Spain. The use of the concept of Castile relies on the assimilation of a 19th-century determinist geographical notion, that of Castile as Spain's centro mesetario with a long-gone historical entity of diachronically variable territorial extension.

Murcia is a city in south-eastern Spain, the capital and most populous city of the autonomous community of the Region of Murcia, and the seventh largest city in the country. It had a population of 460,349 inhabitants in 2021. The total population of the metropolitan area is 672,773 in 2020, covering an urban area of 1,230.9 km2. It is located on the Segura River, in the southeast of the Iberian Peninsula. It has a climate with hot summers, mild winters, and relatively low precipitation.

Albacete is a province of central Spain, in the southern part of the autonomous community of Castile–La Mancha. As of 2012, Albacete had a population of 402,837 people. Its capital city, also called Albacete, is 262 kilometres (163 mi) by road southeast of Madrid.

The Kingdom of Aragon was a medieval and early modern kingdom on the Iberian Peninsula, corresponding to the modern-day autonomous community of Aragon, in Spain. It should not be confused with the larger Crown of Aragon, which also included other territories—the Principality of Catalonia, the Kingdom of Valencia, the Kingdom of Majorca, and other possessions that are now part of France, Italy, and Greece—that were also under the rule of the King of Aragon, but were administered separately from the Kingdom of Aragon.

The Crown of Aragon was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of Barcelona and ended as a consequence of the War of the Spanish Succession. At the height of its power in the 14th and 15th centuries, the Crown of Aragon was a thalassocracy controlling a large portion of present-day eastern Spain, parts of what is now southern France, and a Mediterranean empire which included the Balearic Islands, Sicily, Corsica, Sardinia, Malta, Southern Italy and parts of Greece.

San Pedro del Pinatar is a small town and municipality in the Region of Murcia, southeastern Spain. The municipality is situated at the northern end of Murcia's Mediterranean coastline, the Costa Cálida, and borders the province of Alicante. It has an area of almost 22 km2, and a population of 25,167 as of 2018.

Jumilla is a town and a municipality in southeastern Spain. It is located in the north east of the Region of Murcia, close to the towns of Cieza and Yecla. According to the 2018 census, the town population was 25,547.

The Crown of Castile was a medieval polity in the Iberian Peninsula that formed in 1230 as a result of the third and definitive union of the crowns and, some decades later, the parliaments of the kingdoms of Castile and León upon the accession of the then Castilian king, Ferdinand III, to the vacant Leonese throne. It continued to exist as a separate entity after the personal union in 1469 of the crowns of Castile and Aragon with the marriage of the Catholic Monarchs up to the promulgation of the Nueva Planta decrees by Philip V in 1715.

Both the perceived nationhood of Spain, and the perceived distinctions between different parts of its territory derive from historical, geographical, linguistic, economic, political, ethnic and social factors.

The Region of Murcia is an autonomous community of Spain located in the southeastern part of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Mediterranean coast. The region is 11,313 km2 (4,368 sq mi) in area and had a population of 1,511,251 as at the start of 2020. About a third of its population lives in the capital, Murcia, and a seventh in the second city, Cartagena. At 2,014 m (6,608 ft), the region's highest point is Los Obispos Peak in the Massif of Revolcadores.

The Four Kingdoms of Andalusia was a collective name designating the four kingdoms of the Crown of Castile located in the southern Iberian Peninsula, south of the Sierra Morena. These kingdoms were annexed from other states by the Kingdoms of Castille during the Reconquista: the Kingdom of Córdoba was conquered in 1236, the Kingdom of Jaén in 1246, the Kingdom of Seville in 1248 and the Kingdom of Granada in 1492.

The Kingdom of Granada was a territorial jurisdiction of the Crown of Castile from the conclusion of the Reconquista in 1492 until Javier de Burgos' provincial division of Spain in 1833. This was a "kingdom" ("reino") in the second sense given by the Diccionario de la lengua española de la Real Academia Española: the Crown of Castile consisted of several such kingdoms. Its extent is detailed in Gelo del Cabildo's 1751 Respuestas Generales del Catastro de Ensenada (1750–54), which was part of the documentation of a census. Like the other kingdoms within Spain, the Kingdom of Granada was abolished by the 1833 territorial division.

The Kingdom of Jaén was a territorial jurisdiction of the Crown of Castile since 1246 and until Javier de Burgos' provincial division of Spain in 1833. This was a "kingdom" in the second sense given by the Diccionario de la lengua española de la Real Academia Española: the Crown of Castile consisted of several such kingdoms. Known also as the "Santo Reino", its territory coincided roughly with the present-day province of Jaén. Jaén was one of the Four Kingdoms of Andalusia. Its extent is detailed in Respuestas Generales del Catastro de Ensenada (1750–54), which was part of the documentation of a census.
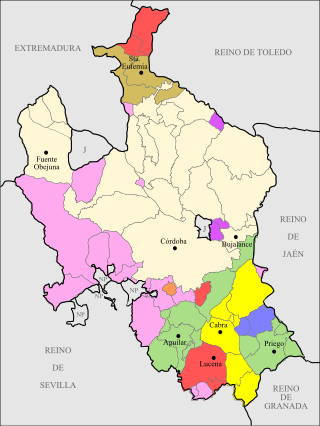
The Kingdom of Córdoba was a territorial jurisdiction of the Crown of Castile since 1236 until Javier de Burgos' provincial division of Spain in 1833. This was a "kingdom" in the second sense given by the Diccionario de la lengua española de la Real Academia Española: the Crown of Castile consisted of several such kingdoms. Córdoba was one of the Four Kingdoms of Andalusia. Its extent is detailed in Respuestas Generales del Catastro de Ensenada (1750-54), which was part of the documentation of a census.

The Kingdom of Seville was a territorial jurisdiction of the Crown of Castile since 1248 until Javier de Burgos' provincial division of Spain in 1833. This was a "kingdom" ("reino") in the second sense given by the Diccionario de la lengua española de la Real Academia Española: the Crown of Castile consisted of several such kingdoms. Seville was one of the Four Kingdoms of Andalusia. Its extent is detailed in Respuestas Generales del Catastro de Ensenada (1750–54), which was part of the documentation of a census. Falling largely within the present day autonomous community of Andalucia, it included roughly the territory of the present-day provinces of Huelva, Seville, and Cádiz, the Antequera Depression in the present-day province of Málaga, and also some municipalities in the present-day autonomous communities of Extremadura in the province of Badajoz.

The 1822 territorial division of Spain was a rearrangement of the territory of Spain into various provinces, enacted briefly during the Trienio Liberal of 1820–1823. It is remembered today largely as a precursor to the similar 1833 territorial division of Spain; the provinces established in the latter remain, by and large, the basis for the present-day division of Spain into provinces.

The Battle of Los Alporchones was a battle of the Spanish Reconquista that took place on 17 March 1452. The battle was fought between the troops of the Emirate of Granada and the combined forces of the Kingdom of Castile and its client kingdom, the Kingdom of Murcia. The Moorish army was commanded by Malik ibn al-Abbas and the Castilian troops were commanded by Alonso Fajardo el Bravo, the head of the House of Fajardo and the Alcalde of Lorca Castle. The battle was fought in the area around the city of Lorca and resulted in a victory for the Kingdom of Castile.

This is the results breakdown of the Congress of Deputies election held in Spain on 1 March 1979. The following tables show detailed results in each of the country's 17 autonomous communities and in the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, as well as a summary of constituency and regional results.

The first instance of a figure of the lion as symbol of the Kingdom of León is found in minted coins of Alfonso VII, called the Emperor (1126–1157). Until then, the cross had a preponderant position on documents and coins of Leonese monarchs since that reign the cross was gradually displaced by the lion. The Spanish historian and heraldist Martín de Riquer explained that the lion was already used as heraldic emblem in 1148. At the end of the reign of Alfonso VII, the figure of this animal began to appear on royal documents as personal device of the monarch and became pervasive during reigns of Ferdinand II (1157-1188) and Alfonso IX (1188-1230).

The current configuration of the province of Granada is the result of a long process of territorial organization that reached its culmination in 1833, by means of the decree of provincialization promulgated by Javier de Burgos, Ministry of Development of the government of the regent Maria Christina of Bourbon. Until that date, what now constitutes the province of Granada was integrated within the limits of the so-called Kingdom of Granada.





















