
The Solway Firth is a firth that forms part of the border between England and Scotland, between Cumbria and Dumfries and Galloway. It stretches from St Bees Head, just south of Whitehaven in Cumbria, to the Mull of Galloway, on the western end of Dumfries and Galloway. The Isle of Man is also very near to the firth. The firth comprises part of the Irish Sea.

Dumfries and Galloway is one of 32 unitary council areas of Scotland and is located in the western Southern Uplands. It comprises the historic counties of Dumfriesshire, Kirkcudbrightshire, and Wigtownshire, the latter two of which are collectively known as Galloway. The administrative centre and largest settlement is the town of Dumfries. The second largest town is Stranraer, 75 miles to the west on the Irish Sea coast.

The River Dee, in south-west Scotland, flows from its source in Loch Dee amongst the Galloway Hills, firstly to Clatteringshaws Loch, then into Loch Ken, where it joins the Water of Ken. From there, the Dee flows 15 miles (24 km) southwards to Kirkcudbright, and into Kirkcudbright Bay to reach the Solway Firth. The distance is just over 38 miles (61 km) in total. Together with its tributaries, the Dee's total catchment area is over 400 square miles (1,000 km2).
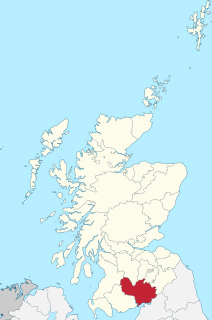
Dumfriesshire or the County of Dumfries is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of southern Scotland.

The River Nith is a river in south-west Scotland. The Nith rises in the Carsphairn hills of East Ayrshire, more precisely between Prickeny Hill and Enoch Hill, 4.4 miles (7.1 km) east of Dalmellington. For the majority of its course it flows in a south-easterly direction through Dumfries and Galloway and then into the Solway Firth at Airds Point.

The River Esk, also known as the Border Esk, is a river in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, that enters the English county of Cumbria and flows into the Solway Firth.
The Vale of Eden is formed by the course of the River Eden, one of the major rivers of Northwest England. It is however of much greater extent than the actual valley of the river, lying between the Cumbrian Mountains, and the northern part of the Pennine Range. It lies entirely within the county of Cumbria. The river has its source in the peat bogs below Hugh Seat, in the dale of Mallerstang. At first it determinedly sets off South before turning back North for the rest of its course – except just before its outlet into the sea which it enters from the East.

The Water of Luce is a river in Dumfries and Galloway, in south west Scotland.

Urr Water or River Urr is a river in which flows through the counties of Dumfriesshire and Kirkcudbrightshire in southwest Scotland.

The Solway Coast is a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty in northern Cumbria, United Kingdom. It incorporates two areas of coastline along the Solway Firth, the first running from just north of the city of Carlisle, at the estuary of the rivers Esk and Eden, in a westerly direction as far as Silloth-on-Solway, including the villages of Bowness-on-Solway, Burgh-by-Sands, Port Carlisle, and Skinburness. The second area begins just north of the hamlet of Beckfoot, and runs south down the coast to the southern end of Allonby Bay near the village of Crosscanonby. Included in this area are the villages of Mawbray and Allonby, and the hamlets of Dubmill, Hailforth and Salta. The hamlet of Wolsty lies just outside the AONB. Beginning at Silloth, the B5300 coast road runs in a south-westerly direction, entering the AONB just north of Beckfoot, and exiting near Crosscanonby.

The Solway Plain or Solway Basin is a coastal plain located mostly in northwest Cumbria in England, extending just over the Scottish border to the low-lying area around Gretna and Annan. It lies generally north and west of Carlisle along the Solway Firth, and is drained by the rivers Esk and Lyne. It is associated with the westernmost part of Hadrian's Wall. In medieval times, clay houses known as dabbins were commonly built on the Solway Plain. The Solway coast has been designated an “Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty”.

The Solway Junction Railway was built by an independent railway company to shorten the route from ironstone mines in Cumberland to ironworks in Lanarkshire and Ayrshire.

Abbey Junction railway station was the railway junction where the branch line to Silloth on the Solway Firth divided from the Solway Junction Railway in the English county of Cumberland.

Coggabata, or Congavata / Concavata, was a Roman fort on Hadrian's Wall, between Aballava to the east and Mais (Bowness-on-Solway) to the west. It was built on a hill commanding views over the flatter land to the east and west and to the shore of the Solway Firth to the north. Its purpose was to guard the southern end of two important Solway fords, the Stonewath and the Sandwath.
The Kirtlebridge rail crash took place in 1872 at Kirtlebridge railway station in Dumfriesshire. An express passenger train ran into a goods train that was shunting; 11 people lost their lives immediately, and one further person succumbed later. The cause was a failure to communicate between the station master in charge of the shunting operation, and the signalman. There was not full interlocking of the points, and the block system of signalling was not in use.

Kirkpatrick-Fleming is a village and civil parish in Dumfries and Galloway, south-west Scotland.

Bowness was a station which served Bowness-on-Solway, a village in Cumbria on the English side of the Solway Firth. The station opened on 8 August 1870 by the Caledonian Railway on a line constructed from the Caledonian Railway Main Line at Kirtlebridge across the Glasgow South Western Line, then forming the Solway Junction Railway over the Solway Viaduct to Brayton. The line opened in 1869 and freight had run since 13 September 1869.

Allonby Bay is a crescent-shaped bay of the Solway Firth on the north-western shore of Cumbria, England. The bay is 5.5 miles (8.9 km) across. Its northern point is at Dubmill, between the village of Mawbray and the hamlet of Salta, and its southern end is just to the north of Maryport, near the village of Crosscanonby. The B5300 coast road follows the shoreline of Allonby Bay, running between Silloth in the north and Maryport in the south.

The Black Dub is a stream in Cumbria, United Kingdom. It rises to the west of the village of Langrigg, in the civil parish of Bromfield, where it is known as Dub Stangs, and flows west past Scroggs Wood and the village of Westnewton. As it passes near the hamlets of New Cowper and Edderside it forms the southern boundary of the civil parish of Holme St. Cuthbert, and the northern boundary of the civil parish of Allonby, before entering the Solway Firth at Dubmill, at the northern end of Allonby Bay. It is seven miles in length.

The Carlisle Canal opened in 1823, to link Carlisle to the Solway Firth, to facilitate the transport of goods to and from the city. It was a short-lived venture, being replaced by a railway which used the canal bed for most of its route in 1854.


















