
The Baudot code is an early character encoding for telegraphy invented by Émile Baudot in the 1870s. It was the predecessor to the International Telegraph Alphabet No. 2 (ITA2), the most common teleprinter code in use before ASCII. Each character in the alphabet is represented by a series of five bits, sent over a communication channel such as a telegraph wire or a radio signal by asynchronous serial communication. The symbol rate measurement is known as baud, and is derived from the same name.

Electrical telegraphs were point-to-point text messaging systems, primarily used from the 1840s until the late 20th century. It was the first electrical telecommunications system and the most widely used of a number of early messaging systems called telegraphs, that were devised to communicate text messages more quickly than physical transportation. Electrical telegraphy can be considered to be the first example of electrical engineering.

Jean-Maurice-Émile Baudot, French telegraph engineer and inventor of the first means of digital communication Baudot code, was one of the pioneers of telecommunications. He invented a multiplexed printing telegraph system that used his code and allowed multiple transmissions over a single line. The baud unit was named after him.

Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called dots and dashes, or dits and dahs. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one of the early developers of the system adopted for electrical telegraphy.

Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas pigeon post is not. Ancient signalling systems, although sometimes quite extensive and sophisticated as in China, were generally not capable of transmitting arbitrary text messages. Possible messages were fixed and predetermined and such systems are thus not true telegraphs.

A teleprinter is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint configurations.

Punched tape or perforated paper tape is a form of data storage device that consists of a long strip of paper through which small holes are punched. It was developed from and was subsequently used alongside punched cards, the difference being that the tape is continuous.

Ticker tape was the earliest electrical dedicated financial communications medium, transmitting stock price information over telegraph lines, in use from around 1870 through 1970. It consisted of a paper strip that ran through a machine called a stock ticker, which printed abbreviated company names as alphabetic symbols followed by numeric stock transaction price and volume information. The term "ticker" came from the sound made by the machine as it printed.
A telegraph code is one of the character encodings used to transmit information by telegraphy. Morse code is the best-known such code. Telegraphy usually refers to the electrical telegraph, but telegraph systems using the optical telegraph were in use before that. A code consists of a number of code points, each corresponding to a letter of the alphabet, a numeral, or some other character. In codes intended for machines rather than humans, code points for control characters, such as carriage return, are required to control the operation of the mechanism. Each code point is made up of a number of elements arranged in a unique way for that character. There are usually two types of element, but more element types were employed in some codes not intended for machines. For instance, American Morse code had about five elements, rather than the two of International Morse Code.

The Friden Flexowriter produced by the Friden Calculating Machine Company, was a teleprinter, a heavy-duty electric typewriter capable of being driven not only by a human typing, but also automatically by several methods, including direct attachment to a computer and by use of paper tape.

Alexander Bain was a Scottish inventor and engineer who was first to invent and patent the electric clock. He installed the railway telegraph lines between Edinburgh and Glasgow.

The Teletype Model 33 is an electromechanical teleprinter designed for light-duty office use. It is less rugged and cost less than earlier Teletype models. The Teletype Corporation introduced the Model 33 as a commercial product in 1963, after it had originally been designed for the United States Navy. The Model 33 was produced in three versions:
Frederick George Creed was a Canadian inventor, who spent most of his adult life in Britain. He worked in the field of telecommunications, and is particularly remembered as a key figure in the development of the teleprinter. He also played an early role in the development of SWATH vessels.
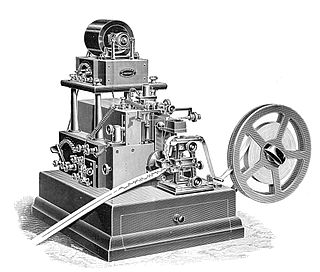
The syphon or siphon recorder is an obsolete electromechanical device used as a receiver for submarine telegraph cables invented by William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin in 1867. It automatically records an incoming telegraph message as a wiggling ink line on a roll of paper tape. Later a trained telegrapher would read the tape, translating the pulses representing the "dots" and "dashes" of the Morse code to characters of the text message.

American Morse Code — also known as Railroad Morse—is the latter-day name for the original version of the Morse Code developed in the mid-1840s, by Samuel Morse and Alfred Vail for their electric telegraph. The "American" qualifier was added because, after most of the rest of the world adopted "International Morse Code," the companies that continued to use the original Morse Code were mainly located in the United States. American Morse is now nearly extinct—it is most frequently seen in American railroad museums and American Civil War reenactments—and "Morse Code" today virtually always means the International Morse which supplanted American Morse.

The Teletype Corporation, a part of American Telephone and Telegraph Company's Western Electric manufacturing arm since 1930, came into being in 1928 when the Morkrum-Kleinschmidt Company changed its name to the name of its trademark equipment. Teletype was responsible for the research, development and manufacture of data and record communications equipment, but it is primarily remembered for the manufacture of electromechanical teleprinters.
Paper data storage refers to the use of paper as a data storage device. This includes writing, illustrating, and the use of data that can be interpreted by a machine or is the result of the functioning of a machine. A defining feature of paper data storage is the ability of humans to produce it with only simple tools and interpret it visually.
Edward Ernst Kleinschmidt was a German-American engineer. He was one of the inventors of the teleprinter, and obtained 118 patents over the course of his lifetime.
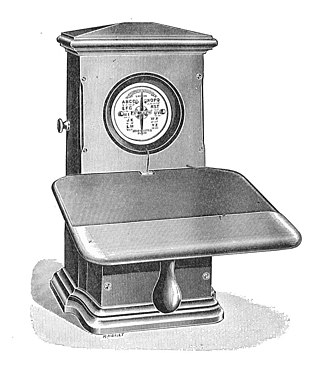
A needle telegraph is an electrical telegraph that uses indicating needles moved electromagnetically as its means of displaying messages. It is one of the two main types of electromagnetic telegraph, the other being the armature system, as exemplified by the telegraph of Samuel Morse in the United States. Needle telegraphs were widely used in Europe and the British Empire during the nineteenth century.

The Wheatstone system was an automated telegraph system that replaced a human operator with machines capable of sending and recording Morse code at a consistent fast rate. The system included a perforator, which prepared punched paper tape called a Wheatstone slip, a transmitter that read the tape and converted the symbols into dots and dashes encoded as mark and space electric currents on the telegraph line, and a receiver at the other end of the telegraph line that printed the Morse symbols. The system was invented by Charles Wheatstone. Enhancements could be made so that it was a duplex system, able to send and receive on the same line simultaneously.

















