
In artificial intelligence (AI), an expert system is a computer system emulating the decision-making ability of a human expert. Expert systems are designed to solve complex problems by reasoning through bodies of knowledge, represented mainly as if–then rules rather than through conventional procedural programming code. Expert systems were among the first truly successful forms of AI software. They were created in the 1970s and then proliferated in the 1980s, being then widely regarded as the future of AI — before the advent of successful artificial neural networks. An expert system is divided into two subsystems: 1) a knowledge base, which represents facts and rules; and 2) an inference engine, which applies the rules to the known facts to deduce new facts, and can include explaining and debugging abilities.

Johns Frederick (Jeff) Rulifson is an American computer scientist.

Douglas Bruce Lenat was an American computer scientist and researcher in artificial intelligence who was the founder and CEO of Cycorp, Inc. in Austin, Texas.

Allen Newell was an American researcher in computer science and cognitive psychology at the RAND Corporation and at Carnegie Mellon University's School of Computer Science, Tepper School of Business, and Department of Psychology. He contributed to the Information Processing Language (1956) and two of the earliest AI programs, the Logic Theorist (1956) and the General Problem Solver (1957). He was awarded the ACM's A.M. Turing Award along with Herbert A. Simon in 1975 for their contributions to artificial intelligence and the psychology of human cognition.

Edward Albert Feigenbaum is a computer scientist working in the field of artificial intelligence, and joint winner of the 1994 ACM Turing Award. He is often called the "father of expert systems."

Dabbala Rajagopal "Raj" Reddy is an Indian-American computer scientist and a winner of the Turing Award. He is one of the early pioneers of artificial intelligence and has served on the faculty of Stanford and Carnegie Mellon for over 50 years. He was the founding director of the Robotics Institute at Carnegie Mellon University. He was instrumental in helping to create Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies in India, to cater to the educational needs of the low-income, gifted, rural youth. He was the founding chairman of International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad. He is the first person of Asian origin to receive the Turing Award, in 1994, known as the Nobel Prize of Computer Science, for his work in the field of artificial intelligence.
In artificial intelligence, symbolic artificial intelligence is the term for the collection of all methods in artificial intelligence research that are based on high-level symbolic (human-readable) representations of problems, logic and search. Symbolic AI used tools such as logic programming, production rules, semantic nets and frames, and it developed applications such as knowledge-based systems, symbolic mathematics, automated theorem provers, ontologies, the semantic web, and automated planning and scheduling systems. The Symbolic AI paradigm led to seminal ideas in search, symbolic programming languages, agents, multi-agent systems, the semantic web, and the strengths and limitations of formal knowledge and reasoning systems.

Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) is a research institute at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) formed by the 2003 merger of the Laboratory for Computer Science (LCS) and the Artificial Intelligence Laboratory. Housed within the Ray and Maria Stata Center, CSAIL is the largest on-campus laboratory as measured by research scope and membership. It is part of the Schwarzman College of Computing but is also overseen by the MIT Vice President of Research.
Dendral was a project in artificial intelligence (AI) of the 1960s, and the computer software expert system that it produced. Its primary aim was to study hypothesis formation and discovery in science. For that, a specific task in science was chosen: help organic chemists in identifying unknown organic molecules, by analyzing their mass spectra and using knowledge of chemistry. It was done at Stanford University by Edward Feigenbaum, Bruce G. Buchanan, Joshua Lederberg, and Carl Djerassi, along with a team of highly creative research associates and students. It began in 1965 and spans approximately half the history of AI research.
Synthetic intelligence (SI) is an alternative/opposite term for artificial intelligence emphasizing that the intelligence of machines need not be an imitation or in any way artificial; it can be a genuine form of intelligence. John Haugeland proposes an analogy with simulated diamonds and synthetic diamonds—only the synthetic diamond is truly a diamond. Synthetic means that which is produced by synthesis, combining parts to form a whole; colloquially, a human-made version of that which has arisen naturally. A "synthetic intelligence" would therefore be or appear human-made, but not a simulation.

Deborah Louise McGuinness is an American computer scientist and researcher at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI). She is a professor of Computer, Cognitive and Web Sciences, Industrial and Systems Engineering, and an endowed chair in the Tetherless World Constellation, a multidisciplinary research institution within RPI that focuses on the study of theories, methods and applications of the World Wide Web. Her fields of expertise include interdisciplinary data integration, artificial intelligence, specifically in knowledge representation and reasoning, description logics, the semantic web, explanation, and trust.
Vasant G. Honavar is an Indian-American computer scientist, and artificial intelligence, machine learning, big data, data science, causal inference, knowledge representation, bioinformatics and health informatics researcher and professor.

Sebastian Thrun is a German-American entrepreneur, educator, and computer scientist. He is CEO of Kitty Hawk Corporation, and chairman and co-founder of Udacity. Before that, he was a Google VP and Fellow, a Professor of Computer Science at Stanford University, and before that at Carnegie Mellon University. At Google, he founded Google X and Google's self-driving car team. He is also an adjunct professor at Stanford University and at Georgia Tech.
Richard Earl Fikes is a computer scientist and Professor (Research) Emeritus in the Computer Science department of Stanford University. He is professionally active as a consultant and expert witness. He led Stanford's Knowledge Systems Laboratory from 1991 to 2006, and has held appointments at Berkeley, Carnegie-Mellon, Price Waterhouse Technology Centre, Xerox PARC, and SRI International.
Arthur Lee Samuel was an American pioneer in the field of computer gaming and artificial intelligence. He popularized the term "machine learning" in 1959. The Samuel Checkers-playing Program was among the world's first successful self-learning programs, and as such a very early demonstration of the fundamental concept of artificial intelligence (AI). He was also a senior member in the TeX community who devoted much time giving personal attention to the needs of users and wrote an early TeX manual in 1983.

The Gates Computer Science Building, or Gates building for short, is an L-shaped building that houses the Computer Science Department as well as the Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI) at 353 Jane Stanford Way, Stanford University, California. Construction on the building began in 1994 and was completed in 1996 at a cost of $36 million. It was named after Microsoft founder Bill Gates, who donated $6 million for the building's construction.

Pamela Ann McCorduck was a British-born American author of books about the history and philosophical significance of artificial intelligence, the future of engineering, and the role of women and technology. She also wrote three novels. She contributed to Omni, The New York Times, Daedalus, and the Michigan Quarterly Review, and was a contributing editor of Wired. She was a former vice president of the PEN American Center. She was married to computer scientist and academic Joseph F. Traub.
Stanford University has many centers and institutes dedicated to the study of various specific topics. These centers and institutes may be within a department, within a school but across departments, an independent laboratory, institute or center reporting directly to the dean of research and outside any school, or semi-independent of the university itself.
The Department of Computer Science at the University of British Columbia was established in May 1968. UBC CS is located at the UBC Point Grey campus in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. As of November 2023, it has 66 faculty, 64 staff, 259 graduate students, and 2,774 undergraduates.
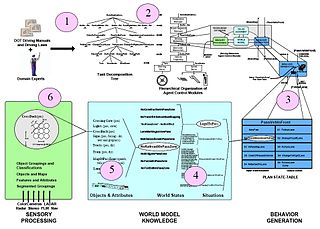
Knowledge acquisition is the process used to define the rules and ontologies required for a knowledge-based system. The phrase was first used in conjunction with expert systems to describe the initial tasks associated with developing an expert system, namely finding and interviewing domain experts and capturing their knowledge via rules, objects, and frame-based ontologies.










