
The Etruscan civilization was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria, and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto, and western Campania.

Magna Graecia was the name given by the Romans to the coastal areas of Southern Italy in the present-day Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania and Sicily; these regions were extensively populated by Greek settlers. These settlers, who began arriving in the 8th century BC, brought with them their Hellenic civilization, which left a lasting imprint on Italy. They also influenced the native peoples, such as the Sicels and the Oenotrians, who became hellenized after they adopted the Greek culture as their own. The Greek colonists of Magna Graecia elaborated a civilization of the highest level, which had peculiar characteristics, due to the distance from the motherland and the influence of the indigenous peoples of southern Italy. The type of government was in the form of city-states (poleis) administered by the aristocracy. The Second Punic War put the end to the independence of the cities of Magna Graecia, which were annexed to the Roman Republic in 205 BC.

Cybele is an Anatolian mother goddess; she may have a possible forerunner in the earliest neolithic at Çatalhöyük. She is Phrygia's only known goddess, and was probably its national deity. Greek colonists in Asia Minor adopted and adapted her Phrygian cult and spread it to mainland Greece and to the more distant western Greek colonies around the 6th century BC.

The island of Delos, near Mykonos, near the centre of the Cyclades archipelago, is one of the most important mythological, historical, and archaeological sites in Greece. The excavations in the island are among the most extensive in the Mediterranean; ongoing work takes place under the direction of the Ephorate of Antiquities of Cyclades, and many of the artifacts found are on display at the Archaeological Museum of Delos and the National Archaeological Museum of Athens.

Angitia was a goddess among the Marsi, the Paeligni and other Oscan-Umbrian peoples of central Italy. She was associated in antiquity with snake-charmers who claimed her as their ancestor. Roman interpretations probably obscure her Marsian significance.

Etruscan religion comprises a set of stories, beliefs, and religious practices of the Etruscan civilization, heavily influenced by the mythology of ancient Greece, and sharing similarities with concurrent Roman mythology and religion. As the Etruscan civilization was gradually assimilated into the Roman Republic from the 4th century BC, the Etruscan religion and mythology were partially incorporated into ancient Roman culture, following the Roman tendency to absorb some of the local gods and customs of conquered lands. The first attestations of an Etruscan religion can be traced back to the Villanovan culture.
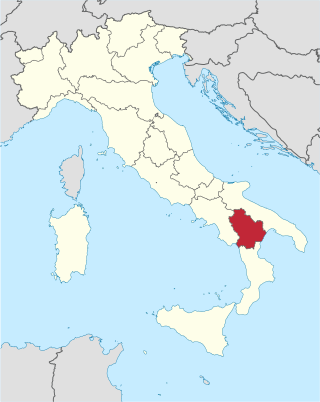
Basilicata, also known by its ancient name Lucania, is an administrative region in Southern Italy, bordering on Campania to the west, Apulia to the north and east, and Calabria to the south. It has two coastlines: a 30-km stretch on the Tyrrhenian Sea between Campania and Calabria, and a longer coastline along the Gulf of Taranto between Calabria and Apulia. The region can be thought of as the "instep" of Italy, with Calabria functioning as the "toe" and Apulia the "heel".

Dura-Europos was a Hellenistic, Parthian, and Roman border city built on an escarpment 90 metres above the southwestern bank of the Euphrates river. It is located near the village of Salhiyé, in present-day Syria. Dura-Europos was founded around 300 BC by Seleucus I Nicator, who founded the Seleucid Empire as one of the Diadochi of Alexander the Great. In 113 BC, Parthians conquered the city, and held it, with one brief Roman intermission, until 165 AD. Under Parthian rule, it became an important provincial administrative centre. The Romans decisively captured Dura-Europos in 165 AD and greatly enlarged it as their easternmost stronghold in Mesopotamia, until it was captured by the Sasanian Empire after a siege in 256–57 AD. Its population was deported, and the abandoned city eventually became covered by sand and mud and disappeared from sight.

In ancient Roman religion, Concordia is the goddess who embodies agreement in marriage and society. Her Greek equivalent is usually regarded as Harmonia, with musical harmony a metaphor for an ideal of social concord or entente in the political discourse of the Republican era. She was thus often associated with Pax ("Peace") in representing a stable society. As such, she is more closely related to the Greek concept of homonoia, which was also represented by a goddess.
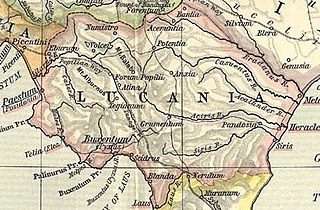
Lucania was a historical region of Southern Italy. It was the land of the Lucani, an Oscan people. It extended from the Tyrrhenian Sea to the Gulf of Taranto. It bordered with Samnium and Campania in the north, Apulia in the east, and Bruttium in the south-west, and was at the tip of the peninsula which is now called Calabria. It comprised almost all the modern region of Basilicata, the southern part of the Province of Salerno and a northern portion of the Province of Cosenza.
The year 1814 in archaeology involved some significant events.

Venosa is a town and comune in the province of Potenza, in the southern Italian region of Basilicata, in the Vulture area. It is bounded by the comuni of Barile, Ginestra, Lavello, Maschito, Montemilone, Palazzo San Gervasio, Rapolla and Spinazzola. It is a member of the I Borghi più belli d'Italia association.
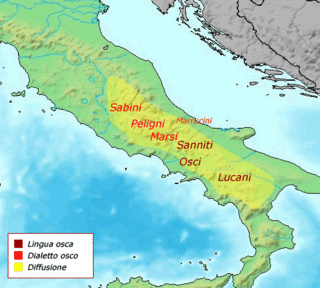
The Lucanians were an Italic tribe living in Lucania, in what is now southern Italy, who spoke an Oscan language, a member of the Italic languages. Today, the inhabitants of the Basilicata region are still called Lucani, and so is their dialect.

Armento is a town and comune in the province of Potenza, in the Southern Italian region of Basilicata. The Armento Rider was found in the vicinity of Armento and is now in the British Museum. The Kritonios Crown, a 4th-century BC gold wreath representing a crown of convolvulus, narcissus, ivy, roses, and myrtle was found there in the 19th century and is now in the Staatliche Antikensammlungen.

The Staatliche Antikensammlungen is a museum in Munich's Kunstareal holding Bavaria's collections of antiquities from Greece, Etruria and Rome, though the sculpture collection is located in the opposite Glyptothek and works created in Bavaria are on display in a separate museum. Ancient Egypt also has its own museum.

The Temple of Hera, or Heraion, is an ancient Archaic Greek temple at Olympia, Greece, that was dedicated to Hera, queen of the Greek gods. It was the oldest temple at Olympia and one of the most venerable in all Greece. It was originally a joint temple of Hera and Zeus, chief of the gods, until a separate temple was built for him. It is at the altar of this temple, which is oriented east-west, that the Olympic flame is lit and carried to all parts of the world. The torch of the Olympic flame is lit in its ruins to this day. The temple was built in approximately 590 BC, but was destroyed by an earthquake in the early 4th century CE.

The Temple of Eshmun is an ancient place of worship dedicated to Eshmun, the Phoenician god of healing. It is located near the Awali river, 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) northeast of Sidon in southwestern Lebanon. The site was occupied from the 7th century BC to the 8th century AD, suggesting an integrated relationship with the nearby city of Sidon. Although originally constructed by Sidonian king Eshmunazar II in the Achaemenid era to celebrate the city's recovered wealth and stature, the temple complex was greatly expanded by Bodashtart, Yatonmilk and later monarchs. Because the continued expansion spanned many centuries of alternating independence and foreign hegemony, the sanctuary features a wealth of different architectural and decorative styles and influences.

The Temple of Artemis or Artemision, also known as the Temple of Diana, was a Greek temple dedicated to an ancient, local form of the goddess Artemis. It was located in Ephesus. By 401 AD it had been ruined or destroyed. Only foundations and fragments of the last temple remain at the site.

The Armento Rider is an ancient bronze sculpture of a rider and a horse that was originally found in the town of Armento in southern Italy. Now part of the British Museum's collection, it is considered one of the oldest works of art from Western Greece or Magna Graecia.

The Temple of the Gadde is a temple in the modern-day Syrian city of Dura-Europos, located near the agora. It contained reliefs dedicated to the protective deities of Dura-Europos and the nearby city of Palmyra, after whom the temple was named by its excavators. The temple was excavated between 1934 and January 1936 by the French/American expedition of Yale University, led by Michael Rostovtzeff.



















