
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CO2H. A colorless, bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Chemical Substance Inventory as an experimental teratogen. The name is from Latin salix for willow tree. It is an ingredient in some anti-acne products. Salts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates.

Salvinorin A is the main active psychotropic molecule in Salvia divinorum. Salvinorin A is considered a dissociative hallucinogen.

The pyrethrins are a class of organic compounds normally derived from Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium that have potent insecticidal activity by targeting the nervous systems of insects. Pyrethrin naturally occurs in chrysanthemum flowers and is often considered an organic insecticide when it is not combined with piperonyl butoxide or other synthetic adjuvants. Their insecticidal and insect-repellent properties have been known and used for thousands of years.
Agmatine, also known as (4-aminobutyl)guanidine, is an aminoguanidine that was discovered in 1910 by Albrecht Kossel. Agmatine is a chemical substance which is naturally created from the amino acid arginine. Agmatine has been shown to exert modulatory action at multiple molecular targets, notably: neurotransmitter systems, ion channels, nitric oxide (NO) synthesis and polyamine metabolism and this provides bases for further research into potential applications.
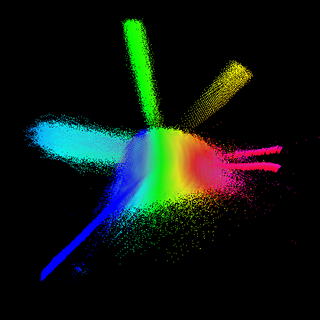
Chemical space is a concept in cheminformatics referring to the property space spanned by all possible molecules and chemical compounds adhering to a given set of construction principles and boundary conditions. It contains millions of compounds which are readily accessible and available to researchers. It is a library used in the method of molecular docking.

Aldicarb is a carbamate insecticide which is the active substance in the pesticide Temik. It is effective against thrips, aphids, spider mites, lygus, fleahoppers, and leafminers, but is primarily used as a nematicide. Aldicarb is a cholinesterase inhibitor which prevents the breakdown of acetylcholine in the synapse. In case of severe poisoning, the victim dies of respiratory failure.
Spermine is a polyamine involved in cellular metabolism that is found in all eukaryotic cells. The precursor for synthesis of spermine is the amino acid ornithine. It is an essential growth factor in some bacteria as well. It is found as a polycation at physiological pH. Spermine is associated with nucleic acids and is thought to stabilize helical structure, particularly in viruses.
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring.
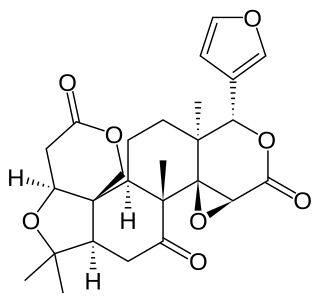
Limonin is a limonoid, and a bitter, white, crystalline substance found in citrus and other plants. It is also known as limonoate D-ring-lactone and limonoic acid di-delta-lactone. Chemically, it is a member of the class of compounds known as furanolactones.

The adenosine A2B receptor, also known as ADORA2B, is a G-protein coupled adenosine receptor, and also denotes the human adenosine A2b receptor gene which encodes it.

Peroxisomal N(1)-acetyl-spermine/spermidine oxidase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PAOX gene.

7-OH-DPAT is a synthetic compound that acts as a dopamine receptor agonist with reasonable selectivity for the D3 receptor subtype, and low affinity for serotonin receptors, unlike its structural isomer 8-OH-DPAT. 7-OH-DPAT is self-administered in several animal models, and is used to study addiction to cocaine.

Quercus infectoria or the Aleppo oak is a species of oak well known for producing galls that have been traditionally used for centuries in Asia medicinally while also used in softening leather and in making black dye and ink.
Momordin is one of several saponins derived from oleanolic acid, a triterpenoid. These chemical compounds are found in some plants of the genus Momordica, which includes the bitter melon and the balsam apple, as well as in other Asian herbal medicine plants such as Kochia scoparia and Ampelopsis radix.
A polyamine is an organic compound having more than two amino groups. Alkyl polyamines occur naturally, but some are synthetic. Alkylpolyamines are colorless, hygroscopic, and water soluble. Near neutral pH, they exist as the ammonium derivatives. Most aromatic polyamines are crystalline solids at room temperature.

Sibiricine is a bioactive isoquinoline alkaloid isolated from Corydalis crispa (Fumariaceae), which is a Bhutanese medicinal plant from the Himalayas.
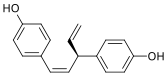
Nyasol, also known as cis-hinokiresinol or as (Z)-hinokiresinol, is a lignan that is found in Anemarrhena asphodeloides. It has estrogenic activity, acting as a selective agonist of the ERβ, and hence is a phytoestrogen. In addition, (-)-nyasol has been found to inhibit the production of eicosanoids and nitric oxide in vitro and shows anti-inflammatory effects.

Apparicine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid. It is named after Apparicio Duarte, a Brazilian botanist who studied the Aspidosperma species from which apparicine was first isolated. It was the first member of the vallesamine group of alkaloids to be isolated and have its structure established, which was first published in 1965. It has also been known by the synonyms gomezine, pericalline, and tabernoschizine.

Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), is a cannabinoid found in cannabis plants. It is most abundant in the glandular trichomes on the female seedless flowers or more accurately infructescence often colloquially referred to as buds. CBDA is the chemical precursor to cannabidiol (CBD). Through the process of decarboxylation cannabidol is derived via a loss of a carbon and two oxygen atoms from the 1 position of the benzoic acid ring.














