
The Euphrates is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia. Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab, which empties into the Persian Gulf.

Irrigation is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been developed by many cultures around the world. Irrigation helps to grow crops, maintain landscapes, and revegetate disturbed soils in dry areas and during times of below-average rainfall. In addition to these uses, irrigation is also employed to protect crops from frost, suppress weed growth in grain fields, and prevent soil consolidation. It is also used to cool livestock, reduce dust, dispose of sewage, and support mining operations. Drainage, which involves the removal of surface and sub-surface water from a given location, is often studied in conjunction with irrigation.

A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions.

The Aswan Dam, or more specifically since the 1980s, the Aswan High Dam, is one of the world's largest embankment dams, which was built across the Nile in Aswan, Egypt, between 1960 and 1970. Its significance largely eclipsed the previous Aswan Low Dam initially completed in 1902 downstream. Based on the success of the Low Dam, then at its maximum utilization, construction of the High Dam became a key objective of the government following the Egyptian Revolution of 1952; with its ability to better control flooding, provide increased water storage for irrigation and generate hydroelectricity, the dam was seen as pivotal to Egypt's planned industrialization. Like the earlier implementation, the High Dam has had a significant effect on the economy and culture of Egypt.

The Dez Dam, formerly known as Mohammad-Reza Shah Pahlavi Dam, before 1979 Revolution, is an arch dam on the Dez River in the southwestern province of Khuzestan, Iran. It is about 23 km of Andimeshk city. It was built between 1959 and 1963 under the rule of Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, the last Shah of Iran, with contacting an Italian consortium and is owned by the Khuzestan Water & Power Authority. The dam is 203 metres (666 ft) high, making it one of the highest in the country, and has a reservoir capacity of 3,340,000,000 m3 (2,710,000 acre⋅ft). At the time of construction the Dez Dam was Iran's biggest development project. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power production and irrigation. It has an associated 520 MW power station and its reservoir helps irrigate up to 80,500 ha of farmland. US$42 million of the cost to construct the dam came from the World Bank.

A reservoir is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.

The Little Zab or Lower Zab is a river that originates in Iran and joins the Tigris just south of Al Zab in the Kurdistan region of Iraq. It is approximately 400 kilometres (250 mi) long and drains an area of about 22,000 square kilometres (8,500 sq mi). The river is fed by rainfall and snowmelt, resulting in a peak discharge in spring and low water in summer and early fall. Two dams have been built on the Little Zab, regulating the river flow, providing water for irrigation and generating hydroelectricity. The Zagros Mountains have been occupied since at least the Lower Palaeolithic, but the earliest archaeological site in the Little Zab basin, Barda Balka, dates to the Middle Palaeolithic. Human occupation of the Little Zab basin has been attested for every period since then.

The environmental impact of reservoirs comes under ever-increasing scrutiny as the global demand for water and energy increases and the number and size of reservoirs increases.

SaltMod is computer program for the prediction of the salinity of soil moisture, groundwater and drainage water, the depth of the watertable, and the drain discharge (hydrology) in irrigated agricultural lands, using different (geo)hydrologic conditions, varying water management options, including the use of ground water for irrigation, and several cropping rotation schedules. The water management options include irrigation, drainage, and the use of subsurface drainage water from pipe drains, ditches or wells for irrigation.

Lake McConaughy is a reservoir on the North Platte River. It is located 9 miles (14 km) north of Ogallala, Nebraska, United States, near U.S. Highway 26 and Nebraska Highway 61. The reservoir was named for Charles W. McConaughy, a grain merchant and mayor of Holdrege, Nebraska, one of the leading promoters of the project. Although he did not live to see the completion of the project, his leadership and perseverance eventually culminated in a public power and irrigation project that helped Nebraska become one of the nation's leading agricultural states.
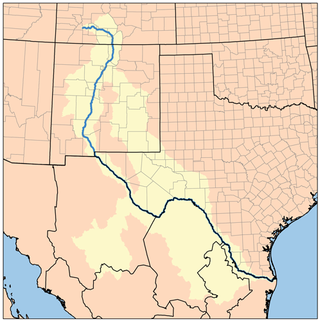
The Rio Grande Project is a United States Bureau of Reclamation irrigation, hydroelectricity, flood control, and interbasin water transfer project serving the upper Rio Grande basin in the southwestern United States. The project irrigates 193,000 acres (780 km2) along the river in the states of New Mexico and Texas. Approximately 60 percent of this land is in New Mexico. Some water is also allotted to Mexico to irrigate some 25,000 acres (100 km2) on the south side of the river. The project was authorized in 1905, but its final features were not implemented until the early 1950s.

New Exchequer Dam is a concrete–faced, rock-fill dam on the Merced River in central California in the United States. It forms Lake McClure, which impounds the river for irrigation and hydroelectric power production and has a capacity of more than 1,000,000 acre-feet (1.2 km3). The Merced Irrigation District (MID) operates the dam and was also responsible for its construction.

Amir Kabir dam, also known as Karaj dam, is a dam on the Karaj River in the Central Alborz mountain range of northern Iran.

The Band-e Kaisar, Pol-e Kaisar, Bridge of Valerian or Shadirwan was an ancient arch bridge in the city of Shushtar, Khuzestan province, Iran, and the first in the country to combine it with a dam. Built by the Sassanids, using Roman prisoners of war as workforce, in the 3rd century AD on Sassanid order, it was also the most eastern example of Roman bridge design and Roman dam, lying deep in Persian territory. Its dual-purpose design exerted a profound influence on Iranian civil engineering and was instrumental in developing Sassanid water management techniques.

The Kebar Dam is a masonry arch dam on the Kebar River, Iran, located near a town of the same name, 23 km southeast of Qom, near the village of Zanburak in Jannatabad, Qom. The dam is an early arch dam and was the first arch dam constructed by the Mongolians, around 1300 AD. It is the oldest surviving arch dam. The dam is 26m tall and 55m wide and was constructed for irrigation water supply. It was originally 24m tall but 2m of height was added in either the beginning or middle of the 17th century. The arch of the dam was of normal curvature with a radius of 35m and angle of 45-degrees. While the dam sat on limestone, its curve rested on two winged walls that served as abutments. The downstream face of the dam was vertical until near its abutment where it slightly curves out. Near the dam's right, or western, abutment there is a 10m deep cylindrical hole which served as an intake and outlet works for the dam. The outlet works is located at the bottom and is a larger opening but there are various smaller openings throughout the shaft to release water. The dam impounded a small reservoir that is no longer used and is mostly filled with silt.

Mahabad Dam is an embankment dam on the Mahabad River near the city of Mahabad, West Azerbaijan province, Iran. It was built before the Islamic revolution by Yugoslavian engineers and is one of the ten largest dams in Iran. On average, the total volume of annual water input is equal to 339.304 million cubic meters. The Mahabad Dam provides water for agriculture (71%), industry (11%), drinking (7%), and other miscellaneous purposes (11%). The dam also has a hydroelectric power station. Construction began in 1968 and the dam was completed in 1970.

Water scarcity in Iran is caused by high climatic variability, uneven distribution of water, over exploitation of available water resources,and prioritization of economic development. Water scarcity in Iran is further exacerbated by climate change.

Little Rock Dam, also known as Littlerock Dam, or officially as Little Rock-Palmdale Dam, is a concrete gravity dam on Little Rock Creek in Los Angeles County, California, about 5 mi (8.0 km) south of Palmdale. The dam and Little Rock Reservoir are owned by the Palmdale Water District and Littlerock Creek Irrigation District and are used for agricultural and municipal water supply and flood control.

Medlow Dam is a heritage-listed major gated concrete-walled arch dam across the Adams Creek in the Blue Mountains region, located at Beauchamp Road, Medlow Bath in the City of Blue Mountains local government area of New South Wales, Australia. The dam was designed and built in 1907 by the NSW Department of Public Works. The dam's purpose is primarily for the potable water supply of the upper Blue Mountains region. The impounded reservoir is called Medlow Bath Reservoir. The dam is also known as Medlow Bath Dam, Lake Medlow Dam, Adams Creek Dam and Medlow Bath Reservoir. The property is owned by Sydney Water, a state-owned corporation of the Government of New South Wales. The dam was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 18 November 1999.





















