
Eospinus daniltshenkoi is an extinct tetraodontid bony fish from the Eocene. Its fossils are from the Danata Formation lagerstatten of Ypresian Turkmenistan.
Beerichthys is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish. It contains a single species, Beerichthys ingens, that was a member of the Ypresian London Clay fauna of lower Eocene England.
Eothynnus salmonens is an extinct species of prehistoric jackfish that lived during the lower Eocene of what is now the Isle of Sheppey (as a part of the London Clay Lagerstatten. It is known exclusively from some preserved skulls.
Bramoides is an extinct genus of marine ray-finned fish that lived during the lower Eocene. It contains a single species, B. brieni, known from the London Clay.
Promegalops is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the lower Eocene.
Protarpon is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the lower Eocene.
Aulopopsis is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish that lived during the lower Eocene. It is considered a relative of lizardfish in the order Aulopiformes, but its exact taxonomic placement is uncertain. Some authorities place it with the Aulopidae, while others place it with the Giganturoidae.
Argilloberyx is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine bony fish that lived during the lower Eocene. It contains one species, A. prestwichae, known from the London Clay Formation on the Isle of Sheppey, United Kingdom. It is considered a member of the family Berycidae.

Berybolcensis is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish that lived in the early Eocene. It contains a single species, B. leptacanthus, from the Monte Bolca lagerstatten of Italy. It was a member of the Holocentridae, making it related to modern squirrelfish and soldierfish, although it was more basal than either, and is thought to have diverged from their common ancestor around the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary. It is thought to be related to Tenuicentrum, another basal holocentrid from the same formation.
Berycomorus is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish that lived during the late Eocene epoch. It contains a single species, B. firdoussi, from the Pabdeh Formation of Iran.

Archaephippus is an extinct genus of prehistoric spadefish that lived from the early Eocene. It contains a single species, A. asper, known from Italy. Several exquisitely preserved fossils have been found from the Monte Bolca lagerstatten. Some juvenile specimens preserve the vertical striped coloration that they would have likely had in life.
Haplolepis is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish that lived during the late Moscovian Stage of the Pennsylvanian Period. Well-preserved specimens are known from the Lagerstätte in the Upper Freeport Coal at Linton, Ohio, and were first described by John Strong Newberry in the 1800s.
Aluvarus praeimperialis is an extinct ray-finned fish, known from two headless fossil specimens found in the Pabdeh Formation, a Late Eocene stratum from the Priabonian epoch, of what is now Iran. A. praeimperialis was originally thought to be a luvar, described as "Luvarus praeimperialis", as it was thought to be a predecessor to the modern luvar. A later reexamination of the specimens showed that they were too incomplete to demonstrate such a conclusion and had no clear exclusive shared traits with luvar, and were renamed "Aluvarus", meaning "not luvar" or "different than luvar". However, some authorities still retain it as a luvar.

Dalpiazella is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine eel from the Eocene of Europe. It contains a single species, D. brevicauda, from the late Ypresian-aged Monte Bolca lagerstatten of Italy. It is though to be closely related to the sympatric genus Paranguilla, with both genera together constituting the family Paranguillidae.

Cylindracanthus is an extinct, enigmatic genus of marine ray-finned fish with fossils known throughout North America, Europe, Asia and Africa from the Late Cretaceous to the late Eocene, with potential Oligocene records and a possible Miocene record also known. It is exclusively known from its distinctive partial remains, which are long cylindrical bony spines that are usually considered rostrum fragments, as well as some associated teeth. These spines are abundant & widespread throughout this timespan, and are useful indicators of a nearshore marine environment, but the taxonomic identity of the fish is still highly uncertain and debated.
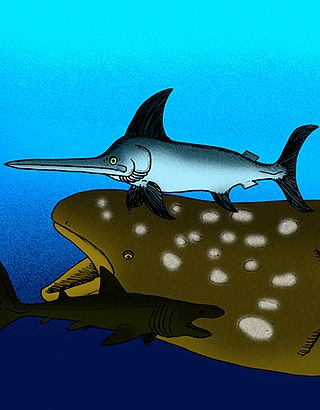
Xiphiorhynchus is an extinct genus of prehistoric swordfish that lived from the Eocene until the Oligocene. Unlike the modern swordfish, both the upper and lower jaws of Xiphiorhynchus were extended into blade-like points.
Proleptolepis is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Leptolepidae.

Lyrolepis is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish found in the Eocene Adaev Formation of Kazakhstan and the Pshekha Formation of Georgia.

Notogoneus is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish. A trace fossil attributed to Notogoneus osculus has been found in the Green River Formation.

Phareodus is a genus of freshwater fish from the Paleocene to the Eocene of Australia, Europe and North and South America.











