Related Research Articles
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, intersex, and asexual (LGBTQIA+) people frequently experience violence directed toward their sexuality, gender identity, or gender expression. This violence may be enacted by the state, as in laws prescribing punishment for homosexual acts, or by individuals. It may be psychological or physical and motivated by biphobia, gayphobia, homophobia, lesbophobia, and transphobia. Influencing factors may be cultural, religious, or political mores and biases.

The following is the timeline of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) history.

LGBT people in Bulgaria face significant challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female same-sex relationships are legal in Bulgaria, but same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex couples. Discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been banned since 2004, with discrimination based on "gender change" being outlawed since 2015. In July 2019, a Bulgarian court recognized a same-sex marriage performed in France in a landmark ruling. For 2020, Bulgaria was ranked 37 of 49 European countries for LGBT rights protection by ILGA-Europe. Like most countries in Central and Eastern Europe, post-Communist Bulgaria holds socially conservative attitudes when it comes to such matters as homosexuality and transgender people.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Spain rank among the highest in the world; having undergone significant advancements within recent decades. Among ancient Romans in Spain, sexual interaction between men was viewed as commonplace, but a law against homosexuality was promulgated by Christian emperors Constantius II and Constans, and Roman moral norms underwent significant changes leading up to the 4th century. Laws against sodomy were later established during the legislative period. They were first repealed from the Spanish Code in 1822, but changed again along with societal attitudes towards homosexuality during the Spanish Civil War and Francisco Franco's regime.

Gay-friendly or LGBT-friendly places, policies, people, or institutions are those that are open and welcoming to gay or LGBT people. They typically aim to create an environment that is supportive, respectful, and non-judgmental towards the LGBT community. The term "gay-friendly" originated in the late 20th century in North America, as a byproduct of a gradual implementation of gay rights, greater acceptance of LGBT people in society, and the recognition of LGBT people as a distinct consumer group for businesses.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in South Africa have the same legal rights as non-LGBT people. South Africa has a complex and diverse history regarding the human rights of LGBT people. The legal and social status of between 400,000–over 2 million lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex South Africans has been influenced by a combination of traditional South African morals, colonialism, and the lingering effects of apartheid and the human rights movement that contributed to its abolition.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Sudan face significant challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity in Sudan is illegal for both men and women, while homophobic attitudes remain ingrained throughout the nation.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Dominica face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Homosexuality has been legal since 2024, when the High Court struck down the country's colonial-era sodomy law. Dominica provides no recognition to same-sex unions, whether in the form of marriage or civil unions, and no law prohibits discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity.
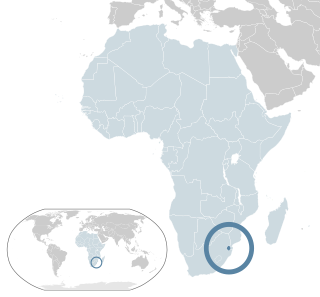
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Eswatini have limited legal rights. According to Rock of Hope, a Swati LGBT advocacy group, "there is no legislation recognising LGBTIs or protecting the right to a non-heterosexual orientation and gender identity and as a result [LGBT people] cannot be open about their orientation or gender identity for fear of rejection and discrimination". Homosexuality is illegal in Eswatini, though this law is in practice unenforced. According to the 2021 Human Rights Practices Report from the US Department of State, "there has never been an arrest or prosecution for consensual same-sex conduct."
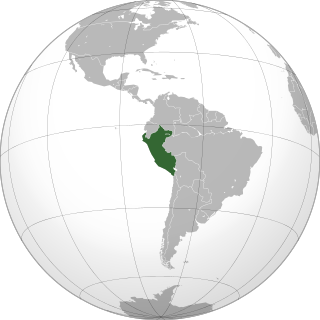
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Peru face some legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity among consenting adults is legal. However, households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex couples.
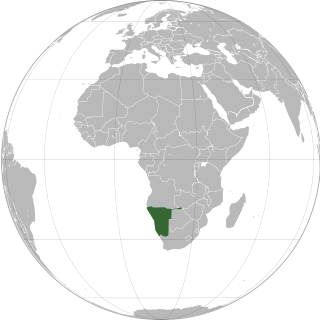
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Namibia have limited legal protections. Sexual contact between men is criminalised within Namibia, although this law is generally unenforced. Discrimination based on sexual orientation is banned in Namibia but not for gender identity.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Scotland are generally in line with the rest of the United Kingdom, which have evolved extensively over time and are now regarded as some of the most progressive in Europe. In both 2015 and 2016, Scotland was recognised as the "best country in Europe for LGBTI legal equality".
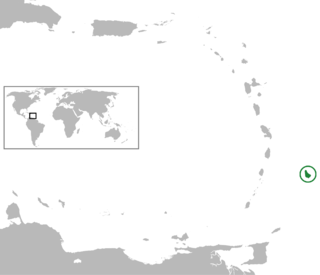
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Barbados do not possess the same legal rights as non-LGBT people. In December 2022, the courts ruled Barbados' laws against buggery and "gross indecency" were unconstitutional and struck them from the Sexual Offences Act. However, there is no recognition of same-sex relationships and only limited legal protections against discrimination.

The history of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender people in the Netherlands has reflected the shades of tolerance or rigidity which were utilized by the rulers of the country at various periods in its history. Since World War II, the movement for LGBT rights has been galvanized by both events abroad and increasing liberalization domestically.

Switzerland, a country which has long held a stance of neutrality in its relations with other nations, has not been immune to the movement of equality for lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender citizens. Prior to the 20th century, sodomy and other types of sexual intercourse between people of the same sex was held in various levels of legal contempt. Today, the modern LGBT rights movement in Switzerland is related to the larger international movement which developed largely after 1969.
This is a timeline of notable events in the history of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender people in South Africa.

Lesbians in the Second Spanish Republic and Civil War period were doubly discriminated against, as a result of their gender and sexual practices. Prior to the Second Republic, lesbians in Spain were largely ignored, eclipsed by gay men. They faced discrimination as they challenged definitions around what it meant to be a woman. While homosexuality was not condemned by law, it was possible for lesbians to face more severe punishment when charged with violation of morals because of their sexual orientation.

Lesbians in Francoist Spain had to contend with a culture where a fascist state met with a form of conservative Roman Catholicism to impose very rigid, traditional gender roles. In the immediate post-Civil War period, the new regime was not concerned with homosexuals in general, but instead were focused on changing laws to enforce restrictive gender norms like repealing divorce. While original laws banning homosexuality were on the books and enforced using a 1933 law, they were changed in 1954 and 1970. Unlike male homosexuality, lesbians were less clearly addressed by these laws and were much less frequently prosecuted for the crime of homosexuality. Lesbians from that period are hard to identify because they were not identified as such, and often identified as prostitutes instead.

Critical pride is the name of several annual protest demonstrations of LGBT people held in Madrid and several other Spanish cities. The organizers of critical pride demonstrations present them as an alternative to the original pride parades and festivals, which they consider depoliticized and institutionalized.

The LGBT community of Sydney, in New South Wales, is the largest in Australia and has a firm place as one of the iconic gay cities of the contemporary world. In a 2013 Pew Research poll, 79% of Australians agreed that homosexuality should be accepted by society, making it the fifth most supportive country in the survey behind Spain (88%), Germany (87%), Canada and the Czech Republic. With a long history of LGBT rights activism and the annual three-week-long Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras festival, Sydney is one of the most gay-friendly cities in Australia and in the world.
References
- ↑ Visigothic Code 3.5.5, 3.5.6; "The doctrine of the orthodox faith requires us to place our censure upon vicious practices, and to restrain those who are addicted to carnal offences. For we counsel well for the benefit of our people and our country, when we take measures to utterly extirpate the crimes of wicked men, and put an end to the evil deeds of vice. For this reason we shall attempt to abolish the horrible crime of sodomy, which is as contrary to Divine precept as it is to chastity. And although the authority of the Holy Scriptures, and the censure of earthly laws, alike, prohibit offences of this kind, it is nevertheless necessary to condemn them by a new decree; lest if timely correction be deferred, still greater vices may arise. Therefore, we establish by this law, that if any man whosoever, of any age, or race, whether he belongs to the clergy, or to the laity, should be convicted, by competent evidence, of the commission of the crime of sodomy, he shall, by order of the king, or of any judge, not only suffer emasculation, but also the penalty prescribed by ecclesiastical decree for such offences, and promulgated in the third year of our reign."
- 1 2 (Fone, 2000)
- ↑ Ward, Sophie (2013-12-23). A Marriage Proposal: The importance of equal marriage for all of us. Guardian Books. ISBN 978-1-78356-034-9.
- ↑ Crompton, Louis (July 2009). Homosexuality and Civilization. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-03006-0.
- ↑ "» A Brief History of Homosexuality and LGBTQ rights in Spain Envisioning Spain's Border". pages.vassar.edu. Retrieved 2017-11-26.
- ↑ "La junta de protección a la infancia de Barcelona: Aproximación histórica y guía de su archivo" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 January 2015. Retrieved 20 January 2011.
- ↑ Rick Nolton. "Represión homosexual en el franquismo". Islaternura.com. Retrieved 20 January 2011.
- ↑ "Where is it illegal to be gay?". BBC News. 10 February 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ↑ Pastor, Enric (December 20, 2000), "El ex ministro Saavedra cree que "ocultar la homosexualidad lleva al psicoanalista"", El Mundo (in Spanish), retrieved 2007-10-25
- ↑ Tremlett, Giles (2001-12-13). "Gays persecuted by Franco lose criminal status at last". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077 . Retrieved 2020-05-03.
- ↑ Cué, Carlos E. (2007-10-31). "La ley de memoria se aprueba entre aplausos de invitados antifranquistas". El País (in Spanish). ISSN 1134-6582 . Retrieved 2020-05-03.
- ↑ Reinlein, Iciar; Sarah Morris (November 6, 2012). "Same-sex marriage upheld by Spain's highest court". Chicago Tribune . Retrieved November 15, 2012.
- ↑ "Lina, la amiga que fue testigo de cómo mataban a Samuel: "Fue un crimen homófobo"". Telecinco (in European Spanish). 5 July 2021. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- ↑ "Cargas policiales y un detenido en Madrid durante las manifestaciones por la muerte de Samuel". www.20minutos.es (in Spanish). 5 July 2021. Retrieved 20 July 2021.