Related Research Articles

Rhys ap Gruffydd or ap Gruffudd was the ruler of the kingdom of Deheubarth in south Wales from 1155 to 1197. Today, he is commonly known as The Lord Rhys, in Welsh Yr Arglwydd Rhys, although this title may have not been used in his lifetime. He usually used the title "Proprietary Prince of Deheubarth" or "Prince of South Wales", but two documents have been discovered in which he uses the title "Prince of Wales" or "Prince of the Welsh". Rhys was one of the most successful and powerful Welsh princes, and, after the death of Owain Gwynedd of Gwynedd in 1170, the dominant power in Wales.

Owain ap Gruffudd was King of Gwynedd, North Wales, from 1137 until his death in 1170, succeeding his father Gruffudd ap Cynan. He was called Owain the Great and the first to be styled "Prince of Wales" and the "Prince of the Welsh". He is considered to be the most successful of all the North Welsh princes prior to his grandson, Llywelyn ab Iorwerth. He became known as Owain Gwynedd to distinguish him from the contemporary king of Powys Wenwynwyn, Owain ap Gruffydd ap Maredudd, who became known as Owain Cyfeiliog.
Gruffydd ap Llywelyn was the first and only Welsh king to unite all of Wales under his rule from 1055 to 1063. He had also previously been King of Gwynedd and Powys from 1039 to 1055. Gruffydd was the son of Llywelyn ap Seisyll, king of Gwynedd, and Angharad daughter of Maredudd ab Owain, king of Deheubarth, and the great-great-grandson of Hywel Dda. After his death, Wales was again divided into separate kingdoms.
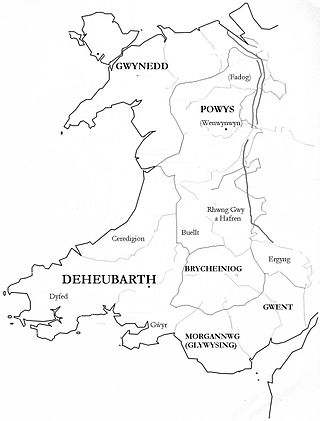
Deheubarth was a regional name for the realms of south Wales, particularly as opposed to Gwynedd. It is now used as a shorthand for the various realms united under the House of Dinefwr, but that Deheubarth itself was not considered a proper kingdom on the model of Gwynedd, Powys, or Dyfed is shown by its rendering in Latin as dextralis pars or as Britonnes dexterales and not as a named land. In the oldest British writers, Deheubarth was used for all of modern Wales to distinguish it from Hen Ogledd, the northern lands whence Cunedda originated.

The Kingdom of Powys was a Welsh successor state, petty kingdom and principality that emerged during the Middle Ages following the end of Roman rule in Britain. It very roughly covered the northern two-thirds of the modern county of Powys and part of today's English West Midlands. More precisely, and based on the Romano-British tribal lands of the Ordovices in the west and the Cornovii in the east, its boundaries originally extended from the Cambrian Mountains in the west to include the modern West Midlands region of England in the east. The fertile river valleys of the Severn and Tern are found there, and this region is referred to in later Welsh literature as "the Paradise of Powys".

Rhys ap Tewdwr was a king of Deheubarth in Wales and member of the Dinefwr dynasty, a branch descended from Rhodri the Great. Following the Norman Conquest, he had to pay William the Conqueror to keep his kingdom, which lasted until the end of William's reign.

Aberystwyth Castle is a Grade I listed Edwardian fortress located in Aberystwyth, Ceredigion, Mid Wales. It was built in response to the First Welsh War in the late 13th century, replacing an earlier fortress located a mile to the south. During a national uprising by Owain Glyndŵr, the Welsh captured the castle in 1404, but it was recaptured by the English four years later. From 1637 it housed a Royal mint of Charles I, which minted coins from locally mined silver. The castle was slighted by Oliver Cromwell in 1649.
Gruffydd ap Rhys was Prince of Deheubarth, in Wales. His sister was the Princess Nest ferch Rhys. He was the father of Rhys ap Gruffydd, known as 'The Lord Rhys', who was one of the most successful rulers of Deheubarth during this period.

Aberdyfi Castle is a castle located near Glandyfi, Ceredigion, in Wales. All that now remains is the motte, which is referred to as Domen Las.
Gwenllian ferch Gruffydd was a 12th century Welsh rebel and Princess consort of Deheubarth. The daughter of Prince of Gwynedd Gruffudd ap Cynan and member of the House of Aberffraw, she married Gruffydd ap Rhys, the Prince of Deheubarth, and would lead a "patriotic revolt" with him during the Great Revolt of 1136 until her death at the battle at Kidwelly Castle.
Anarawd ap Gruffydd was a Prince of Deheubarth in Southwest Wales.
Cadell ap Gruffydd was prince of the Kingdom of Deheubarth in Southwest Wales.

The Battle of Crug Mawr, sometimes referred to as the Battle of Cardigan, took place in September or October 1136, as part of a struggle between the Welsh and Normans for control of Ceredigion, West Wales.

Wiston Castle is a motte and bailey castle in the Pembrokeshire village of Wiston in south west Wales and is one of the best examples of its type in Wales. The castle and village were founded by Wizo, a Flemish settler who was granted the land by Henry I of England after he had wrested control from the previous owner, Arnulf de Montgomery. The castle was captured by the Welsh on several occasions but on each occasion it was retaken. It was abandoned during the thirteenth century when the then owner moved to nearby Picton Castle.

The Royal House of Dinefwr was a cadet branch of the Royal House of Gwynedd, founded by King Cadell ap Rhodri, son of Rhodri the Great. Their ancestor, Cunedda Wledig, born in late Roman Britain, was a Sub-Roman warlord who founded the Kingdom of Gwynedd during the 5th century, following the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. As Celtic Britons, the House of Dinefwr was ruling before the Norman conquest, having to fight with their neighbors such as the Anglo-Saxons and Vikings, before struggling with the Normans afterwards. Many members of this family were influential in Welsh history, such as Hywel Dda, who codified Welsh law under his rule, and achieved the important title of King of the Britons, or Lord Rhys, Prince of Wales, who rebelled against Richard the Lionheart, and became one of the most powerful Welsh leaders of the Middle Ages.
This article is about the particular significance of the century 1101–1200 to Wales and its people.
This article is about the particular significance of the century 1001–1100 to Wales and its people.

Wales in the High Middle Ages covers the 11th to 13th centuries in Welsh history. Beginning shortly before the Norman invasion of the 1060s and ending with the Conquest of Wales by Edward I between 1278 and 1283, it was a period of significant political, cultural and social change for the country.
Morgan ap Hywel was Lord of Gwynllwg in Wales from about 1215 until his death in 1245, and for many years laid claim to the lordship of Caerleon, which had been seized by the Earl of Pembroke. For most of his life he was at peace with the English, at a time when there were periodic revolts by Welsh leaders against their rule. He may have participated in a crusade between 1227 and 1231.

Rhayader Castle is the remains of a motte-and-bailey castle in the town of Rhayader, Powys, Wales. The available documentary sources are not clear enough to distinguish between this site and the castle mound across the river and one or the other was probably built by Rhys ap Gruffydd, Prince of Deheubarth, in 1177. At that time the river formed the border between Gwrtheyrnion and the independent state of Buellt; the town of Rhayader is on the Gwrtheyrnion side of the river.
References
- ↑ The Acts of Welsh Rulers: 1120-1283. University of Wales Press. 2010. pp. 166–167. ISBN 978-0-7083-2387-8.
- ↑ Thomas, Jeffrey L. (2009). "Lampeter Castle". Castles of Wales. Retrieved 5 April 2016.
- ↑ Wiles, J. (15 December 2003). "Stephen's Castle, Lampeter; Lampeter Motte". Coflein. Retrieved 5 April 2016.