
The Birmingham Small Arms Company Limited (BSA) was a major British industrial combine, a group of businesses manufacturing military and sporting firearms; bicycles; motorcycles; cars; buses and bodies; steel; iron castings; hand, power, and machine tools; coal cleaning and handling plants; sintered metals; and hard chrome process.

The Daimler Company Limited, before 1910 known as the Daimler Motor Company Limited, was an independent British motor vehicle manufacturer founded in London by H. J. Lawson in 1896, which set up its manufacturing base in Coventry. The company bought the right to the use of the Daimler name simultaneously from Gottlieb Daimler and Daimler-Motoren-Gesellschaft of Cannstatt, Germany. After early financial difficulty and a reorganisation of the company in 1904, the Daimler Motor Company was purchased by Birmingham Small Arms Company (BSA) in 1910, which also made cars under its own name before the Second World War. In 1933, BSA bought the Lanchester Motor Company and made it a subsidiary of the Daimler Company.

Frederick William Lanchester LLD, Hon FRAeS, FRS, was an English polymath and engineer who made important contributions to automotive engineering and to aerodynamics, and co-invented the topic of operations research.

The Longbridge plant is an industrial complex in Longbridge, Birmingham, England, currently leased by SAIC as a research and development facility for its MG Motor subsidiary. Vehicle assembly ended in 2016.

The Benz Velo was one of the first cars, introduced by Carl Benz in 1894 as the followup to the Patent-Motorwagen. 67 Benz Velos were built in 1894 and 134 in 1895. The early Velo had a 1L 1.5-metric-horsepower engine, and later a 3-metric-horsepower engine giving a top speed of 19 km/h (12 mph). The Velo was officially introduced by Karl Benz as the Velocipede, and became the world's first standardized serial production car. The Velocipede remained in production between 1894 and 1902, with a final count of over 1,200 produced.
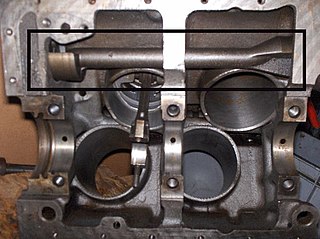
Balance shafts are used in piston engines to reduce vibration by cancelling out unbalanced dynamic forces. The counter balance shafts have eccentric weights and rotate in opposite direction to each other, which generates a net vertical force.
The Lanchester Motor Company Limited was a British car manufacturer in active trade between 1899 and 1955. Though the Lanchester Motor Company Limited is still registered as an active company and accounts are filed each year, the marque has been dormant since. As of 2014 it is marked as "non-trading".
Forward Gas Engine Company was an engineering company making stationary internal combustion gas engines in Nechells, Birmingham, England.

Nechells is a district ward in central Birmingham, England, whose population in 2011 was 33,957. It is also a ward within the formal district of Ladywood. Nechells local government ward includes areas, for example parts of Birmingham city centre, which are not part of the historic district of Nechells as such, now often referred to in policy documents as "North Nechells, Bloomsbury and Duddeston".

Swallow Sidecar Company, Swallow Sidecar and Coachbuilding Company, and Swallow Coachbuilding Company were trading names used by Walmsley & Lyons, partners and joint owners of a British manufacturer of motorcycle sidecars and automobile bodies in Blackpool, Lancashire, before incorporating a company in 1930 to own their business, which they named Swallow Coachbuilding Company Limited.

Old Square is a public square and road junction in the Core area of Birmingham City Centre, England.

HMS Forward is a Royal Naval Reserve unit located in Birmingham, England, close to St. Andrews football stadium. It has a crew of nearly 100 naval and marine reservists, in addition to a handful of full-time staff. The Birmingham University Royal Naval Unit, the Defence Technical Undergraduate Scheme 'Taurus Squadron' and a detachment of the Royal Marine Reserves Merseyside are also located on the site. The ship is particularly unusual in that it is situated 80 miles from the sea.

St George's Church, Edgbaston, is a parish church in the Church of England in Edgbaston, Birmingham.
George Herbert Lanchester was an English engineer. He was one of three brothers who played a leading role in the early development of the UK auto-industry.

BSA cars were manufactured between 1907 and 1912 in Birmingham then until 1939 in Coventry as well as Birmingham, England. BSA had established a motor-car department in an unsuccessful effort to make use of the Sparkbrook Birmingham factory. An independent part of the same site was occupied by The Lanchester Motor Company Limited. Sales were handled by BSA Cycles Limited. After 1912, manufacture was carried out by group subsidiary Daimler in Coventry or BSA Cycles in Birmingham.

The Lanchester Thirty-Eight was manufactured from 1910 to 1914 by the Lanchester Motor Company, located in Birmingham, England.

The Lanchester petrol-electric car is a prototype motor vehicle, designed in 1927 by Frederick W. Lanchester of the Lanchester Motor Company in his workshop in Birmingham, England. It is now on display in Thinktank, Birmingham Science Museum.
Henry Jones Lanchester (1834–1914) F.R.I.B.A was an English architect and surveyor. Most of his building work was carried out in Greenwich and Hove.
The Lanchester 8 hp Phaeton is a brass era automobile designed by Frederick W. Lanchester, developed and built by the Lanchester Motor Company, produced between 1895 and 1900. It was notably the first production vehicle to be powered by a flat twin-cylinder engine.















