
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere. It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove between tissues called the central sulcus and from the temporal lobe by a deeper groove called the lateral sulcus. The most anterior rounded part of the frontal lobe is known as the frontal pole, one of the three poles of the cerebrum.

Brodmann area 10 is the anterior-most portion of the prefrontal cortex in the human brain. BA10 was originally defined broadly in terms of its cytoarchitectonic traits as they were observed in the brains of cadavers, but because modern functional imaging cannot precisely identify these boundaries, the terms anterior prefrontal cortex, rostral prefrontal cortex and frontopolar prefrontal cortex are used to refer to the area in the most anterior part of the frontal cortex that approximately covers BA10—simply to emphasize the fact that BA10 does not include all parts of the prefrontal cortex.
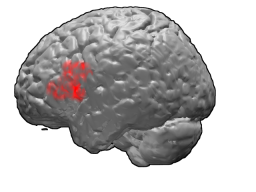
Brodmann area 45 (BA45), is part of the frontal cortex in the human brain. It is situated on the lateral surface, inferior to BA9 and adjacent to BA46.
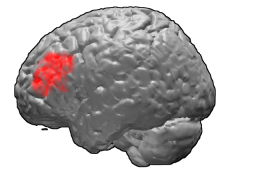
Brodmann area 46, or BA46, is part of the frontal cortex in the human brain. It is between BA10 and BA45.

Brodmann area 47, or BA47, is part of the frontal cortex in the human brain. It curves from the lateral surface of the frontal lobe into the ventral (orbital) frontal cortex. It is below areas BA10 and BA45, and beside BA11. This cytoarchitectonic region most closely corresponds to the gyral region the orbital part of inferior frontal gyrus, although these regions are not equivalent. Pars orbitalis is not based on cytoarchitectonic distinctions, and rather is defined according to gross anatomical landmarks. Despite a clear distinction, these two terms are often used liberally in peer-reviewed research journals.

The inferior frontal gyrus (IFG),, is the lowest positioned gyrus of the frontal gyri, of the frontal lobe, and is part of the prefrontal cortex.
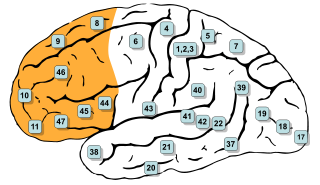
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. It is the association cortex in the frontal lobe. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46, and BA47.

The somatic marker hypothesis, formulated by Antonio Damasio and associated researchers, proposes that emotional processes guide behavior, particularly decision-making.
Affective neuroscience is the study of how the brain processes emotions. This field combines neuroscience with the psychological study of personality, emotion, and mood. The basis of emotions and what emotions are remains an issue of debate within the field of affective neuroscience.
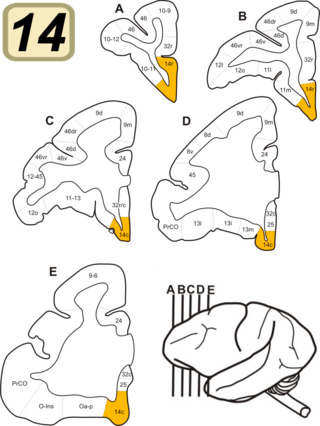
Brodmann Area 14 is one of Brodmann's subdivisions of the cerebral cortex in the brain. It was defined by Brodmann in the guenon monkey . While Brodmann, writing in 1909, argued that no equivalent structure existed in humans, later work demonstrated that area 14 has a clear homologue in the human ventromedial prefrontal cortex.

In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions are a set of cognitive processes that are necessary for the cognitive control of behavior: selecting and successfully monitoring behaviors that facilitate the attainment of chosen goals. Executive functions include basic cognitive processes such as attentional control, cognitive inhibition, inhibitory control, working memory, and cognitive flexibility. Higher-order executive functions require the simultaneous use of multiple basic executive functions and include planning and fluid intelligence.
The Iowa gambling task (IGT) is a psychological task thought to simulate real-life decision making. It was introduced by Antoine Bechara, Antonio Damasio, Hanna Damasio and Steven Anderson, then researchers at the University of Iowa. It has been brought to popular attention by Antonio Damasio in his best-selling book Descartes' Error.

The ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) is a part of the prefrontal cortex in the mammalian brain. The ventral medial prefrontal is located in the frontal lobe at the bottom of the cerebral hemispheres and is implicated in the processing of risk and fear, as it is critical in the regulation of amygdala activity in humans. It also plays a role in the inhibition of emotional responses, and in the process of decision-making and self-control. It is also involved in the cognitive evaluation of morality.
Consumer neuroscience is the combination of consumer research with modern neuroscience. The goal of the field is to find neural explanations for consumer behaviors in individuals both with or without disease.
The neurocircuitry that underlies executive function processes and emotional and motivational processes are known to be distinct in the brain. However, there are brain regions that show overlap in function between the two cognitive systems. Brain regions that exist in both systems are interesting mainly for studies on how one system affects the other. Examples of such cross-modal functions are emotional regulation strategies such as emotional suppression and emotional reappraisal, the effect of mood on cognitive tasks, and the effect of emotional stimulation of cognitive tasks.

The dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (dmPFC or DMPFC is a section of the prefrontal cortex in some species' brain anatomy. It includes portions of Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA24 and BA32, although some authors identify it specifically with BA8 and BA9. Some notable sub-components include the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, the prelimbic cortex, and the infralimbic cortex.

Prefrontal synthesis is the conscious purposeful process of synthesizing novel mental images. PFS is neurologically different from the other types of imagination, such as simple memory recall and dreaming. Unlike dreaming, which is spontaneous and not controlled by the prefrontal cortex (PFC), PFS is controlled by and completely dependent on the intact lateral prefrontal cortex. Unlike simple memory recall that involves activation of a single neuronal ensemble (NE) encoded at some point in the past, PFS involves active combination of two or more object-encoding neuronal ensembles (objectNE). The mechanism of PFS is hypothesized to involve synchronization of several independent objectNEs. When objectNEs fire out-of-sync, the objects are perceived one at a time. However, once those objectNEs are time-shifted by the lateral PFC to fire in-phase with each other, they are consciously experienced as one unified object or scene.
Neuromorality is an emerging field of neuroscience that studies the connection between morality and neuronal function. Scientists use fMRI and psychological assessment together to investigate the neural basis of moral cognition and behavior. Evidence shows that the central hub of morality is the prefrontal cortex guiding activity to other nodes of the neuromoral network. A spectrum of functional characteristics within this network to give rise to both altruistic and psychopathological behavior. Evidence from the investigation of neuromorality has applications in both clinical neuropsychiatry and forensic neuropsychiatry.
Social cognitive neuroscience is the scientific study of the biological processes underpinning social cognition. Specifically, it uses the tools of neuroscience to study "the mental mechanisms that create, frame, regulate, and respond to our experience of the social world". Social cognitive neuroscience uses the epistemological foundations of cognitive neuroscience, and is closely related to social neuroscience. Social cognitive neuroscience employs human neuroimaging, typically using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Human brain stimulation techniques such as transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct-current stimulation are also used. In nonhuman animals, direct electrophysiological recordings and electrical stimulation of single cells and neuronal populations are utilized for investigating lower-level social cognitive processes.











