
Latrodectus mactans, known as southern black widow or simply black widow, and the shoe-button spider, is a venomous species of spider in the genus Latrodectus. The females are well known for their distinctive black and red coloring and for the fact that they will occasionally eat their mates after reproduction. The species is native to North America. The venom can cause pain and other symptoms, but is rarely fatal to healthy humans.

Latrodectus is a broadly distributed genus of spiders with several species that are commonly known as the true widows. This group is composed of those often loosely called black widow spiders, brown widow spiders, and similar spiders. However, the diversity of species is much greater. A member of the family Theridiidae, this genus contains 34 species, which include several North American "black widows". Besides these, North America also has the red widow Latrodectus bishopi and the brown widow Latrodectus geometricus, which, in addition to North America, has a much wider geographic distribution. Elsewhere, others include the European black widow, the Australian redback spider and the closely related New Zealand katipō, several different species in Southern Africa that can be called button spiders, and the South American black-widow spiders. Species vary widely in size. In most cases, the females are dark-coloured and can be readily identified by reddish markings on the central underside (ventral) abdomen, which are often hourglass-shaped.

The redback spider, also known as the Australian black widow, is a species of highly venomous spider believed to originate in South Australia or adjacent Western Australian deserts, but now found throughout Australia, Southeast Asia and New Zealand, with colonies elsewhere outside Australia. It is a member of the cosmopolitan genus Latrodectus, the widow spiders. The adult female is easily recognised by her spherical black body with a prominent red stripe on the upper side of her abdomen and an hourglass-shaped red/orange streak on the underside. Females usually have a body length of about 10 millimetres (0.4 in), while the male is much smaller, being only 3–4 mm (0.12–0.16 in) long.

Latrodectus bishopi is the scientific name for the red widow spider, which is endemic to certain habitats of central and southern Florida, where it lives primarily in sand dunes dominated by sand pine, Pinus clausa – a type of vegetation found only in peninsular Florida.

The katipō is an endangered species of spider native to New Zealand. It is one of many species in the genus Latrodectus, such as the Australian redback, and the North American black widow. The species is venomous to humans, capable of delivering a potentially dangerous bite. It is a small to medium-sized spider, with the female having a round black or brown pea-sized body. Red katipō females found in the South Island and the lower half of the North Island, are always black, and their abdomen has a distinctive red stripe bordered in white. In black katipō females found in the upper half of the North Island, this stripe is absent, pale, yellow, or replaced with cream-coloured blotches. These two forms were previously thought to be separate species. The male is much smaller than the female and quite different in appearance: white with black stripes and red diamond-shaped markings. Katipō are mainly found living in sand dunes close to the seashore. They are found throughout most of coastal New Zealand except the far south and west. Katipō feed mainly on ground dwelling insects, caught in an irregular tangled web spun amongst dune plants or other debris.

Latrodectus geometricus, commonly known as the brown widow, brown button spider, grey widow, brown black widow, house button spider or geometric button spider, is one of the widow spiders in the genus Latrodectus. As such, it is a 'cousin' to the more infamous Latrodectus mactans. L. geometricus has black and white patterns on the sides of its abdomen as well as an orange-yellow colored hourglass shape marking. Their eggs are easily identified by points that project from all over the egg sacs. L. geometricus are found all over the world, but are believed to originate in Africa or South America. Their bites, though painful, are not considered to be dangerous.

The spider genus Steatoda, in the family Theridiidae, includes about 120 recognized species, distributed around the world. One common name is cupboard spider, for many species build their webs in dark, sheltered, undisturbed places around the house or garden, in sheds and garages, under garden, compost bins, and the like. Signs of the cupboard spider include small white spots of spider droppings, like small splashes of paint, on the floor underneath the web.

The woodlouse spider is a species of spider that preys primarily upon woodlice. Other common names refer to variations on the common name of its prey, including woodlouse hunter, sowbug hunter, sowbug killer, pillbug hunter and slater spider.
A latrotoxin is a high-molecular mass neurotoxin found in the venom of spiders of the genus Latrodectus as well as at least one species of another genus in the same family, Steatoda nobilis. Latrotoxins are the main active components of the venom and are responsible for the symptoms of latrodectism.

A spider bite, also known as arachnidism, is an injury resulting from the bite of a spider. The effects of most bites are not serious. Most bites result in mild symptoms around the area of the bite. Rarely they may produce a necrotic skin wound or severe pain.

Steatoda grossa, commonly known as the cupboard spider, the dark comb-footed spider, the brown house spider, or the false widow or false black widow, is a common species of spider in the genus Steatoda.

Latrodectus pallidus is a species of spider commonly found throughout North Africa, the Middle East, and central Asia. A common name in English is the white widow spider, and it is known in Russian as белый каракурт, or white steppe spider. It is a member of the genus Latrodectus, which includes species known as widow spiders, which is placed in the family Theridiidae. It occurs both in the steppes of southern Russia, Kazakhstan, and other southwest Asian countries, as well as in the desert regions of the Middle East. Compared to other widow spiders in the region, the white widow spider is comparatively rare.

Latrodectus variolus, the northern black widow spider or northern widow, is a venomous species of spider in the genus Latrodectus of the family Theridiidae. The population is closely related to the southern black widow, Latrodectus mactans, and the western black widow, Latrodectus hesperus, of the genus.

Latrodectus hesperus, the western black widow spider or western widow, is a venomous spider species found in western regions of North America. The female's body is 14–16 mm in length and is black, often with an hourglass-shaped red mark on the lower abdomen. This "hourglass" mark can be yellow, and on rare occasions, white. The male of the species is around half this length and generally a tan color with lighter striping on the abdomen. The population was previously described as a subspecies of Latrodectus mactans and it is closely related to the northern species Latrodectus variolus. The species, as with others of the genus, build irregular or "messy" webs: unlike the spiral webs or the tunnel-shaped webs of other spiders, the strands of a Latrodectus web have no apparent organization.

Latrodectism is the illness caused by the bite of Latrodectus spiders. Pain, muscle rigidity, vomiting, and sweating are the symptoms of latrodectism.
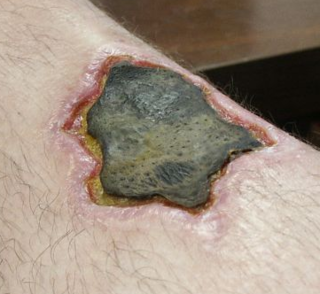
Loxoscelism is a condition occasionally produced by the bite of the recluse spiders. The area becomes dusky and a shallow open sore forms as the skin around the bite dies (necrosis). It is the only proven type of necrotic arachnidism in humans. While there is no known therapy effective for loxoscelism, there has been research on antibiotics, surgical timing, hyperbaric oxygen, potential antivenoms and vaccines. Because of the number of diseases that may mimic loxoscelism, it is frequently misdiagnosed by physicians.

Latrodectus elegans is a species of black widow spider, found in South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia. It was first collected by the Swedish arachnologist Tamerlan Thorell in the Karen Hills in Myanmar, but is also found in Thailand, India, Nepal, Vietnam, China and Japan. As of July 2022, the World Spider Catalog lists only India, Nepal, Myanmar, China and Japan. This species has been recorded in India and Nepal only since 2012, and Indochina in 2015, which is thought to reflect historical under-surveying of arachnids in this region.
The pathophysiology of a spider bite is due to the effect of its venom. A spider envenomation occurs whenever a spider injects venom into the skin. Not all spider bites inject venom – a dry bite, and the amount of venom injected can vary based on the type of spider and the circumstances of the encounter. The mechanical injury from a spider bite is not a serious concern for humans. Some spider bites do leave a large enough wound that infection may be a concern. However, it is generally the toxicity of spider venom that poses the most risk to human beings; several spiders are known to have venom that can cause injury to humans in the amounts that a spider will typically inject when biting.
Latrodectus revivensis, also known as the desert widow, is a species of venomous spider belonging to the Latrodectus genus and located in the Negev desert and the Arava valley (Arabah).

















