Related Research Articles

Common law is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions.

Liaquat Ali Khan was a Pakistani lawyer, politician and statesman who served as the first prime minister of Pakistan from 1947 until his assassination in 1951. He was as pivotal to the consolidation of Pakistan as the Quaid-i-Azam, Muhammad Ali Jinnah, was central to the creation of Pakistan. He was one of the leading figures of the Pakistan Movement and is revered as Quaid-e-Millat and later on as "Shaheed e Millat".

The legal system of India consists of civil law, common law, customary law, religious law and corporate law within the legal framework inherited from the colonial era and various legislation first introduced by the British are still in effect in modified forms today. Since the drafting of the Indian Constitution, Indian laws also adhere to the United Nations guidelines on human rights law and the environmental law. Personal law is fairly complex, with each religion adhering to its own specific laws. In most states, registering of marriages and divorces is not compulsory. Separate laws govern Hindus including Sikhs, Jains and Buddhist, Muslims, Christians, and followers of other religions. The exception to this rule is in the state of Goa, where a uniform civil code is in place, in which all religions have a common law regarding marriages, divorces, and adoption. On February 7, 2024, the Indian state of Uttarakhand also incorporated a uniform civil code. In the first major reformist judgment for the 2010s, the Supreme Court of India banned the Islamic practice of "Triple Talaq". The landmark Supreme Court of India judgment was welcomed by women's rights activists across India.

The Pakistan Movement was a political movement in the first half of the 20th century that aimed for the creation of Pakistan from the Muslim-majority areas of British India. It was connected to the perceived need for self-determination for Muslims under British rule at the time. Muhammad Ali Jinnah, a barrister and politician led this movement after the Lahore Resolution was passed by All-India Muslim League on 23 March 1940.

Alvin Robert Cornelius, H.Pk was a Pakistani jurist, legal philosopher and judge, serving as the 4th Chief Justice of Pakistan from 1960 until 1968. In addition, he served as Law Minister in the cabinet of Yahya Khan, 1969 – 16 December 1971.
A jirga is an assembly of leaders that makes decisions by consensus according to Pashtunwali, the Pashtun social code. It is conducted in order to settle disputes among the Pashtuns, but also by members of other ethnic groups who are influenced by them in present-day Afghanistan and Pakistan.

The Indian Independence Act 1947 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that partitioned British India into the two new independent dominions of India and Pakistan. The Act received Royal Assent on 18 July 1947 and thus modern-day India and Pakistan, comprising west and east regions, came into being on 15 August.

The Government of Pakistan, constitutionally known as the Federal Government, commonly known as the Centre, is the national authority of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, a federal republic located in South Asia, consisting of four provinces and one federal territory. The territories of Gilgit-Baltistan and Azad Kashmir are also part of the country but have separate systems and are not part of the federation.
Islamization or Shariazation, has a long history in Pakistan since the 1950s, but it became the primary policy, or "centerpiece" of the government of General Muhammad Zia-ul-Haq, the ruler of Pakistan from 1977 until his death in 1988.
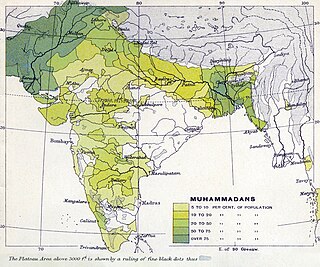
The two-nation theory was an ideology of religious nationalism that advocated Muslim Indian nationhood, with separate homelands for Indian Muslims and Indian Hindus within a decolonised British India, which ultimately led to the Partition of India in 1947. Its various descriptions of religious differences were the main factor in Muslim separatist thought in the Indian subcontinent, asserting that Indian Muslims and Indian Hindus are two separate nations, each with their own customs, traditions, art, architecture, literature, interests, and ways of life.

The history of Balochistan refers to the history of the Balochistan region of Pakistan, Iran and Afghanistan. Vague allusions to the region were found in Greek historical records of around 650 BCE. Prehistoric Balochistan dates to the Paleolithic.

Fatima Jinnah was a Pakistani politician, stateswoman, author, and activist. She was the younger sister of Muhammad Ali Jinnah, the founder and first Governor-General of Pakistan. She served as the Leader of the Opposition of Pakistan from 1960 until her death in 1967.

East Bengal was the eastern province of the Dominion of Pakistan, which covered the territory of modern-day Bangladesh. It consisted of the eastern portion of the Bengal region, and existed from 1947 until 1955, when it was renamed as East Pakistan. East Bengal had a coastline along the Bay of Bengal to the south, and bordered India to the north, west, and east and shared a small border with Burma to the southeast. It was situated near, but did not share a border with Nepal, Tibet, the Kingdom of Bhutan and the Kingdom of Sikkim. Its capital was Dacca, now known as Dhaka.

Syed Ameer Ali Order of the Star of India was an Indian jurist, a prominent political leader, and author of a number of influential books on Muslim history and the modern development of Islam.

The Urdu movement was a socio-political movement aimed at making Urdu, as the universal lingua-franca and symbol of the cultural and political identity of the Muslim communities of the Indian subcontinent during the British Raj. The movement began with the fall of the Mughal Empire in the mid-19th century, fuelled by the Aligarh movement of Sir Syed Ahmed Khan. It strongly influenced the All India Muslim League and the Pakistan movement.

Chaudhry Niaz Ali Khan was a civil engineer, agriculturalist, and philanthropist who founded "Dar ul Islam Movement" and "Dar ul Islam Trust" in South Asia and "Dar ul Islam Trust" Institutes in Pathankot and Jauharabad. Besides a philanthropist, Niaz was also a civil servant, and a landowner. He was the member of All-India Muslim League and a participant of the Pakistan Movement with the ultimate aim of creating the Muslim-majority areas of British India.

When the All-India Muslim League was founded at Dacca, on 30 December 1906 at the occasion of the annual All India Muhammadan Educational Conference, It was participated by the Muslim leaders from Punjab, i.e., Sir Mian Muhammad Shafi, Mian Fazl-i-Hussain, Abdul Aziz, Khawaja Yusuf Shah and Sh. Ghulam Sadiq. Earlier Mian Muhammad Shafi organised a Muslim Association in early 1906, but when the All-India Muslim League was formed, he established its powerful branch in the Punjab of which he became the general secretary. Shah Din was elected as its first president. This branch, organised in November 1907, was known as the Punjab Provincial Muslim League.
The concept of the Two-Nation Theory on which Pakistan was founded, was largely based on Muslim nationalism. Secularism in Pakistan went from being a matter of practice in law by the Government of Pakistan to a political movement opposing the Islamization policies of the military dictator General Zia-ul-Haq in the 1980s. The supporters of Islamisation on the other hand assert that Pakistan was founded as a Muslim state and that in its status as an Islamic republic, it must thereby implement Islamic laws, known as Sharia. Secularists feel that Mohammad Ali Jinnah wanted a state where religious oligarchy will be absent and all Muslims will be liberal, he envisioned for a progressive and liberal Muslim state of Pakistan.

Muhammad Ali Jinnah was a barrister, politician, and the founder of Pakistan. Jinnah served as the leader of the All-India Muslim League from 1913 until the inception of Pakistan on 14 August 1947, and then as the Republic of Pakistan's first governor-general until his death.
The Pashtun National Jirga or Pashtun National Court, also known as the Khyber Jirga, is scheduled to commence on 11 October 2024 under the leadership of the Pashtun Tahafuz Movement (PTM) in the Khyber District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. The jirga is set to address key issues affecting the Pashtuns, including security concerns, political autonomy, and socio-economic challenges in the region of Pashtunistan.
References
- ↑ Ponka, Rubina (2009). "Pakistan's Long March". Development and Cooperation. 36 (5). Frankfurt am Main: Frankfurter-Societät: 208–210. Archived from the original on 2009-07-29.
- ↑ "Pakistan Law". Archived from the original on 2018-11-09. Retrieved 2010-11-27.
- ↑ Imperial Gazetteer of India vol. II (1908), The Indian Empire, Historical, Published under the authority of His Majesty's Secretary of State for India in Council, Oxford at the Clarendon Press. Pp. xxxv, 1 map, 573., pp. 59–60