Related Research Articles
Petroleum geology is the study of origin, occurrence, movement, accumulation, and exploration of hydrocarbon fuels. It refers to the specific set of geological disciplines that are applied to the search for hydrocarbons.

Hydrocarbon exploration is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for deposits of hydrocarbons, particularly petroleum and natural gas, in the Earth's crust using petroleum geology.
The Fischer–Tropsch process is a collection of chemical reactions that converts a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, known as syngas, into liquid hydrocarbons. These reactions occur in the presence of metal catalysts, typically at temperatures of 150–300 °C (302–572 °F) and pressures of one to several tens of atmospheres. The Fischer–Tropsch process is an important reaction in both coal liquefaction and gas to liquids technology for producing liquid hydrocarbons.
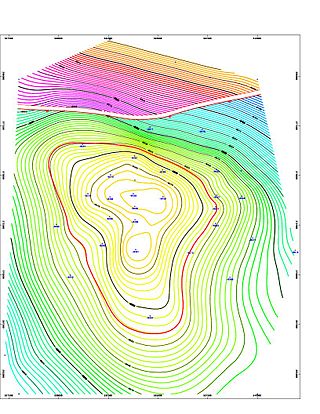
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations.

Mari Petroleum Company Limited (MPCL) (Urdu: مری پیٹرولیم کمپنی لیمٹڈ) is a Pakistani petroleum exploration and production company based in Islamabad, Pakistan. The company is controlled by the Fauji Foundation with 40 percent shares.
Propantes is a pothole on the mountain of Parnon within the borders of the Paliochori community of the Municipality of Leonidio in Greece. The entrance is about three by seven metres wide. The entrance shaft drops to -289m without the need for a re-belay, making it the deepest daylight shaft in mainland Greece. The shaft was first explored using modern caving single rope techniques in the early 1980s by a Polish team and the exploration repeated soon after by veteran Greek caver Petros Romanas. All subsequent visits for many years halted at the deepest point leading off the main shaft at -310m. Between 1998 and 2001, the depth of the pothole was surveyed to -316m following exploration carried out by SELAS caving club of Greece. This exploration followed leads in the form of windows coming off the main shaft. In 2005 and 2006, teams from SELAS continued the exploration in the main shaft beyond the squeeze which had halted previous exploration at -316m. The current surveyed depth of the cave is -360m with leads still to be explored.
The controlled source electromagnetic (CSEM) method, also called sea bed logging, is a mostly offshore geophysical technique, employing electromagnetic remote-sensing technology to map the electric resistivity distribution of the subsurface. The electrical resistivity helps to discriminate between different types of rocks. CSEM is mostly used to indicate the presence and extent of hydrocarbon below the seabed.
Resistivity logging is a method of well logging that works by characterizing the rock or sediment in a borehole by measuring its electrical resistivity. Resistivity is a fundamental material property which represents how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. In these logs, resistivity is measured using four electrical probes to eliminate the resistance of the contact leads. The log must run in holes containing electrically conductive mud or water, i.e., with enough ions present in the drilling fluid.

Fred F. Meissner was an American geologist and engineer who contributed to the fields of geology, geophysics, engineering, petroleum engineering, geochemistry, mineralogy, physics, mining, economic geology, and fishing.
The world's 932 giant oil and gas fields are considered those with 500 million barrels (79,000,000 m3) of ultimately recoverable oil or gas equivalent. Geoscientists believe these giants account for 40 percent of the world's petroleum reserves. They are clustered in 27 regions of the world, with the largest clusters in the Persian Gulf and Western Siberian basin. The past three decades reflect declines in discoveries of giant fields. The years 2000–11 reflect an upturn in discoveries and appears on track to be the third best decade for discovery of giant oil and gas fields in the 150-year history of modern oil and gas exploration.
KazMunayGas Exploration Production JSC is a KazMunayGas-majority-owned oil and gas company operating in the Republic of Kazakhstan.

Ligeia Mare is a lake in the north polar region of Titan, the planet Saturn's largest moon. It is the second largest body of liquid on the surface of Titan, after Kraken Mare. Larger than Lake Superior on Earth, it is mostly composed of liquid methane, with unknown but lesser components of dissolved nitrogen and ethane, as well as other organic compounds. It is located at 78° N, 249° W, and has been fully imaged by the Cassini spacecraft. Measuring roughly 420 km (260 mi) by 350 km (217 mi) across, it has a surface area of about 126,000 km2, and a shoreline over 2,000 km (1,240 mi) in length. The lake may be hydrologically connected to the larger Kraken Mare. Its namesake is Ligeia, one of the sirens in Greek mythology.

Titan Mare Explorer (TiME) is a proposed design for a lander for Saturn's moon Titan. TiME is a relatively low-cost, outer-planet mission designed to measure the organic constituents on Titan and would have performed the first nautical exploration of an extraterrestrial sea, analyze its nature and, possibly, observe its shoreline. As a Discovery-class mission it was designed to be cost-capped at US$425 million, not counting launch vehicle funding. It was proposed to NASA in 2009 by Proxemy Research as a scout-like pioneering mission, originally as part of NASA's Discovery Program. The TiME mission design reached the finalist stage during that Discovery mission selection, but was not selected, and despite attempts in the U.S. Senate failed to get earmark funding in 2013. A related Titan Submarine has also been proposed.

Thin-skinned deformation is a style of deformation in plate tectonics at a convergent boundary which occurs with shallow thrust faults that only involves cover rocks, and not deeper basement rocks.
New Exploration Licensing Policy (NELP) was conceptualised by the Government of India, during 1997-98 to provide an equal platform to both Public and Private sector companies in exploration and production of hydrocarbons with Directorate General of Hydrocarbons (DGH) as a nodal agency for its implementation. It was introduced to boost the production of oil and natural gas and providing level playing field for both public and private players.
Petroleum licensing or exploration license is the act of giving licenses to a company or a joint venture allowing them to search for commercially feasible deposits for the extraction of petroleum.
The Directorate General of Hydrocarbon (DGH) is the Indian governmental regulatory body under the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas.
The Kaveri delta coal-bed methane extraction project is a series of projects to extract methane gas and hydrocarbon from coal-bed by using hydraulic fracturing in the Kaveri river basin in Tamil Nadu, India. The extraction projects faced series of opposition from the farmers, environmentalists, and experts as exploration areas covering Nagapattinam, Thanjavur and Thiruvarur districts which are the major rice cultivating area of Tamil Nadu.
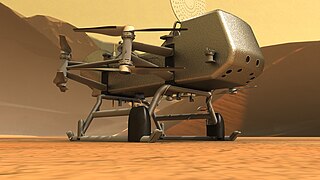
Dragonfly is a planned spacecraft and NASA mission, which will send a robotic rotorcraft to the surface of Titan, the largest moon of Saturn. It would be the first aircraft on Titan and is intended to make the first powered and fully controlled atmospheric flight on any moon, with the intention of studying prebiotic chemistry and extraterrestrial habitability. It will then use its vertical takeoffs and landings (VTOL) capability to move between exploration sites.
The Officer Basin is an intracratonic sedimentary basin that covers roughly 320,000 km2 along the border between southern and western Australia. Exploration for hydrocarbons in this basin has been sparse, but the geology has been examined for its potential as a hydrocarbon reservoir. This basin's extensive depositional history, with sedimentary thicknesses exceeding 6 km and spanning roughly 350 Ma during the Neoproterozoic, make it an ideal candidate for hydrocarbon production.
References
- ↑ Jahn, F.; Cook M.; Graham M. (2008). Hydrocarbon exploration and production. Developments in petroleum science. Vol. 55. Elsevier. p. 444. ISBN 9780444532367 . Retrieved 2009-11-29.