Related Research Articles
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in the Northern Atlantic, between Great Britain, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost part of the United Kingdom.

Lerwick is the main town and port of the Shetland archipelago, Scotland. Shetland's only burgh, Lerwick had a population of about 7,000 residents in 2010.

Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time.

Enwave Energy Corporation is a Canadian energy company headquartered in Toronto that provides sustainable district energy solutions including heating, cooling, hot water, combined heat and power, geoexchange, energy storage, sewer heat, waste-to-energy, biomass, solar energy systems. It is one of the largest district energy systems in North America and has been referred as the leading energy district system providing its services for over three decades across Canadian cities including Toronto, London, Charlottetown, Windsor, and Markham. With the help of proven, sustainable technologies, Enwave Energy Corporation has built its reputation on solving the cooling, heating and energy needs of over 700 customers including commercial properties, single- and multi-family homes, hospitals, data centers, educational centers, and mixed use developments.

Tavish Hamilton Scott is a former Scottish politician. He was the Member of the Scottish Parliament (MSP) for Shetland from 1999 to 2019, and Leader of the Scottish Liberal Democrats from 2008 to 2011. He stepped down as Leader after the 2011 Scottish Parliament election, in which the Liberal Democrats were reduced to five seats, down from 16 in the previous parliament.

District heating is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heating and water heating. The heat is often obtained from a cogeneration plant burning fossil fuels or biomass, but heat-only boiler stations, geothermal heating, heat pumps and central solar heating are also used, as well as heat waste from factories and nuclear power electricity generation. District heating plants can provide higher efficiencies and better pollution control than localized boilers. According to some research, district heating with combined heat and power (CHPDH) is the cheapest method of cutting carbon emissions, and has one of the lowest carbon footprints of all fossil generation plants.
Micro combined heat and power, micro-CHP, µCHP or mCHP is an extension of the idea of cogeneration to the single/multi family home or small office building in the range of up to 50 kW. Usual technologies for the production of heat and power in one common process are e.g. internal combustion engines, micro gas turbines, stirling engines or fuel cells.

Leirvík is a town on the Faroe Islands and was an important regional ferry harbour at the east coast of the second-largest island Eysturoy. Leirvík has 925 inhabitants.
Tingwall Airport, also known as Lerwick/Tingwall Airport, is located in the Tingwall valley, near the village of Gott, 4 NM northwest of Lerwick in Mainland, Shetland, Scotland. Although it is the nearest airport to Lerwick, it is not Shetland's main airport, which is at Sumburgh. It is the one most used for inter-island flights within Shetland.

Waste heat is heat that is produced by a machine, or other process that uses energy, as a byproduct of doing work. All such processes give off some waste heat as a fundamental result of the laws of thermodynamics. Waste heat has lower utility than the original energy source. Sources of waste heat include all manner of human activities, natural systems, and all organisms, for example, incandescent light bulbs get hot, a refrigerator warms the room air, a building gets hot during peak hours, an internal combustion engine generates high-temperature exhaust gases, and electronic components get warm when in operation.
The utility infrastructure of London, England comprises a range of services and facilities that support and enable the functioning of London as a world city. Infrastructure includes facilities associated with products and materials that are consumed such as electricity, gas, water, heating and liquid fuels; materials that are produced such as sewage and solid waste; and facilities that enable communication and connectivity – telecommunications.
A sustainable community energy system is an integrated approach to supplying a local community with its energy requirements from renewable energy or high-efficiency co-generation energy sources. The approach can be seen as a development of the distributed generation concept.

The Sheffield Energy Recovery Facility, also known as the Energy from Waste Plant, is a modern incinerator which treats Sheffield's household waste. It is notable as it not only provides electricity from the combustion of waste but also supplies heat to a local district heating scheme, making it one of the most advanced, energy efficient incineration plants in the UK. In 2004, the district heating network prevented 15,108 tonnes of CO2 from being released from buildings across the city, compared to energy derived from fossil fuels. The incinerator is a 'static asset' owned by Sheffield City Council and operated by Veolia Environmental Services under a 35 year integrated waste management contract (IWMC)/PFI contract.

The production of renewable energy in Scotland is a topic that has come to the fore in technical, economic, and political terms during the opening years of the 21st century. The natural resource base for renewable energy is high by European, and even global standards, with the most important potential sources being wind, wave, and tide. Renewables produced the equivalent of 97.4% of Scotland's electricity consumption in 2020, mostly from the country's wind power.

The potential for exploiting geothermal energy in the United Kingdom on a commercial basis was initially examined by the Department of Energy in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis. Several regions of the country were identified, but interest in developing them was lost as petroleum prices fell. Although the UK is not actively volcanic, a large heat resource is potentially available via shallow geothermal ground source heat pumps, shallow aquifers and deep saline aquifers in the mesozoic basins of the UK. Geothermal energy is plentiful beneath the UK, although it is not readily accessible currently except in specific locations.
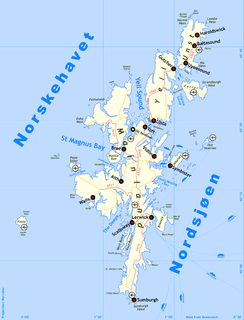
The Sullom Voe Terminal is an oil and gas terminal at Sullom Voe in the Shetland Islands of Scotland. It handles production from oilfields in the North Sea and East Shetland Basin and stores oil before it is transported by tanker.

Energy in Finland describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Finland. Energy policy of Finland describes the politics of Finland related to energy. Electricity sector in Finland is the main article of electricity in Finland.
Viking Wind Farm is a wind farm under construction which is being developed by Viking Energy, a partnership between Shetland Islands Council and SSE plc.

The main power supply for Shetland is provided by Lerwick Power Station, located in Gremista, 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) northwest of Lerwick town centre. This is the principal source of electrical energy for Shetland, however currently about 20 MWe is provided by the Sullom Voe Terminal power station which comprises 4 x 23 MWe Gas Turbines, the future of which is uncertain. Opened on 27 May 1953 the station is diesel-fuelled and generates a total of 66 MW of power.

The Southampton District Energy Scheme is a district heating and cooling system in Southampton, United Kingdom. The system is owned and operated by ENGIE.
References
- ↑ "Shetland Heat Energy and Power - Lerwick's District Heating". www.sheap-ltd.co.uk.
- ↑ "Shetland Islands Council - Council Information". www.shetland.gov.uk.