Related Research Articles

Maat or Maʽat refers to the ancient Egyptian concepts of truth, balance, order, harmony, law, morality, and justice. Ma'at was also the goddess who personified these concepts, and regulated the stars, seasons, and the actions of mortals and the deities who had brought order from chaos at the moment of creation. Her ideological opposite was Isfet, meaning injustice, chaos, violence or to do evil.

Hathor was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sky god Horus and the sun god Ra, both of whom were connected with kingship, and thus she was the symbolic mother of their earthly representatives, the pharaohs. She was one of several goddesses who acted as the Eye of Ra, Ra's feminine counterpart, and in this form she had a vengeful aspect that protected him from his enemies. Her beneficent side represented music, dance, joy, love, sexuality, and maternal care, and she acted as the consort of several male deities and the mother of their sons. These two aspects of the goddess exemplified the Egyptian conception of femininity. Hathor crossed boundaries between worlds, helping deceased souls in the transition to the afterlife.

Hieratic is the name given to a cursive writing system used for Ancient Egyptian and the principal script used to write that language from its development in the third millennium BC until the rise of Demotic in the mid-first millennium BC. It was primarily written in ink with a reed pen on papyrus.

The ancient Egyptians believed that a soul was made up of many parts. In addition to these components of the soul, there was the human body.
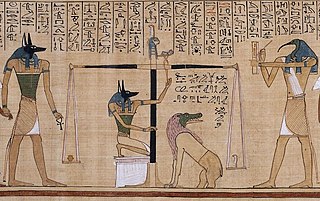
The Book of the Dead is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom to around 50 BCE. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated rw nw prt m hrw, is translated as Book of Coming Forth by Day or Book of Emerging Forth into the Light. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the Duat, or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name Todtenbuch, translated to English as Book of the Dead.

The Middle Kingdom of Egypt is the period in the history of ancient Egypt following a period of political division known as the First Intermediate Period. The Middle Kingdom lasted from approximately 2040 to 1782 BC, stretching from the reunification of Egypt under the reign of Mentuhotep II in the Eleventh Dynasty to the end of the Twelfth Dynasty. The kings of the Eleventh Dynasty ruled from Thebes and the kings of the Twelfth Dynasty ruled from el-Lisht.

The Elephantine Papyri and Ostraca consist of thousands of documents from the Egyptian border fortresses of Elephantine and Aswan, which yielded hundreds of papyri and ostraca in hieratic and demotic Egyptian, Aramaic, Koine Greek, Latin and Coptic, spanning a period of 100 years in the 5th to 4th centuries BCE. The documents include letters and legal contracts from family and other archives, and are thus an invaluable source of knowledge for scholars of varied disciplines such as epistolography, law, society, religion, language and onomastics. The Elephantine documents include letters and legal contracts from family and other archives: divorce documents, the manumission of slaves, and other business. The dry soil of Upper Egypt preserved the documents.

In Ancient Egyptian religion, Taweret is the protective ancient Egyptian goddess of childbirth and fertility. The name "Taweret" (Tȝ-wrt) means "she who is great" or simply "great one", a common pacificatory address to dangerous deities. The deity is typically depicted as a bipedal female hippopotamus with feline attributes, pendulous female human breasts, the limbs and paws of a lion, and the back and tail of a Nile crocodile. She commonly bears the epithets "Lady of Heaven", "Mistress of the Horizon", "She Who Removes Water", "Mistress of Pure Water", and "Lady of the Birth House".

The Eye of Horus, wedjat eye or udjat eye is a concept and symbol in ancient Egyptian religion that represents well-being, healing, and protection. It derives from the mythical conflict between the god Horus with his rival Set, in which Set tore out or destroyed one or both of Horus's eyes and the eye was subsequently healed or returned to Horus with the assistance of another deity, such as Thoth. Horus subsequently offered the eye to his deceased father Osiris, and its revitalizing power sustained Osiris in the afterlife. The Eye of Horus was thus equated with funerary offerings, as well as with all the offerings given to deities in temple ritual. It could also represent other concepts, such as the moon, whose waxing and waning was likened to the injury and restoration of the eye.

The ushabti was a funerary figurine used in ancient Egyptian funerary practices. The Egyptological term is derived from 𓅱𓈙𓃀𓏏𓏭𓀾 wšbtj, which replaced earlier 𓆷𓍯𓃀𓏏𓏭𓀾 šwbtj, perhaps the nisba of 𓈙𓍯𓃀𓆭 šwꜣb "Persea tree".

Huni was an ancient Egyptian king and the last pharaoh of the Third Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom period. Following the Turin king list, he is commonly credited with a reign of 24 years, ending c. 2613 BC.

The ancient Egyptians had an elaborate set of funerary practices that they believed were necessary to ensure their immortality after death. These rituals included mummifying the body, casting magic spells, and burials with specific grave goods thought to be needed in the afterlife.

Ancient Egyptian literature was written in the Egyptian language from ancient Egypt's pharaonic period until the end of Roman domination. It represents the oldest corpus of Egyptian literature. Along with Sumerian literature, it is considered the world's earliest literature.

The Kahun Gynaecological Papyrus is the oldest known medical text in Egypt, although not the oldest in the world as in Philadelphia museum a Sumerian medical clay tablet from 3rd millennium is preserved. Dated to c. 1800 BCE, it deals with women's health—gynaecological diseases, fertility, pregnancy, contraception, etc.

Egyptian medical papyri are ancient Egyptian texts written on papyrus which permit a glimpse at medical procedures and practices in ancient Egypt. These papyri give details on disease, diagnosis, and remedies of disease, which include herbal remedies, surgery, and magical incantations. Many of these papyri have been lost due to grave robbery. The largest study of the medical papyri to date has been undertaken by Humboldt University of Berlin and was titled Medizin der alten Ägypter.
The ancient Egyptian Papyrus stem hieroglyph is one of the oldest language hieroglyphs from Ancient Egypt. The papyrus stalk, was incorporated into designs of columns on buildings, also facades, and is also in the iconographic art portrayed in ancient Egyptian decorated scenes.

Harper's Songs are ancient Egyptian texts that originated in tomb inscriptions of the Middle Kingdom, which in the main praise life after death and were often used in funerary contexts. These songs display varying degrees of hope in an afterlife that range from the skeptical through to the more traditional expressions of confidence. These texts are accompanied by drawings of blind harpists and are therefore thought to have been sung. Thematically they have been compared with The Immortality of Writers in their expression of rational skepticism.
This page list topics related to ancient Egypt.
The Egyptian Book of the Dead of Qenna is a papyrus document housed at the Dutch National Museum of Antiquities in Leiden. One of several thousand papyri containing material drawn from Book of the Dead funerary texts, Qenna uniquely includes a passage that describes a deceased person’s activity in an afterlife location it calls the “house of hearts.” While the house of hearts is mentioned in at least two tomb inscriptions, Qenna treats it in more detail. The passage appears as an addendum within Spell 151 of the Book of the Dead:
"You will enter the house of hearts, the place which is full of hearts. You will take the one that is yours and put it in its place, without your hand being hindered. Your foot will not be stopped from walking. You will not walk upside down. You will walk upright."

Martin Bommas is a German Egyptologist, archaeologist, and philologist. He is a professor and Museum Director at the Macquarie University History Museum in Sydney, Australia and the Director of the Qubbet el-Hawa Research Project (QHRP) in Aswan, Egypt. He has published widely on ancient Egyptian mortuary liturgies, rituals and religious texts spanning the Old Kingdom to the Christian era. In archaeology, he has examined the Old and Middle Kingdom settlement remains and the 18th Dynasty temple of Khnum at Elephantine as well as the Old and Middle Kingdom Lower Necropolis at Qubbet el-Hawa. As a museum director, his focus is on historical anthropology, decolonisation and the repatriation of illicitly trafficked artefacts.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Troche, Julia (2018-09-11). "Letters to the Dead". UCLA Encyclopedia of Egyptology. 1 (1).
- ↑ "Letters to the Dead". www.ucl.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 2022-07-17. Retrieved 2021-03-19.
- ↑ Harrington, Nicola (2013). Living with the dead : ancestor worship and mortuary ritual in ancient Egypt. Oxford: Oxbow Books. pp. 34–37. ISBN 978-1-84217-493-7. OCLC 813220916.
- ↑ "Qau tomb 7695". www.ucl.ac.uk. Retrieved 2021-03-19.
- 1 2 "Qau tomb 7695, The Letter to the Dead of Shepsi". www.ucl.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 2022-12-20. Retrieved 2021-03-19.
- 1 2 "Papyrus Inscribed in Abnormal Hieratic". www.brooklynmuseum.org. Archived from the original on 2022-08-10. Retrieved 2021-03-19.