Related Research Articles

The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest, called the mediastinum.

Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the arteries and veins that supply the heart muscle (myocardium). Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Cardiac veins then drain away the blood after it has been deoxygenated. Because the rest of the body, and most especially the brain, needs a steady supply of oxygenated blood that is free of all but the slightest interruptions, the heart is required to function continuously. Therefore its circulation is of major importance not only to its own tissues but to the entire body and even the level of consciousness of the brain from moment to moment. Interruptions of coronary circulation quickly cause heart attacks, in which the heart muscle is damaged by oxygen starvation. Such interruptions are usually caused by coronary ischemia linked to coronary artery disease, and sometimes to embolism from other causes like obstruction in blood flow through vessels.

A heart valve is a biological one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. Four valves are usually present in a mammalian heart and together they determine the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart valve opens or closes according to differential blood pressure on each side.

A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles, while intraventricular means within one ventricle.

dextro-Transposition of the great arteries is a potentially life-threatening birth defect in the large arteries of the heart. The primary arteries are transposed.

Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this does not naturally close after birth it is referred to as a patent (open) foramen ovale (PFO). It is common in patients with a congenital atrial septal aneurysm (ASA).

The atrium is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves.

Transposition of the great vessels (TGV) is a group of congenital heart defects involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the great vessels: superior and/or inferior venae cavae, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and aorta. Congenital heart diseases involving only the primary arteries belong to a sub-group called transposition of the great arteries (TGA), which is considered the most common congenital heart lesion that presents in neonates.

Tricuspid atresia is a form of congenital heart disease whereby there is a complete absence of the tricuspid valve. Therefore, there is an absence of right atrioventricular connection. This leads to a hypoplastic (undersized) or absent right ventricle. This defect is contracted during prenatal development, when the heart does not finish developing. It causes the systemic circulation to be filled with relatively deoxygenated blood. The causes of tricuspid atresia are unknown.

The cardiac cycle is the performance of the human heart from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood, called diastole, following a period of robust contraction and pumping of blood, called systole. After emptying, the heart relaxes and expands to receive another influx of blood returning from the lungs and other systems of the body, before again contracting to pump blood to the lungs and those systems. A normally performing heart must be fully expanded before it can efficiently pump again. Assuming a healthy heart and a typical rate of 70 to 75 beats per minute, each cardiac cycle, or heartbeat, takes about 0.8 second to complete the cycle. There are two atrial and two ventricle chambers of the heart; they are paired as the left heart and the right heart—that is, the left atrium with the left ventricle, the right atrium with the right ventricle—and they work in concert to repeat the cardiac cycle continuously. At the start of the cycle, during ventricular diastole–early, the heart relaxes and expands while receiving blood into both ventricles through both atria; then, near the end of ventricular diastole–late, the two atria begin to contract, and each atrium pumps blood into the ventricle below it. During ventricular systole the ventricles are contracting and vigorously pulsing two separated blood supplies from the heart—one to the lungs and one to all other body organs and systems—while the two atria are relaxed. This precise coordination ensures that blood is efficiently collected and circulated throughout the body.
A right-to-left shunt is a cardiac shunt which allows blood to flow from the right heart to the left heart. This terminology is used both for the abnormal state in humans and for normal physiological shunts in reptiles.
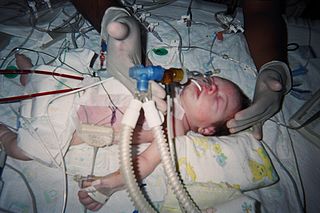
Arterial switch operation (ASO) or arterial switch, is an open heart surgical procedure used to correct dextro-transposition of the great arteries (d-TGA).
A cardiac shunt is a pattern of blood flow in the heart that deviates from the normal circuit of the circulatory system. It may be described as right-left, left-right or bidirectional, or as systemic-to-pulmonary or pulmonary-to-systemic. The direction may be controlled by left and/or right heart pressure, a biological or artificial heart valve or both. The presence of a shunt may also affect left and/or right heart pressure either beneficially or detrimentally.
The Mustard procedure was developed in 1963 by Dr. William Mustard at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, Ontario, Canada.

Atrial septostomy is a surgical procedure in which a small hole is created between the upper two chambers of the heart, the atria. This procedure is primarily used to palliate dextro-Transposition of the great arteries or d-TGA, a life-threatening cyanotic congenital heart defect seen in infants. It is performed prior to an arterial switch operation. Atrial septostomy has also seen limited use as a surgical treatment for pulmonary hypertension. The first atrial septostomy was developed by Vivien Thomas in a canine model and performed in humans by Alfred Blalock. The Rashkind balloon procedure, a common atrial septostomy technique, was developed in 1966 by American cardiologist William Rashkind at the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
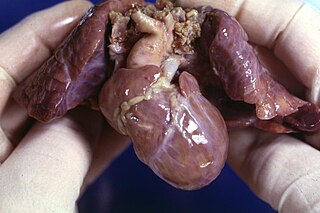
Hypoplastic right heart syndrome is a congenital heart defect in which the structures on the right side of the heart, particularly the right ventricle, are underdeveloped. This defect causes inadequate blood flow to the lungs, and thus a cyanotic infant.
Pulmonary Artery Banding (PAB) was introduced by Muller and Dammann in 1951 as a surgical technique to reduce excessive pulmonary blood flow in infants suffering from congenital heart defects. PAB is a palliative operation as it does not correct the problems, but attempts to improve abnormal heart function, relieve symptoms and reduce high pressure in the lungs. The use of PAB has decreased over the years due to advancements in definitive surgical repairs, however PAB still has widespread clinical use. PAB is commonly used in patients when definitive surgical repair is not feasible.
The Senning procedure is an atrial switch heart operation performed to treat transposition of the great arteries. It is named after its inventor, the Swedish cardiac surgeon Åke Senning (1915–2000), also known for implanting the first permanent cardiac pacemaker in 1958.
Raghib syndrome is rare a congenital heart defect where the left superior vena cava (LSVC) is draining into the left atrium in addition to an absent coronary sinus and an atrial septal defect. This can be considered a dangerous heart condition because it puts the individual at a high risk of stroke. Other defects that are often associated with Raghib syndrome can include ventricular septal defects, enlargement of the tricuspid annulus, and pulmonary stenosis. While this is considered an extremely rare developmental complex, cases regarding a persistent left superior vena cava (PLSVC) are relatively common among congenital heart defects. It is also important to note that the PLSVC often drains into the right atrium, and only drains into the left atrium in approximately 10 to 20% of individuals with the defect.
References
- ↑ RESERVED, INSERM US14 -- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Congenitally corrected transposition of the great arteries". www.orpha.net. Retrieved 2017-10-14.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)