Related Research Articles
Lexicography is the study of lexicons, and is divided into two separate academic disciplines. It is the art of compiling dictionaries.

A parallel text is a text placed alongside its translation or translations. Parallel text alignment is the identification of the corresponding sentences in both halves of the parallel text. The Loeb Classical Library and the Clay Sanskrit Library are two examples of dual-language series of texts. Reference Bibles may contain the original languages and a translation, or several translations by themselves, for ease of comparison and study; Origen's Hexapla placed six versions of the Old Testament side by side. A famous example is the Rosetta Stone, whose discovery allowed the Ancient Egyptian language to begin being deciphered.
Terminology is a group of specialized words and respective meanings in a particular field, and also the study of such terms and their use; the latter meaning is also known as terminology science. A term is a word, compound word, or multi-word expressions that in specific contexts is given specific meanings—these may deviate from the meanings the same words have in other contexts and in everyday language. Terminology is a discipline that studies, among other things, the development of such terms and their interrelationships within a specialized domain. Terminology differs from lexicography, as it involves the study of concepts, conceptual systems and their labels (terms), whereas lexicography studies words and their meanings.
Computer-aided translation (CAT), also referred to as computer-assisted translation or computer-aided human translation (CAHT), is the use of software to assist a human translator in the translation process. The translation is created by a human, and certain aspects of the process are facilitated by software; this is in contrast with machine translation (MT), in which the translation is created by a computer, optionally with some human intervention.
A specialized dictionary is a dictionary that covers a relatively restricted set of phenomena. The definitive book on the subject includes chapters on some of the dictionaries included below:

A law dictionary is a dictionary that is designed and compiled to give information about terms used in the field of law.
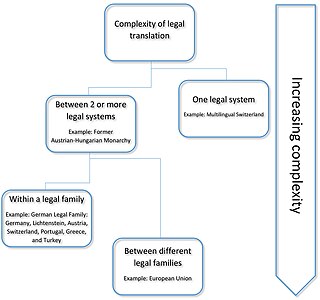
Legal translation is the translation of language used in legal settings and for legal purposes. Legal translation may also imply that it is a specific type of translation only used in law, which is not always the case. As law is a culture-dependent subject field, legal translation is not necessarily linguistically transparent. Intransparency in translation can be avoided somewhat by use of Latin legal terminology, where possible, but in non-western languages debates are centered on the origins and precedents of specific terms, such as in the use of particular Chinese characters in Japanese legal discussions.

An electronic dictionary is a dictionary whose data exists in digital form and can be accessed through a number of different media. Electronic dictionaries can be found in several forms, including software installed on tablet or desktop computers, mobile apps, web applications, and as a built-in function of E-readers. They may be free or require payment.

A bilingual dictionary or translation dictionary is a specialized dictionary used to translate words or phrases from one language to another. Bilingual dictionaries can be unidirectional, meaning that they list the meanings of words of one language in another, or can be bidirectional, allowing translation to and from both languages. Bidirectional bilingual dictionaries usually consist of two sections, each listing words and phrases of one language alphabetically along with their translation. In addition to the translation, a bilingual dictionary usually indicates the part of speech, gender, verb type, declension model and other grammatical clues to help a non-native speaker use the word. Other features sometimes present in bilingual dictionaries are lists of phrases, usage and style guides, verb tables, maps and grammar references. In contrast to the bilingual dictionary, a monolingual dictionary defines words and phrases instead of translating them.
Beryl T. "Sue" Atkins was a British lexicographer, specialising in computational lexicography, who pioneered the creation of bilingual dictionaries from corpus data.
Linguistic categories include
In digital lexicography, natural language processing, and digital humanities, a lexical resource is a language resource consisting of data regarding the lexemes of the lexicon of one or more languages e.g., in the form of a database.
Contrastive linguistics is a practice-oriented linguistic approach that seeks to describe the differences and similarities between a pair of languages.

Microsoft Translator is a multilingual machine translation cloud service provided by Microsoft. Microsoft Translator is a part of Microsoft Cognitive Services and integrated across multiple consumer, developer, and enterprise products, including Bing, Microsoft Office, SharePoint, Microsoft Edge, Microsoft Lync, Yammer, Skype Translator, Visual Studio, and Microsoft Translator apps for Windows, Windows Phone, iPhone and Apple Watch, and Android phone and Android Wear.
National Translation Mission (NTM) is a Government of India initiative to make knowledge texts accessible, in all 22 official languages of the Indian Republic listed in the VIII schedule of the Constitution, through translation. NTM was set up on the recommendation of the National Knowledge Commission. The Ministry of Human Resource Development has designated Central Institute of Indian Languages as the nodal organization for the operationalization of NTM.
Pamela Faber Benítez is an American/Spanish linguist. She has held the Chair of Translation and Interpreting at the Department of Translation and Interpreting of the University of Granada since 2001.
The Terminology Coordination Unit (TermCoord) is a supporting unit to the translation units of the Directorate-General for Translation of the European Parliament. TermCoord was created in 2008 by Rodolfo Maslias, professor at the Universities Luxembourg and Savoie-Mont Blanc, to stimulate and coordinate the terminology work of the 24 translation units of the European Parliament in Luxembourg.
Lexicography evolved in order to serve one of two needs i.e. in order to explain in a simple way difficult words and expressions or in order to explain the words and expressions of one language in another. In this case we can trace the tradition of lexicography in Irish back to the 8th century.

Sketch Engine is a corpus manager and text analysis software developed by Lexical Computing CZ s.r.o. since 2003. Its purpose is to enable people studying language behaviour to search large text collections according to complex and linguistically motivated queries. Sketch Engine gained its name after one of the key features, word sketches: one-page, automatic, corpus-derived summaries of a word's grammatical and collocational behaviour. Currently, it supports and provides corpora in 90+ languages.
OntoLex is the short name of a vocabulary for lexical resources in the web of data (OntoLex-Lemon) and the short name of the W3C community group that created it.
References
- 1 2 "LEXSITE DICTIONARY". Language Interface, Inc. Retrieved 7 February 2024.
- Elena Berg, Mark Kit.Suggested Solutions for Bilingual Internet Lexicography Problems..... Russian Journal of Lexicography, 2019, 16, pp. 92–112
- Elena Berg, Mark Kit. Reference and Educational System LexSite-LexTutor . CEUR Workshop Proceedings, Aachen, Germany, 2020. С. 1-14.
- Mark Kit, Elena Berg. Sense Ranking in Dual-Language Online Dictionaries. The 10th International Conference ICT for Language Learning. Conference Proceeding: November, 7-9. Florence, Italy: Libreria Universitaria, 2017.
- Elena Berg, Mark Kit. Cognitive Approach to The Compilation of Test Materials for The Evaluation of Translator’s Skills. Cognitive Studies / Ètudes Cognitives. – Warsaw: Institute of Slavic Studies of the Polish Academy of Sciences, 2016. – P. 100-106.
- Mark Kit, Elena Berg. Online Bilingual Dictionary as a Learning Tool: Today and Tomorrow. The 9th International Conference ICT for Language Learning. Conference Proceedings: November, 17-18. Florence, Italy: Libreria Universitaria, 2016.
- Елена Берг, Марк Кит. Формирование контрольных материалов для оценки когнитивной способности переводчика. Науковий часопис Нацiонального педагогiчного унiверситету iм.М.П. Драгоманова. – Сер.9, Вип.13. Киiв: НПУ iм. М.П. Драгоманова, 2015– С.14-21.
- Mark Kit, Elena Berg. Lexical need as a Two-way Reality Cognition Tool. Cognitive Studies / Ètudes Cognitives 14, SOW Publishing House, Warsaw 2014.
- Mark Kit, Violetta Koseska-Toszewa. Dialog Between a Lexicographer and a Translator. Cognitive Studies / Ètudes Cognitives 13, SOW Publishing House, Warsaw 2013. P.13-23.
- Kit M., Kit D. On Development of “Smart” Dictionaries. Cognitive Studies / Ètudes Cognitives 12, SOW Publishing House, Warsaw 2012.