Related Research Articles

The General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina, also known as the Dayton Agreement or the Dayton Accords, is the peace agreement reached at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base near Dayton, Ohio, United States, finalised on 21 November 1995, and formally signed in Paris, on 14 December 1995. These accords put an end to the three-and-a-half-year-long Bosnian War, which was part of the much larger Yugoslav Wars.

The Tashkent Declaration was signed between India and Pakistan on 10 January 1966 to resolve the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965. Peace was achieved on 23 September through interventions by the Soviet Union and the United States, both of which pushed the two warring countries towards a ceasefire in an attempt to avoid any escalation that could draw in other powers.
The Lomé Peace Agreement was a peace agreement signed on 7 July 1999 between the warring parties in the civil war that gripped Sierra Leone for almost a decade. President Ahmad Tejan Kabbah signed with the Revolutionary United Front (RUF) leader, Foday Sankoh and granted Sankoh a position in the transitional government as well as amnesty for him and all combatants. The accord is named for Lomé, the capital of Togo, where the negotiations took place and the agreement was signed.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1325 (S/RES/1325), on women, peace, and security, was adopted unanimously by the UN Security Council on 31 October 2000, after recalling resolutions 1261 (1999), 1265 (1999), 1296 (2000), and 1314 (2000). The resolution acknowledged the disproportionate and unique impact of armed conflict on women and girls. It calls for the adoption of a gender perspective to consider the special needs of women and girls during conflict, repatriation and resettlement, rehabilitation, reintegration, and post-conflict reconstruction.
The OSCE Minsk Group was created in 1992 by the Conference on Security and Cooperation in Europe (CSCE), now Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), to encourage a peaceful, negotiated resolution to the conflict between Azerbaijan and Armenia over Nagorno-Karabakh.

The apartheid system in South Africa was ended through a series of bilateral and multi-party negotiations between 1990 and 1993. The negotiations culminated in the passage of a new interim Constitution in 1993, a precursor to the Constitution of 1996; and in South Africa's first non-racial elections in 1994, won by the African National Congress (ANC) liberation movement.

The Centre for Humanitarian Dialogue (HD), otherwise known as the Henry Dunant Centre for Humanitarian Dialogue, works to prevent and resolve armed conflicts around the world through mediation and discreet diplomacy. A non-profit organisation based in Switzerland, HD was founded in 1999 on the principles of humanity, impartiality and independence. HD is supervised by an independent board, regularly reports to donors and undergoes financial audits every year.
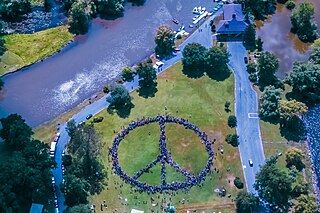
Peacebuilding is an activity that aims to resolve injustice in nonviolent ways and to transform the cultural and structural conditions that generate deadly or destructive conflict. It revolves around developing constructive personal, group, and political relationships across ethnic, religious, class, national, and racial boundaries. The process includes violence prevention; conflict management, resolution, or transformation; and post-conflict reconciliation or trauma healing before, during, and after any given case of violence.

The United Nations Peacebuilding Commission (PBC) is a United Nations intergovernmental advisory body of both the General Assembly and the Security Council that supports peace efforts in conflict affected countries. A key addition to the capacity of the international community in the broad peace agenda, it was established in 2005 with the passage of both A/RES/60/180 and S/RES/1645 Mr. Ivan Šimonović (Croatia) is the incumbent chair of PBC.

The National Forces of Liberation is a political party and former rebel group in Burundi. An ethnic Hutu group, the party was previously known as the Party for the Liberation of the Hutu People and adhered to a radical Hutu Power ideology, but since the mid- to late-2000s has moderated its stance and cooperated with the Tutsi-supported Union for National Progress party in opposition to the rule of Pierre Nkurunziza and the CNDD-FDD.

Inter-Korean summits are meetings between the leaders of North and South Korea. To date, there have been five such meetings so far, three of them being in Pyongyang, with another two in Panmunjom. The importance of these summits lies in the lack of formal communication between North and South Korea, which makes discussing political and economic issues difficult. The summits' agendas have included topics such as the ending of the 1950-53 war, the massive deployment of troops at the DMZ, the development of nuclear weapons by North Korea, and human rights issues.
The Holy See is not a member of the United Nations but was granted permanent observer state status on 6 April 1964. In that capacity, it has the right to attend all sessions of the United Nations General Assembly, the United Nations Security Council, and the United Nations Economic and Social Council to observe their work. Accordingly, the Holy See has established permanent observer missions in New York and in Geneva and has been able to influence the decisions and recommendations of the United Nations.

The Six plus Two Group on Afghanistan describes an informal coalition of the six nations bordering with Afghanistan, plus the United States and Russia, which functioned from 1997 to 2001 under the aegis of the United Nations. The coalition worked to find a peaceful solution that would have included the participation of the Afghan Northern Alliance. Later it explored the issue of a post-Taliban government for Afghanistan.
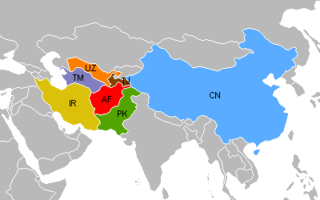
United Nations Security Council resolution 1453, adopted unanimously on 24 December 2002, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Afghanistan, the Council endorsed the "Kabul Declaration on Good-Neighbourly Relations" signed by the Afghan government and six neighbouring countries on 22 December 2002.

The Vienna peace talks for Syria, as of 14 November 2015 known as the talks of the International Syria Support Group (ISSG), were negotiations of foreign powers that began in Vienna, Austria in October 2015 at the level of foreign ministers, to resolve the conflict in Syria, after unsuccessful previous Syrian peace initiatives.
Clotilde Niragira was a Burundian politician and lawyer. She served as head of three separate ministries in Pierre Nkurunziza's government and was Secretary-General of Burundi's Truth and Reconciliation Commission.

The United Nations Observer Mission in Sierra Leone (UNOMSIL) was a United Nations peacekeeping operation in Sierra Leone from 1998 to 1999 that was established with the passage of United Nations Security Council Resolution 1181. Its mission was to monitor the military and security situation in Sierra Leone. The mission was terminated in October 1999, when the Security Council authorized deployment of a new, and significantly larger peacekeeping operation, the United Nations Mission in Sierra Leone (UNAMSIL).

Joseph Biroli-Baranyanka or Joseph Biroli was a Burundian politician and was the first Burundian to receive a university education. Born in 1929 to a prominent chief, he was a Ganwa of the Batare clan. He performed well as a student and earned a diploma from the Institut universitaire des Territoires d'Outre-Mer in 1953. After continuing his education at several other universities he took up work for the European Economic Community. In 1960 his brother Jean-Baptiste Ntidendereza co-founded the Christian Democratic Party, and Biroli became the party's president. His main political rival was Prince Louis Rwagasore, a Ganwa of the Bezi clan who led the Union for National Progress. Biroli was friendly to the Belgian colonial administration in Ruanda-Urundi, while UPRONA demanded immediate independence.

The Burundian Basketball Championship, for sponsorship reason the Viva Basketball League, is a semi-professional basketball league that is the highest level of the sport in Burundi. The league is organised by the Fédération de Basketball du Burundi (FEBABU).
Anastase Manirambona is a Burundian retired colonel and politician currently serving as an elected member of the East African Legislative Assembly (EALA) since 2022. A member of the Eagle party - National Council for the Defense of Democracy – Forces for the Defense of Democracy (CNDD-FDD), he is a national secretary in charge of ideology, mobilization and diaspora. He was elected to the 5th session of East African Legislative Assembly running from 2022 to 2027.
References
- ↑ "Burundi: List of groups involved in the conflict and peace process - Burundi | ReliefWeb". reliefweb.int. Retrieved 2022-10-03.
- 1 2 "Le fondateur du parti libéral (PL) n'est plus – IWACU". www.iwacu-burundi.org. Retrieved 2022-10-03.
- ↑ "Declaration by the Participants to the Peace Negotiations on Burundi | UN Peacemaker". peacemaker.un.org. Retrieved 2022-10-03.