
Otorhinolaryngology is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face, scalp, and neck.

Plastic surgery is a surgical specialty involving the restoration, reconstruction, or alteration of the human body. It can be divided into two main categories: reconstructive surgery and cosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery includes craniofacial surgery, hand surgery, microsurgery, and the treatment of burns. While reconstructive surgery aims to reconstruct a part of the body or improve its functioning, cosmetic surgery aims to improve the appearance of it. A comprehensive definition of plastic surgery has never been established, because it has no distinct anatomical object and thus overlaps with practically all other surgical specialties. An essential feature of plastic surgery is that it involves the treatment of conditions that require or may require tissue relocation skills.
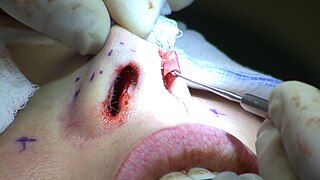
Rhinoplasty, commonly called nose job, medically called nasal reconstruction is a plastic surgery procedure for altering and reconstructing the nose. There are two types of plastic surgery used – reconstructive surgery that restores the form and functions of the nose and cosmetic surgery that changes the appearance of the nose. Reconstructive surgery seeks to resolve nasal injuries caused by various traumas including blunt, and penetrating trauma and trauma caused by blast injury. Reconstructive surgery can also treat birth defects, breathing problems, and failed primary rhinoplasties. Rhinoplasty may remove a bump, narrow nostril width, change the angle between the nose and the mouth, or address injuries, birth defects, or other problems that affect breathing, such as a deviated nasal septum or a sinus condition. Surgery only on the septum is called a septoplasty.
Facial feminization surgery (FFS) is a set of reconstructive surgical procedures that alter typically male facial features to bring them closer in shape and size to typical female facial features. FFS can include various bony and soft tissue procedures such as brow lift, rhinoplasty, cheek implantation, and lip augmentation.
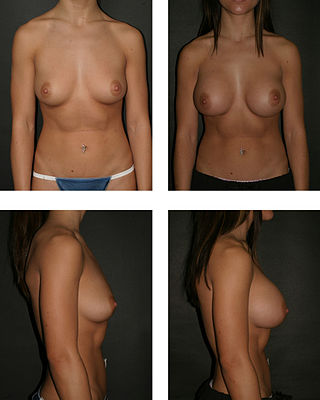
Breast augmentation and augmentation mammoplasty is a cosmetic surgery technique using breast-implants and fat-graft mammoplasty techniques to increase the size, change the shape, and alter the texture of the breasts. Augmentation mammoplasty is applied to correct congenital defects of the breasts and the chest wall. As an elective cosmetic surgery, primary augmentation changes the aesthetics – of size, shape, and texture – of healthy breasts.
Oral and maxillofacial surgery is a surgical specialty focusing on reconstructive surgery of the face, facial trauma surgery, the oral cavity, head and neck, mouth, and jaws, as well as facial cosmetic surgery/facial plastic surgery including cleft lip and cleft palate surgery.

A facelift, technically known as a rhytidectomy, is a type of cosmetic surgery procedure used to give a more youthful facial appearance. There are multiple surgical techniques and exercise routines. Surgery usually involves the removal of excess facial skin, with or without the tightening of underlying tissues, and the redraping of the skin on the patient's face and neck. Exercise routines tone underlying facial muscles without surgery. Surgical facelifts are effectively combined with eyelid surgery (blepharoplasty) and other facial procedures and are typically performed under general anesthesia or deep twilight sleep.
Chin augmentation using surgical implants alter the underlying structure of the face, intended to balance the facial features. The specific medical terms mentoplasty and genioplasty are used to refer to the reduction and addition of material to a patient's chin. This can take the form of chin height reduction or chin rounding by osteotomy, or chin augmentation using implants. Altering the facial balance is commonly performed by modifying the chin using an implant inserted through the mouth. The intent is to provide a suitable projection of the chin as well as the correct height of the chin which is in balance with the other facial features.

Reconstructive surgery is surgery performed to restore normal appearance and function to body parts malformed by a disease or medical condition.
Chondrolaryngoplasty is a surgical procedure in which the thyroid cartilage is reduced in size by shaving down the cartilage through an incision in the throat, generally to aid those who are uncomfortable with the girth of their Adam's apple.

Blepharoplasty is the plastic surgery operation for correcting defects, deformities, and disfigurations of the eyelids; and for aesthetically modifying the eye region of the face. With the excision and the removal, or the repositioning of excess tissues, such as skin and adipocyte fat, and the reinforcement of the corresponding muscle and tendon tissues, the blepharoplasty procedure resolves functional and cosmetic problems of the periorbita, which is the area from the eyebrow to the upper portion of the cheek. The procedure is more common among women, who accounted for approximately 85% of blepharoplasty procedures in 2014 in the US and 88% of such procedures in the UK.
Robert Kotler, M.D. FACS, born in 1942, is an American ear, nose, and throat surgeon. He has performed more than 10,000 major cosmetic procedures, with over 40 years in private practice, and was a featured surgeon in the first season of the E! cosmetic surgery series Dr. 90210.

Buccal fat pad extraction or buccal fat removal is a plastic surgery procedure that removes a piece of buccal fat-pad tissue from each side of the face. This reduces the appearance of cheek puffiness, creating a sharper jawline. The amount of fat removed varies based on the desired facial shape. It is a strictly cosmetic surgery.
Aesthetic medicine is a branch of modern medicine that focuses on altering cosmetic appearance through the treatment of conditions including scars, skin laxity, wrinkles, moles, liver spots, excess fat, cellulite, unwanted hair, skin discoloration, and spider veins. Traditionally, it includes dermatology, oral and maxillofacial surgery, reconstructive surgery and plastic surgery, surgical procedures, non-surgical procedures, and a combination of both. Aesthetic medicine procedures are usually elective. There is a long history of aesthetic medicine procedures, dating back to many notable cases in the 19th century, though techniques have developed much since then.

A lip lift is a plastic surgery procedure that modifies the cosmetic appearance of the lips by reshaping them to increase the prominence of the vermilion border; and to enhance the facial area above the lips into a more aesthetically pleasing shape. In corrective praxis, a lip lift procedure is distinguished from lip enhancement, the augmentation of the lips, which can be effected with a non-surgical procedure.
Andrew A. Jacono, M.D., FACS is an American facial surgeon and creator of the minimal access deep-plane extended facelift, a minimally invasive hybrid facelift. Jacono starred in the Discovery Fit & Health television program Facing Trauma as the volunteer surgeon who reconstructed faces disfigured in abusive relationships and other violent circumstances.

Babak Azizzadeh, MD, FACS is an American facial plastic and reconstructive surgeon. He is the founder and president of the FPBPF, a non-profit organization committed to the treatment of individuals with facial nerve paralysis and Bell's palsy.
Facial Autologous Muscular Injection is also known as Fat Autograft Muscular Injection, as Autologous Fat Injection, as Micro-lipoinjection, as Fat Transfer and as Facial Autologous Mesenchymal Integration, abbreviated as FAMI. The technique is a non-incisional pan-facial rejuvenation procedure using the patient'own stem cells from fat deposits. FAMI is an Adult stem cell procedure used to address the loss of volume in the face due to aging or surgery repair in restoring facial muscles, bone surfaces and very deep fat pads. The procedure involves removing adult stem cells of fatty tissue from lower body, and refining it to be able to re-inject living adipose stem cells into specific areas of the face without incision. FAMI is an outpatient procedure and an alternative to artificial fillers, blepharoplasty or various face lifts. The procedure does not require general anesthesia and risks of an allergic reaction are minimal due to the use of the patient's own tissue used as the facial injection.
Monica Tadros, MD, FACS,(born 1974) is an American plastic and reconstructive surgeon at the Center for Sinus Sleep & Facial Plastic Surgery in Manhattan and in Bergen County, New Jersey. She specializes in rhinoplasty, sinus surgery, plastic surgery and holds a dual board certification in Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery and Facial plastic & Reconstructive surgery. Since 2006, she has been appointed director of facial plastic & reconstructive surgery and assistant professor of otolaryngology-head & neck surgery at Columbia University.
Nasal surgery is a medical procedure designed to treat various conditions that cause nasal blockages in the upper respiratory tract, for example nasal polyps, inferior turbinate hypertrophy, and chronic rhinosinusitis. It encompasses several types of techniques, including rhinoplasty, septoplasty, sinus surgery, and turbinoplasty, each with its respective postoperative treatments. Furthermore, nasal surgery is also conducted for cosmetic purposes. While there are potential risks and complications associated, the advancement of medical instruments and enhanced surgical skills have helped mitigate them.










