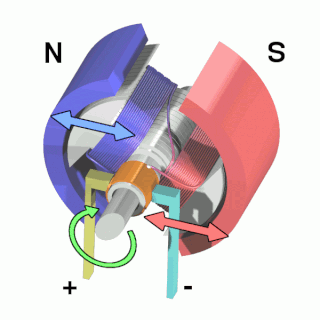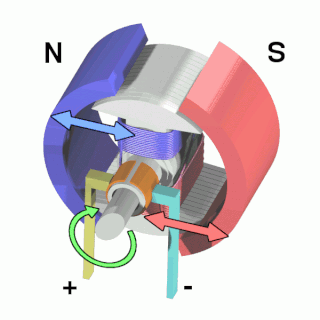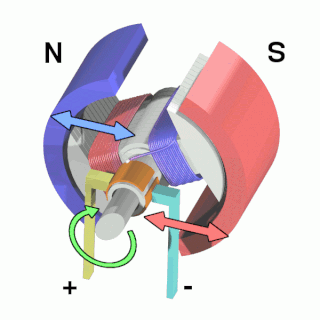
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates with a reversed flow of power, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
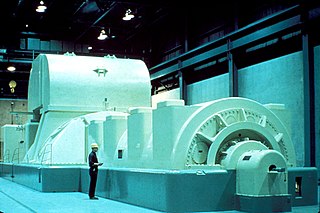
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. Generators provide nearly all of the power for electric power grids.

An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature. Occasionally, a linear alternator or a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field is used. In principle, any AC electrical generator can be called an alternator, but usually the term refers to small rotating machines driven by automotive and other internal combustion engines.

An induction motor or asynchronous motor is an AC electric motor in which the electric current in the rotor needed to produce torque is obtained by electromagnetic induction from the magnetic field of the stator winding. An induction motor can therefore be made without electrical connections to the rotor. An induction motor's rotor can be either wound type or squirrel-cage type.

A polyphase system is a means of distributing alternating-current (AC) electrical power where the power transfer is constant during each electrical cycle. AC phase refers to the phase offset value between AC in multiple conducting wires; phases may also refer to the corresponding terminals and conductors, as in color codes. Polyphase systems have three or more energized electrical conductors carrying alternating currents with a defined phase between the voltage waves in each conductor; for three-phase voltage, the phase angle is 120° or 2π/3 radians. Polyphase systems are particularly useful for transmitting power to electric motors which rely on alternating current to rotate. The most common example is the three-phase power system used for industrial applications and for power transmission. Compared to a single-phase, two-wire system, a three-phase three-wire system transmits three times as much power for the same conductor size and voltage.

A synchronous electric motor is an AC electric motor in which, at steady state, the rotation of the shaft is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current; the rotation period is exactly equal to an integral number of AC cycles. Synchronous motors contain multiphase AC electromagnets on the stator of the motor that create a magnetic field which rotates in time with the oscillations of the line current. The rotor with permanent magnets or electromagnets turns in step with the stator field at the same rate and as a result, provides the second synchronized rotating magnet field of any AC motor. A synchronous motor is termed doubly fed if it is supplied with independently excited multiphase AC electromagnets on both the rotor and stator.

A brushless DC electric motor, also known as an electronically commutated motor or synchronous DC motor, is a synchronous motor using a direct current (DC) electric power supply. It uses an electronic controller to switch DC currents to the motor windings producing magnetic fields which effectively rotate in space and which the permanent magnet rotor follows. The controller adjusts the phase and amplitude of the DC current pulses to control the speed and torque of the motor. This control system is an alternative to the mechanical commutator (brushes) used in many conventional electric motors.

A squirrel-cage rotor is the rotating part of the common squirrel-cage induction motor. It consists of a cylinder of steel laminations, with aluminum or copper conductors embedded in its surface. In operation, the non-rotating stator winding is connected to an alternating current power source; the alternating current in the stator produces a rotating magnetic field. The rotor winding has current induced in it by the stator field, like a transformer except that the current in the rotor is varying at the stator field rotation rate minus the physical rotation rate. The interaction of the magnetic fields of currents in the stator and rotor produce a torque on the rotor.

The shaded-pole motor is the original type of AC single-phase induction motor, dating back to at least as early as 1890. A shaded-pole motor is a small squirrel-cage motor in which the auxiliary winding is composed of a copper ring or bar surrounding a portion of each pole. When single phase AC supply is applied to the stator winding, due to shading provided to the poles, a rotating magnetic field is generated. This auxiliary single-turn winding is called a shading coil. Currents induced in this coil by the magnetic field create a second electrical phase by delaying the phase of magnetic flux change for that pole enough to provide a 2-phase rotating magnetic field. The direction of rotation is from the unshaded side to the shaded (ring) side of the pole. Since the phase angle between the shaded and unshaded sections is small, shaded-pole motors produce only a small starting torque relative to torque at full speed. Shaded-pole motors of the asymmetrical type shown are only reversible by disassembly and flipping over the stator, though some similar looking motors have small, switch-shortable auxiliary windings of thin wire instead of thick copper bars and can reverse electrically. Another method of electrical reversing involves four coils.

A reluctance motor is a type of electric motor that induces non-permanent magnetic poles on the ferromagnetic rotor. The rotor does not have any windings. It generates torque through magnetic reluctance.

An AC motor is an electric motor driven by an alternating current (AC). The AC motor commonly consists of two basic parts, an outside stator having coils supplied with alternating current to produce a rotating magnetic field, and an inside rotor attached to the output shaft producing a second rotating magnetic field. The rotor magnetic field may be produced by permanent magnets, reluctance saliency, or DC or AC electrical windings.
Doubly-fed electric machines also slip-ring generators are electric motors or electric generators, where both the field magnet windings and armature windings are separately connected to equipment outside the machine.
An induction generator or asynchronous generator is a type of alternating current (AC) electrical generator that uses the principles of induction motors to produce electric power. Induction generators operate by mechanically turning their rotors faster than synchronous speed. A regular AC induction motor usually can be used as a generator, without any internal modifications. Because they can recover energy with relatively simple controls, induction generators are useful in applications such as mini hydro power plants, wind turbines, or in reducing high-pressure gas streams to lower pressure.

The rotor is a moving component of an electromagnetic system in the electric motor, electric generator, or alternator. Its rotation is due to the interaction between the windings and magnetic fields which produces a torque around the rotor's axis.
In electrical engineering, electric machine is a general term for machines using electromagnetic forces, such as electric motors, electric generators, and others. They are electromechanical energy converters: an electric motor converts electricity to mechanical power while an electric generator converts mechanical power to electricity. The moving parts in a machine can be rotating or linear. Besides motors and generators, a third category often included is transformers, which although they do not have any moving parts are also energy converters, changing the voltage level of an alternating current.
Vector control, also called field-oriented control (FOC), is a variable-frequency drive (VFD) control method in which the stator currents of a three-phase AC or brushless DC electric motor are identified as two orthogonal components that can be visualized with a vector. One component defines the magnetic flux of the motor, the other the torque. The control system of the drive calculates the corresponding current component references from the flux and torque references given by the drive's speed control. Typically proportional-integral (PI) controllers are used to keep the measured current components at their reference values. The pulse-width modulation of the variable-frequency drive defines the transistor switching according to the stator voltage references that are the output of the PI current controllers.
The direct-quadrature-zerotransformation or zero-direct-quadraturetransformation is a tensor that rotates the reference frame of a three-element vector or a three-by-three element matrix in an effort to simplify analysis. The DQZ transform is the product of the Clarke transform and the Park transform, first proposed in 1929 by Robert H. Park.

An induction regulator is an alternating current electrical machine, somewhat similar to an induction motor, which can provide a continuously variable output voltage. The induction regulator was an early device used to control the voltage of electric networks. Since the 1930s it has been replaced in distribution network applications by the tap transformer. Its usage is now mostly confined to electrical laboratories, electrochemical processes and arc welding. With minor variations, its setup can be used as a phase-shifting power transformer.
A power system consists of a number of synchronous machines operating synchronously under all operating conditions. Under normal operating conditions, the relative position of the rotor axis and the resultant magnetic field axis is fixed. The angle between the two is known as the power angle or torque angle. During any disturbance, the rotor decelerates or accelerates with respect to the synchronously rotating air gap magnetomotive force, creating relative motion. The equation describing the relative motion is known as the swing equation, which is a non-linear second order differential equation that describes the swing of the rotor of synchronous machine. The power exchange between the mechanical rotor and the electrical grid due to the rotor swing is called Inertial response.
Electromagnetically induced acoustic noise , electromagnetically excited acoustic noise, or more commonly known as coil whine, is audible sound directly produced by materials vibrating under the excitation of electromagnetic forces. Some examples of this noise include the mains hum, hum of transformers, the whine of some rotating electric machines, or the buzz of fluorescent lamps. The hissing of high voltage transmission lines is due to corona discharge, not magnetism.












