
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the 14th-largest country by area, at 1,904,569 square kilometres. With over 279 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most-populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population.

Papua is a province of Indonesia, comprising the northern coast of Western New Guinea together with island groups in Cenderawasih Bay to the west. It roughly follows the borders of Papuan customary region of Tabi Saireri. It is bordered by the sovereign state of Papua New Guinea to the east, the Pacific Ocean to the north, Cenderawasih Bay to the west, and the provinces of Central Papua and Highland Papua to the south. The province also shares maritime boundaries with Palau in the Pacific. Following the splitting off of twenty regencies to create the three new provinces of Central Papua, Highland Papua, and South Papua on 30 June 2022, the residual province is divided into eight regencies and one city (kota), the latter being the provincial capital of Jayapura. The province has a large potential in natural resources, such as gold, nickel, petroleum, etc. Papua, along with five other Papuan provinces, has a higher degree of autonomy level compared to other Indonesian provinces.
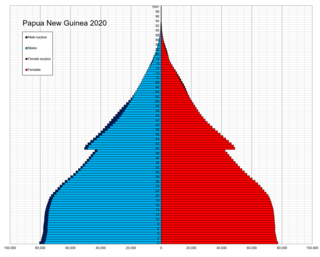
The indigenous population of Papua New Guinea is one of the most heterogeneous in the world. Papua New Guinea has several thousand separate communities, most with only a few hundred people. Divided by language, customs, and tradition, some of these communities have engaged in endemic warfare with their neighbors for centuries. It is the second most populous nation in Oceania, with a total population estimated variously as being between 9.5 and 10.1 million inhabitants.

The economy of Papua New Guinea (PNG) is largely underdeveloped with the vast majority of the population living below the poverty line. However, according to the Asian Development Bank its GDP is expected to grow 3.4% in 2022 and 4.6% in 2023. It is dominated by the agricultural, forestry, and fishing sector and the minerals and energy extraction sector. The agricultural, forestry, and fishing sector accounts for most of the labour force of PNG while the minerals and energy extraction sector, including gold, copper, oil and natural gas is responsible for most of the export earnings.

Jayapura is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of Papua. It is situated on the northern coast of New Guinea island and covers an area of 940.0 km2 (362.9 sq mi). The city borders the Pacific Ocean and Yos Sudarso Bay to the north, the country of Papua New Guinea to the east, Keerom Regency to the south, and Jayapura Regency to the west.

East Nusa Tenggara is the southernmost province of Indonesia. It comprises the eastern portion of the Lesser Sunda Islands, facing the Indian Ocean in the south and the Flores Sea in the north. It consists of more than 500 islands, with the largest ones being Sumba, Flores, and the western part of Timor; the latter shares a land border with the separate nation of East Timor. The province is subdivided into twenty-one regencies and the regency-level city of Kupang, which is the capital and largest city.

The transmigration program was an initiative of the Dutch colonial government and later continued by the Indonesian government to move landless people from densely populated areas of Indonesia to less populous areas of the country. This involved moving people permanently from the island of Java, but also to a lesser extent from Bali and Madura to less densely populated areas including Kalimantan, Sumatra, Sulawesi, Maluku and Papua. The program is currently coordinated by Ministry of Villages, Development of Disadvantaged Regions, and Transmigration.

West Papua, formerly Irian Jaya Barat, is a province of Indonesia located in the land of Papua. It covers most of the two western peninsulas of the island of New Guinea, the eastern half of the Bird's Head Peninsula and the whole of the Bomberai Peninsula, along with nearby smaller islands. The province is bordered to the north by the Pacific Ocean, to the west by Southwest Papua Province, the Halmahera Sea and the Ceram Sea, to the south by the Banda Sea, and to the east by the province of Central Papua and the Cenderawasih Bay. Manokwari is the province's capital and largest city. With an estimated population of 561,403 in mid-2022, West Papua is the least populous province in Indonesia after Southwest Papua, which was a part of West Papua until separated off in 2022.

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, and Indonesian Papua, is the western half of the island of New Guinea occupied since 1962 by Indonesia. Given the island is alternatively named Papua, the region is also called West Papua.
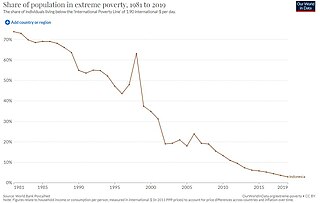
Poverty in Indonesia is a widespread issue though in recent years the official numbers show a declining trend. Due to the dense rural nature of parts of the Java, Bali, Lombok, and parts of Sumatra, poverty can be classified into rural and urban poverty. Urban poverty is prevalent in not only in Jabodetabek, but also in Medan and Surabaya.

Boven Digoel Regency is an inland regency (kabupaten) in the northeastern part of the Indonesian province of South Papua. It was split off from Merauke Regency on 12 November 2002. It is bordered to the south by the residual Merauke Regency, to the west by Mappi Regency, and to the north by the province of Highland Papua. At the same time, to the east lies the international border with Papua New Guinea.
Turkey made steady progress in reducing poverty from the early 2000s to the mid-2010s.

Highland Papua is a province of Indonesia, which roughly follows the borders of Papuan customary region of Lano-Pago, shortened to La Pago. It covers an area of 51,213.34 km2 (19,773.58 sq mi) and had a population of 1,430,459 according to the official estimates as at mid 2022.











