Related Research Articles

After independence in 1964, Malta followed a policy of close co-operation with NATO countries. Since 1971, the country sought relations with the rest of the world, including communist countries in Eastern Europe and the non-aligned countries.

China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), has full diplomatic relations with 178 out of the other 193 United Nations member states, Cook Islands, Niue and the State of Palestine. China has had the second most diplomatic missions of any state.

Saint Lucia maintains friendly relations with the major powers active in the Caribbean, including the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, and France. Saint Lucia has no extant international disputes, aside from tension resulting from the island's status as a transit point for South American drugs destined for the United States and Europe.

Saint Vincent and the Grenadines maintains close ties to the US, Canada, and the United Kingdom, and cooperates with regional political and economic organizations such as the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS) and CARICOM. St. Vincent and the Grenadines is a member of the United Nations, the Commonwealth of Nations, the Organization of American States, and the Association of Caribbean States (ACS). Saint Vincent is also the smallest nation ever to be on the United Nations Security Council.
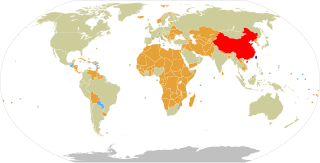
The Republic of China (ROC), commonly known as Taiwan, has full diplomatic relations with 13 of the 193 United Nations member states and with the Holy See. In addition to these relations, the ROC also maintains unofficial relations with 59 UN member states, one self-declared state (Somaliland), three territories, and the European Union via its representative offices and consulates under the One China principle. Taiwan has the 31st largest diplomatic network in the world with 110 offices.

George William Odlum was a Saint Lucian left-wing politician who served as Deputy Prime Minister and Foreign Minister. Born in Castries, Odlum studied at Bristol University and Oxford University in the United Kingdom before returning to Saint Lucia as Permanent Secretary to the Ministry of Trade. After working for the Commonwealth Secretariat and the West Indies Associated States, he formed the Saint Lucia Forum, a left-wing pressure group. This group merged with the Saint Lucia Labour Party in time for the 1974 elections; although the Party did not win, the progress they made allowed them to take power in 1979, with Odlum as Deputy Prime Minister.

Since its founding in 1949, the People's Republic of China (PRC) has had a diplomatic tug-of-war with its rival in Taiwan, the Republic of China (ROC). Throughout the Cold War, both governments claimed to be the sole legitimate government of all China and allowed countries to recognize either one or the other. Until the 1970s, most Western countries in the Western Bloc recognized the ROC while the Eastern Bloc and Third World countries generally recognized the PRC. This gradually shifted and today only 13 UN member states recognize the ROC while the PRC is recognized by the United Nations, 179 UN member states and the State of Palestine as well as Cook Islands and Niue. Both the ROC and the PRC maintain the requirement of recognizing its view of the One China policy to establish or maintain diplomatic relations.

Oceania is, to the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China, a stage for continuous diplomatic competition. The PRC dictates that no state can have diplomatic relations with both the PRC and the ROC. As of 2019, ten states in Oceania have diplomatic relations with the PRC, and four have diplomatic relations with the ROC. These numbers fluctuate as Pacific Island nations re-evaluate their foreign policies, and occasionally shift diplomatic recognition between Beijing and Taipei. The issue of which "Chinese" government to recognize has become a central theme in the elections of numerous Pacific Island nations, and has led to several votes of no-confidence.

Bilateral relations between the United States and Cambodia, while strained throughout the Cold War, have strengthened considerably in modern times. The U.S. supports efforts in Cambodia to combat terrorism, build democratic institutions, promote human rights, foster economic development, eliminate corruption, achieve the fullest possible accounting for Americans missing from the Indochina Wars-era, and to bring to justice those most responsible for serious violations of international humanitarian law committed under the Khmer Rouge regime.

China-Niuean relations are relations between China and Niue.
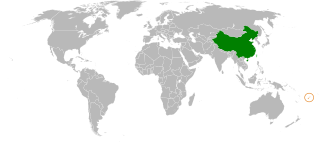
The Republic of the Fiji Islands was the first Pacific Island country to establish diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China, in 1975. China established an embassy in Fiji in 1976, and Fiji opened its embassy in China in 2001.

The Republic of Kiribati and the People's Republic of China (PRC) established diplomatic relations on June 25, 1980, and resumed on September 27, 2019. Between 2003 and 2019, The government of Kiribati recognized the Republic of China, and, in accordance with the "One China" policy, the People's Republic of China did not have diplomatic relations to the country.
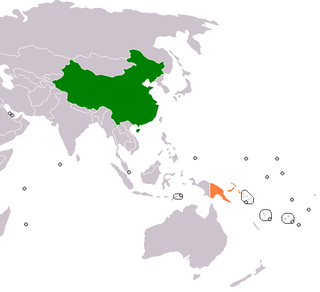
The Independent State of Papua New Guinea and China (PRC) established official diplomatic relations in 1976, soon after Papua New Guinea became independent. The two countries currently maintain diplomatic, economic and, to a lesser degree, military relations. Relations are cordial; China is a significant provider of both investments and development aid to Papua New Guinea.
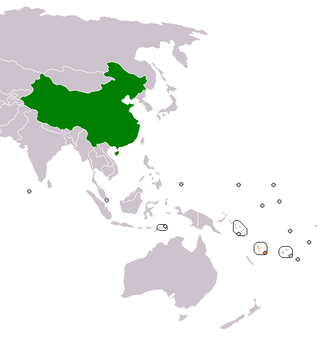
The Republic of Vanuatu and the People's Republic of China (PRC) established official diplomatic relations on March 26, 1982. China established an embassy in Vanuatu in 1989, while Vanuatu established an honorary consulate in China in 1999; it officially became an embassy in 2005. The current Ambassador of China in Vanuatu is Liu Quan. The current Ambassador of Vanuatu in China is former Minister of Finance Willie Jimmy.

Relations between Barbados and China began on 4 September 1967 with Barbados recognizing the People's Republic of China from 30 May 1977, just over one decade after the eastern Caribbean island nation's independence from the United Kingdom.

Diplomatic relations between the People's Republic of China and Grenada were established on 1 October 1985. Prime Minister Herbert Blaize established diplomatic relations with the Republic of China in 1989, prompting Beijing to sever diplomatic ties to Grenada. This position was later reversed under Prime Minister Keith Mitchell.

Robert Kennedy Lewis is a St Lucian politician affiliated with the Saint Lucia Labour Party. He was elected to the House of Assembly of Saint Lucia following the election of 11 December 2006 as the member of parliament for Castries South. Previous to his election Lewis was supervisor and examiner of National Examinations in Mathematics from 1992 to 2006. In January 2005 he received a Phd in mathematics from the University of Otago.

São Tomé and Príncipe–Taiwan relations are relations between São Tomé and Príncipe and the Republic of China (ROC). Official bilateral relations began in 1997 and ended in 2016.
References
- ↑ Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the People's Republic of China , Chinese Ambassadors to St. Lucia, , 驻圣卢西亚历任大使,
- ↑ "ADDRESS TO THE NATION BY PRIME MINISTER THE HON. KENNY D. ANTHONY ON THE ESTABLISHMENT OF DIPLOMATIC RELATIONS WITH THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA". Government of Saint Lucia. 29 August 1997. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "China suspends ties with St Lucia". Al Jazeera. 6 May 2007. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "China irate over Saint Lucia-Taiwan ties". United Press International. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "Saint Lucia set to rejoin ROC allies". Taiwan Today. 1 May 2007. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ Gu Pine
- ↑ Gu Huaming