Related Research Articles

A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body whose orbit around the Sun can bring it near the Earth. By convention, a small natural Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical units (AU). If a NEO's orbit crosses the Earth's orbit, and the object is larger than 140 meters (460 ft) across, it is considered a potentially hazardous object (PHO). Most known PHOs and NEOs are asteroids, but about 0.35% are comets.
The Torino scale is a method for categorizing the impact hazard associated with near-Earth objects (NEOs) such as asteroids and comets. It is intended as a communication tool for astronomers and the public to assess the seriousness of collision predictions, by combining probability statistics and known kinetic damage potentials into a single threat value. The Palermo Technical Impact Hazard Scale is a similar, but more complex scale.

(29075) 1950 DA is a risk-listed asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 1.1 kilometers in diameter. It once had the highest known probability of impacting Earth. In 2002, it had the highest Palermo rating with a value of 0.17 for a possible collision in 2880. Since that time, the estimated risk has been updated several times. In December 2015, the odds of an Earth impact were revised to 1 in 8,300 (0.012%) with a Palermo rating of −1.42. As of 2022, It is listed on the Sentry Risk Table with the second highest cumulative Palermo rating of −2.05. 1950 DA is not assigned a Torino scale rating, because the 2880 date is over 100 years in the future.
99942 Apophis (provisional designation 2004 MN4) is a near-Earth asteroid and a potentially hazardous object with a diameter of 370 metres (1,210 feet) that caused a brief period of concern in December 2004 when initial observations indicated a probability up to 2.7% that it would hit Earth on April 13, 2029. Additional observations provided improved predictions that eliminated the possibility of an impact on Earth in 2029. Until 2006, a small possibility nevertheless remained that, during its 2029 close encounter with Earth, Apophis would pass through a gravitational keyhole of no more than about 800 kilometres (500 mi) in diameter, which would have set up a future impact exactly seven years later on April 13, 2036. This possibility kept it at Level 1 on the Torino impact hazard scale until August 2006, when the probability that Apophis would pass through the keyhole was determined to be very small and Apophis's rating on the Torino scale was lowered to zero. By 2008, the keyhole had been determined to be less than 1 km wide. During the short time when it had been of greatest concern, Apophis set the record for highest rating ever on the Torino scale, reaching level 4 on December 27, 2004.

(308635) 2005 YU55, provisionally named 2005 YU55, is a potentially hazardous asteroid 360±40 meters in diameter, as measured after its Earth flyby. Previously it was estimated to be 310 meters or about 400 m (1,300 feet) in diameter. It was discovered on 28 December 2005 by Robert S. McMillan at Steward Observatory, Kitt Peak. On 8 November 2011 it passed 0.85 lunar distances (324,900 kilometers; 201,900 miles) from Earth.
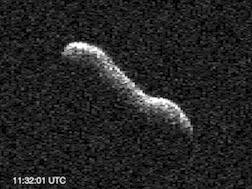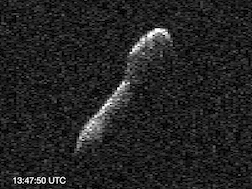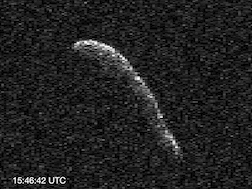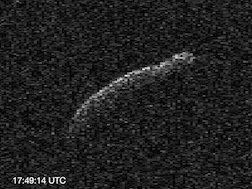
(367789) 2011 AG5, provisional designation 2011 AG5, is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. It has a diameter of about 140 meters (460 ft). It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 21 December 2012 and as such it now has a rating of 0 on the Torino Scale. It was recovered in December 2022 extending the observation arc from 4.8 years to 14 years. As of 2023, the distance between the orbits of Earth and 2011 AG5 is 0.0004 AU (60,000 km; 0.16 LD)
(456938) 2007 YV56, provisional designation 2007 YV56, is a sub-kilometer asteroid on an eccentric orbit, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 190–360 meters (620–1,200 ft) in diameter. It was discovered on 31 December 2007, by astronomers of the Catalina Sky Survey conducted at the Catalina Station in Arizona, United States.
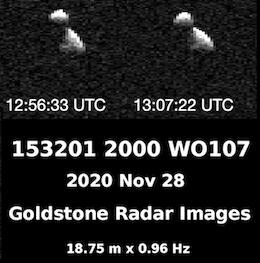
(153201) 2000 WO107 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Aten group with a very well determined orbit. It was discovered on 29 November 2000, by astronomers of the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR) at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States. It is a contact binary.

(163899) 2003 SD220 is a sub-kilometer asteroid and tumbling slow rotator, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Aten group, which orbit the Sun between Venus and Earth. Its orbital period of 0.75 years means that it orbits the Sun about 4 times for every 3 of the Earth. It was discovered on 29 September 2003, by astronomers of the Lowell Observatory Near-Earth-Object Search at Anderson Mesa Station near Flagstaff, Arizona.
(85713) 1998 SS49 (provisional designation 1998 SS49) is an asteroid on an eccentric orbit, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 3 kilometers (1.9 miles) in diameter. The asteroid was discovered on 29 September 1998, by astronomers of the LINEAR program at Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States. It is one of the largest potentially hazardous asteroids and has a notably low Earth-MOID of less than the distance to the Moon.

(52768) 1998 OR2 (provisional designation 1998 OR2) is an asteroid on an eccentric orbit, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Amor group, with a diameter of 2 kilometers (1.2 mi). It was discovered on 24 July 1998, by astronomers of the Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking (NEAT) program at the Haleakala Observatory, Hawaii. It is one of the brightest and therefore largest potentially hazardous asteroids known to exist. With an observation arc of 35 years, the asteroid has a well-determined orbit, and its trajectory is well known through the year 2197. The asteroid's orbit is only potentially hazardous on a time scale of thousands of years.

2018 CN2 is a very small asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 5 to 16 meters in diameter. It was first observed by astronomers of the Mount Lemmon Survey at Mount Lemmon Observatory, Arizona, on 8 February 2018, one day prior its close encounter with Earth at 0.18 lunar distances.

2018 CY2 is an asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Apollo group, with an estimated diameter of 59–190 metres (190–620 ft). It was first observed on 9 February 2018, by astronomers of the Catalina Sky Survey at Mount Lemmon Observatory, Arizona, during its close approach to Earth.

(164121) 2003 YT1, provisional designation 2003 YT1, is a bright asteroid and synchronous binary system on a highly eccentric orbit, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 2 kilometers (1.2 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 18 December 2003, by astronomers with the Catalina Sky Survey at the Catalina Station near Tucson, Arizona, in the United States. The V-type asteroid has a short rotation period of 2.3 hours. Its 210-meter sized minor-planet moon was discovered at Arecibo Observatory in May 2004.

2020 LD is an Apollo near-Earth asteroid roughly 140 meters in diameter. It was discovered on 7 June 2020 when the asteroid was about 0.03 AU from Earth and had a solar elongation of 154 degrees. The glare of the Sun had masked the approach of the asteroid since November 2019. The asteroid passed closest approach to Earth on 5 June 2020 at a distance of 0.002 AU. The close approach distance is now known with an accuracy of roughly ± 1000 km. This is the largest asteroid to pass closer than the Moon this year and possibly the largest since (308635) 2005 YU55 in November 2011. The asteroid makes close approaches to Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. It will be brighter than apparent magnitude 24 until 18 July 2020.

(231937) 2001 FO32 is a near-Earth asteroid classified as a potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. With an estimated diameter around 550 m (1,800 ft), it was discovered by the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at Socorro, New Mexico on 23 March 2001. The asteroid safely passed by Earth on 21 March 2021 16:03 UTC from a closest approach distance of 0.0135 AU (2.02 million km; 1.25 million mi), or 5.25 lunar distances (LD). During the day before closest approach, 2001 FO32 reached a peak apparent magnitude of 11.7 and was visible to ground-based observers with telescope apertures of at least 20 cm (8 in). It is the largest and one of the fastest asteroids to approach Earth within 10 LD (3.8 million km; 2.4 million mi) in 2021.

(620094) 2016 AJ193 (provisional designation 2016 AJ193; also known as 2010 KV134) is a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 1.4 kilometres (0.87 mi) in diameter. It was discovered on 17 May 2010 by the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) satellite, but was lost until it was reobserved on 16 January 2016. With an observation arc over 11 years, 2016 AJ193 has a well-determined orbit and trajectory through the year 2086. The asteroid's orbit is only potentially hazardous on a time scale of thousands of years.
References
- ↑ "Next Five Asteroid Approaches". Asteroid Watch Dashboard. NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved January 23, 2024.
- ↑ Johnson, Arianna (February 2, 2024). "'Potentially Hazardous' Asteroid Passes Earth Today: How To See It". Forbes.
- ↑ "2011MD close approaches". Newton - NEODyS. European Space Agency . Retrieved 2023-11-08.
