
The Tigray, officially the Tigray National Regional State, is the northernmost regional state in Ethiopia. The Tigrai Region is the homeland of the Tigrayan (Tegaru), Irob people and Kunama people. Its capital and largest city is Mekelle. Tigray is the fifth-largest by area, the fourth-most populous, and the fifth-most densely populated of the 11 regional states.

Shewa, formerly romanized as Shua, Shoa, Showa, Shuwa, is a historical region of Ethiopia which was formerly an autonomous kingdom within the Ethiopian Empire. The modern Ethiopian capital Addis Ababa is located at its center.

Gondar, also spelled Gonder, is a city and woreda in Ethiopia. Located in the North Gondar Zone of the Amhara Region, Gondar is north of Lake Tana on the Lesser Angereb River and southwest of the Simien Mountains. As of 2023, Gondar has an estimated population of 487,224.

Gorgora is a town and peninsula in northwestern Ethiopia. It is located south of Gondar on the north shore of Lake Tana, in the Semien Gondar Zone of the Amhara Region. Gorgora has a latitude and longitude of 12°14′N37°18′E.

Debre Tabor is a town and woreda in northern Ethiopia. Located in the Debub Gondar Zone of the Amhara Region, about 100 kilometers southeast of Gondar and 50 kilometers east of Lake Tana, this historic town has a latitude and longitude of 11°51′N38°1′E with an elevation of 2,706 metres (8,878 ft) above sea level. The presence of at least 48 springs in the area contributed to the development of Debre Tabor.

Debre Libanos is an Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo monastery, lying northwest of Addis Ababa in the North Shewa Zone of the Oromia Region. It was founded in 1284 by Saint Tekle Haymanot as Debre Atsbo and was renamed as Debre Libanos in the 15th century. He meditated in a cave above the current monastery for 29 years. The monastery's chief abbot, called the Ichege, was the second most powerful official in the Ethiopian Church after the Abuna.

Sodo or officially Wolaita Sodo is a city in south Ethiopia. The City is a political and administrative center of the Wolaita Zone and South Ethiopia Regional State. It has a latitude and longitude of 6°54′N37°45′E with an elevation between 1,600 and 2,100 metres above sea level. It was part of the former Sodo woreda which included Sodo Zuria which completely surrounds it.

The Central Statistical Agency is an agency of the government of Ethiopia designated to provide all surveys and censuses for that country used to monitor economic and social growth, as well as to act as an official training center in that field. It is part of the Ethiopian Ministry of Finance and Economic Development. The Directress General of the CSA is Samia Gutu. Before 9 March 1989 the CSA was known as the Central Statistical Office (CSO).

South Gondar or Debub Gondar, is one of Zones in Amhara Region, Ethiopia. This zone is named for the city of Gondar, which was the capital of Ethiopia until the mid-19th century, and has often been used as a name for the local province.
Ethiopian ecclesiastical titles refers to the offices of the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church, a hierarchical organization. Some of the more important offices are unique to it.

Debre Bizen is an Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church monastery. Located at the top of Debre Bizen the mountain near the town of Nefasit in Eritrea. Its library contains many important Ge'ez manuscripts.

The University of Gondar, until 2003 known as the Gondar College of Medical Sciences, is the oldest medical school in Ethiopia. Established as the Public Health College in 1954, it is located in Gondar, in Amhara Region of Ethiopia. In 2010, the university offered 42 undergraduate and 17 postgraduate programs.

The Battle of Shire was fought on the northern front of what was known as the Second Italo-Abyssinian War. This battle consisted of attacks and counterattacks by Italian forces under Marshal of Italy Pietro Badoglio and Ethiopian forces under Ras Imru Haile Selassie. This battle was primarily fought in the Shire area of Ethiopia.
Ethiopian Greeks, or Greeks in Ethiopia, are ethnic Greeks from Ethiopia. Today they number about 500 persons and can be traced back to ancient times. They are mainly located in the capital, Addis Ababa, and the city of Dire Dawa.
Dembecha is a town in northwestern Ethiopia 349 km north of Addis Ababa. Located in the Mirab Gojjam Zone of the Amhara Region, this town has a latitude and longitude of 10°33′N37°29′E with an elevation of 2083 meters above sea level. It is one of three towns in Dembecha woreda.
St. Paul's Hospital Millennium Medical College is Health Sciences teaching institution at St. Paul Hospital, Addis Ababa Ethiopia.

Kercheche or is a town in Diguna Fango woreda, Wolayita Zone of South Ethiopia Regional State. Kercheche is about 10 km (6.2 mi) north of Bedessa and about 8 km (5.0 mi) southwest of Bitena on the road of Sodo-Dimtu Hawassa. The approximate distance from the city of Addis Ababa to the town is 362 km (225 mi) on Addis-Hawassa-Dimtu-Sodo road. It is 38 km (24 mi) from Sodo, the capital of Wolayita Zone. The coordinate point of Kercheche lies between 6°57'21"N 37°59'29"E. The amenities in the town are 24-hours electric light, pure water service, kindergarten, primary school, high school, all time market, health stations and others. Kercheche has also dry weather and all weather roads which connect it to other surrounding areas.

Higher education in Ethiopia is the lowest in quality of standard relevance and academic freedom, despite an expansion of private higher education and rising enrollment. Higher education supposed originated by Saint Yared music school in the sixth century in line with centuries old traditional education of the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church. Modern higher education was commenced during the reign of Emperor Haile Selassie with the establishment of the University College of Addis Ababa, now called Addis Ababa University in 1950. It then followed by Haramaya University. By the time, there were only three secondary schools in the country, used as preparatory for college entrance.
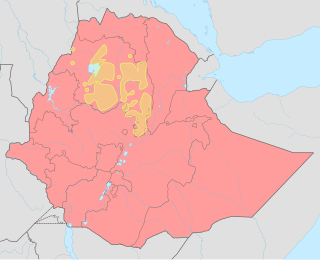
The War in Amhara is an armed conflict in the Amhara Region of Ethiopia that began in April 2023 between the Amhara regional forces along with the Fano militia, and the Ethiopian government. The conflict began after the Ethiopian military raided the Amhara Region to disarm the Amhara Special Forces and other regional allies, which resulted in resistance of local armed forces and a series of protests in Gondar, Kobo, Sekota, Weldiya and other cities on 9 April.
















