A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses.

In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion and spherochromatism, is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same point. It is caused by dispersion: the refractive index of the lens elements varies with the wavelength of light. The refractive index of most transparent materials decreases with increasing wavelength. Since the focal length of a lens depends on the refractive index, this variation in refractive index affects focusing. Chromatic aberration manifests itself as "fringes" of color along boundaries that separate dark and bright parts of the image.
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative focal length indicates that the system diverges light. A system with a shorter focal length bends the rays more sharply, bringing them to a focus in a shorter distance or diverging them more quickly. For the special case of a thin lens in air, a positive focal length is the distance over which initially collimated (parallel) rays are brought to a focus, or alternatively a negative focal length indicates how far in front of the lens a point source must be located to form a collimated beam. For more general optical systems, the focal length has no intuitive meaning; it is simply the inverse of the system's optical power.

An achromatic lens or achromat is a lens that is designed to limit the effects of chromatic and spherical aberration. Achromatic lenses are corrected to bring two wavelengths into focus on the same plane.

A camera lens is an optical lens or assembly of lenses used in conjunction with a camera body and mechanism to make images of objects either on photographic film or on other media capable of storing an image chemically or electronically.

A telephoto lens, in photography and cinematography, is a specific type of a long-focus lens in which the physical length of the lens is shorter than the focal length. This is achieved by incorporating a special lens group known as a telephoto group that extends the light path to create a long-focus lens in a much shorter overall design. The angle of view and other effects of long-focus lenses are the same for telephoto lenses of the same specified focal length. Long-focal-length lenses are often informally referred to as telephoto lenses although this is technically incorrect: a telephoto lens specifically incorporates the telephoto group.

The Angénieux retrofocus photographic lens is a wide-angle lens design that uses an inverted telephoto configuration. The popularity of this lens design made the name retrofocus synonymous with this type of lens. The Angénieux retrofocus for still cameras was introduced in France in 1950 by Pierre Angénieux.
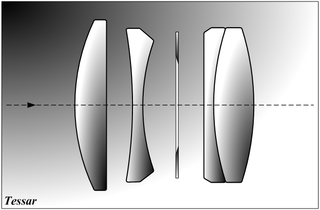
The Tessar is a photographic lens design conceived by the German physicist Paul Rudolph in 1902 while he worked at the Zeiss optical company and patented by Zeiss in Germany; the lens type is usually known as the Zeiss Tessar.

A refracting telescope is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens as its objective to form an image. The refracting telescope design was originally used in spyglasses and astronomical telescopes but is also used for long-focus camera lenses. Although large refracting telescopes were very popular in the second half of the 19th century, for most research purposes, the refracting telescope has been superseded by the reflecting telescope, which allows larger apertures. A refractor's magnification is calculated by dividing the focal length of the objective lens by that of the eyepiece.
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties.

A zoom lens is a mechanical assembly of lens elements for which the focal length can be varied, as opposed to a fixed-focal-length (FFL) lens.

In optical engineering, the objective is the optical element that gathers light from the object being observed and focuses the light rays to produce a real image. Objectives can be a single lens or mirror, or combinations of several optical elements. They are used in microscopes, binoculars, telescopes, cameras, slide projectors, CD players and many other optical instruments. Objectives are also called object lenses, object glasses, or objective glasses.

An eyepiece, or ocular lens, is a type of lens that is attached to a variety of optical devices such as telescopes and microscopes. It is so named because it is usually the lens that is closest to the eye when someone looks through the device. The objective lens or mirror collects light and brings it to focus creating an image. The eyepiece is placed near the focal point of the objective to magnify this image. The amount of magnification depends on the focal length of the eyepiece.

In film and photography, a prime lens is a fixed focal length photographic lens, typically with a maximum aperture from f2.8 to f1.2. The term can also mean the primary lens in a combination lens system. Confusion between these two meanings can occur if context doesn't make the interpretation clear. People sometimes use alternate terms—primary focal length, fixed focal length, or FFL to avoid ambiguity.

A catadioptric optical system is one where refraction and reflection are combined in an optical system, usually via lenses (dioptrics) and curved mirrors (catoptrics). Catadioptric combinations are used in focusing systems such as searchlights, headlamps, early lighthouse focusing systems, optical telescopes, microscopes, and telephoto lenses. Other optical systems that use lenses and mirrors are also referred to as "catadioptric", such as surveillance catadioptric sensors.

Large format lenses are photographic optics that provide an image circle large enough to cover large format film or plates. Large format lenses are typically used in large format cameras and view cameras.
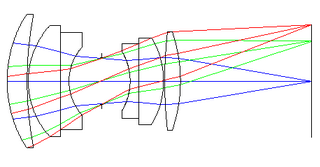
The double Gauss lens is a compound lens used mostly in camera lenses that reduces optical aberrations over a large focal plane.

The achromatic telescope is a refracting telescope that uses an achromatic lens to correct for chromatic aberration.
The design of photographic lenses for use in still or cine cameras is intended to produce a lens that yields the most acceptable rendition of the subject being photographed within a range of constraints that include cost, weight and materials. For many other optical devices such as telescopes, microscopes and theodolites where the visual image is observed but often not recorded the design can often be significantly simpler than is the case in a camera where every image is captured on film or image sensor and can be subject to detailed scrutiny at a later stage. Photographic lenses also include those used in enlargers and projectors.

The invention of the camera in the early 19th century led to an array of lens designs intended for photography. The problems of photographic lens design, creating a lens for a task that would cover a large, flat image plane, were well known even before the invention of photography due to the development of lenses to work with the focal plane of the camera obscura.