
Oceania is a geographical region that is described as a continent in most parts of the world. It includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western Hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of 8,525,989 square kilometres (3,291,903 sq mi) and a population of around 44.4 million as of 2022. Oceania is described as a geographical region in most of the English-speaking world, but outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is described as one of the continents. In this model of the world, Australia is only seen as an island nation contained inside of the continent of Oceania, and not a continent by itself. When compared to the other continents, Oceania is the smallest in land area and the second least populated after Antarctica.

Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, Pacificans or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of Oceania.

The Pacific Rim comprises the lands around the rim of the Pacific Ocean. The Pacific Basin includes the Pacific Rim and the islands in the Pacific Ocean. The Pacific Rim roughly overlaps with the geologic Pacific Ring of Fire.

A subregion is a part of a larger region or continent and is usually based on location. Cardinal directions, such as south are commonly used to define a subregion.
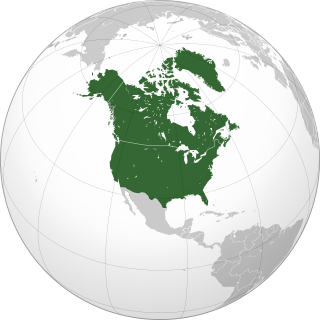
Northern America is the northernmost subregion of North America. The boundaries may be drawn slightly differently. In one definition, it lies directly north of Middle America. Northern America's land frontier with the rest of North America then coincides with the Mexico–United States border. Geopolitically, according to the United Nations' scheme of geographical regions and subregions, Northern America consists of Bermuda, Canada, Greenland, Saint Pierre and Miquelon and the United States.

The following is an alphabetical list of countries in the United Nations geoscheme for the Americas grouped by subregion and intermediate region. Note that the continent of North America comprises the intermediate regions of the Caribbean, Central America, and Northern America.

The following is an alphabetical list of subregions in the United Nations geoscheme for Oceania, created by the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD).
There are six monarchies in Oceania where supreme power resides with an individual hereditary head, who is recognised as the head of state. Each is a constitutional monarchy, wherein the sovereign inherits his or her office, usually keeps it until death or abdication, and is bound by laws and customs in the exercise of their powers. Five of these independent states share King Charles III as their respective head of state, making them part of a global grouping known as the Commonwealth realms; in addition, all monarchies of Oceania are members of the Commonwealth of Nations. The only sovereign monarchy in Oceania that does not share a monarch with another state is Tonga. Australia and New Zealand have dependencies within the region and outside it, although five non-sovereign constituent monarchs are recognized by New Zealand, Papua New Guinea and France.
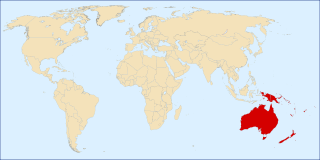
The following outline is provided as an overview and topical guide to Oceania.
The decolonisation of Oceania occurred after World War II when nations in Oceania achieved independence by transitioning from European colonial rule to full independence.

Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania vary, with it being defined in various ways, often geopolitically or geographically. In the geopolitical conception used by the United Nations, International Olympic Committee, and many atlases, the Oceanic region includes Australia and the nations of the Pacific from Papua New Guinea east, but not the Malay Archipelago or Indonesian New Guinea. The term is sometimes used more specifically to denote Australasia as a geographic continent, or biogeographically as a synonym for either the Australasian realm or the Oceanian realm.








