| Part of a series on the |
| Wildlife of Great Britain |
|---|
 |
The reptiles of Great Britain include three native snakes and three native lizards. A number of sea turtles visit Great Britain's shores. There are also at least seven introduced reptile species.
| Part of a series on the |
| Wildlife of Great Britain |
|---|
 |
The reptiles of Great Britain include three native snakes and three native lizards. A number of sea turtles visit Great Britain's shores. There are also at least seven introduced reptile species.
| Image | Name | Distribution |
|---|---|---|
 | Common adder, Vipera berus [1] | 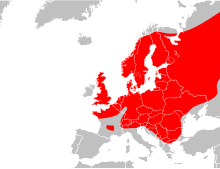 |
 | Barred grass snake, Natrix helvetica [2] [lower-alpha 1] |  |
 | Smooth snake, Coronella austriaca [4] |  |
| Image | Name | Distribution |
|---|---|---|
 | Slow worm, Anguis fragilis [5] [6] | 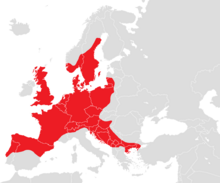 |
 | Viviparous lizard, Zootoca vivipara [7] |  |
 | Sand lizard, Lacerta agilis | 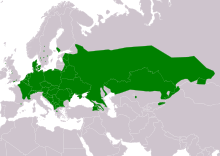 |
| Image | Name | Distribution | |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Leatherback sea turtle, Dermochelys coriacea | 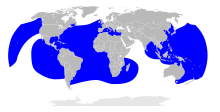 | Foraging [8] |
 | Loggerhead sea turtle, Caretta caretta | 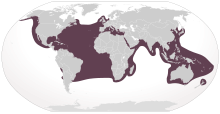 | Vagrant [9] |
 | Green sea turtle, Chelonia mydas | 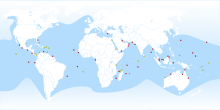 | Vagrant [10] |
 | Hawksbill sea turtle, Eretmochelys imbricata |  | Vagrant [10] |
 | Kemp's ridley sea turtle, Lepidochelys kempii |  | Vagrant [10] |
 | Olive ridley sea turtle, Lepidochelys olivacea | 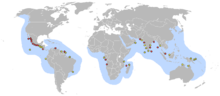 | Vagrant [11] |

The Blanding's turtle is a semi-aquatic turtle of the family Emydidae. This species is native to central and eastern parts of Canada and the United States. It is considered to be an endangered species throughout much of its range. The Blanding's turtle is of interest in longevity research, as it shows few or no common signs of aging and is physically active and capable of reproduction into eight or nine decades of life.

The slow worm is a reptile native to western Eurasia. It is also called a deaf adder, a slowworm, a blindworm, or regionally, a long-cripple and hazelworm. These legless lizards are also sometimes called common slowworms. The "blind" in blindworm refers to the lizard's small eyes, similar to a blindsnake.

The grass snake, sometimes called the ringed snake or water snake, is a Eurasian semi-aquatic non-venomous colubrid snake. It is often found near water and feeds almost exclusively on amphibians.

The East African black mud turtle, also known as the Pan terrapin, is a species of turtle in the family Pelomedusidae, native to eastern and southeastern Africa.

The fauna of England is similar to that of other areas British Isles and lies within the Palearctic realm. England's fauna is mainly made up of small animals and is notable for having few large mammals, but in similarity with other island nations; many bird species.
In the 10th edition of Systema Naturae, Carl Linnaeus described the Amphibia as:
Animals that are distinguished by a body cold and generally naked; stern and expressive countenance; harsh voice; mostly lurid color; filthy odor; a few are furnished with a horrid poison; all have cartilaginous bones, slow circulation, exquisite sight and hearing, large pulmonary vessels, lobate liver, oblong thick stomach, and cystic, hepatic, and pancreatic ducts: they are deficient in diaphragm, do not transpire (sweat), can live a long time without food, are tenatious of life, and have the power of reproducing parts which have been destroyed or lost; some undergo a metamorphosis; some cast (shed) their skin; some appear to live promiscuously on land or in the water, and some are torpid during the winter.
Wyoming is home to 12 amphibian species and 22 species of reptiles.

The barred grass snake is a non-venomous colubrid snake from Western Europe, living in and close to water. It was included within the grass snake species, Natrix natrix, until August 2017, when genetic analysis led to its reclassification as a separate species.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)