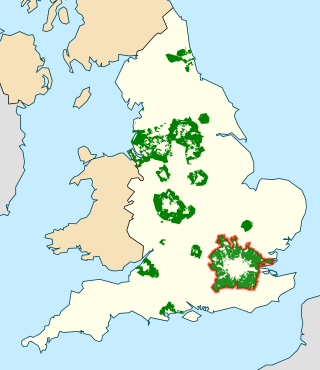
In British town planning, the green belt is a policy for controlling urban growth. The term, coined by Octavia Hill in 1875, refers to a ring of countryside where urbanisation will be resisted for the foreseeable future, maintaining an area where agriculture, forestry and outdoor leisure can be expected to prevail. The fundamental aim of green belt policy is to prevent urban sprawl by keeping land permanently open, and consequently the most important attribute of green belts is their openness.

In the United Kingdom a listed building is a structure of particular architectural and/or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, Cadw in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland. The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000, although the statutory term in Ireland is "protected structure".

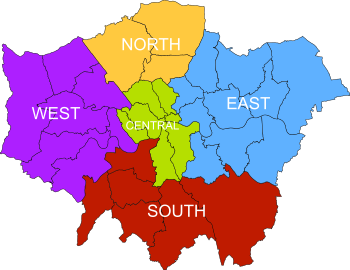
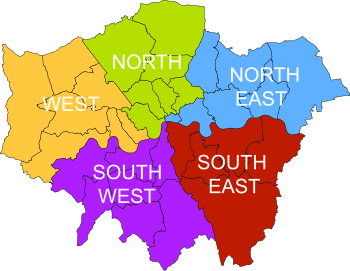
South London is the southern part of London, England, south of the River Thames. The region consists of the boroughs, in whole or in part, of Bexley, Bromley, Croydon, Greenwich, Kingston, Lambeth, Lewisham, Merton, Richmond, Southwark, Sutton and Wandsworth.
Central London is the innermost part of London, in England, spanning several boroughs. Over time, a number of definitions have been used to define the scope of Central London for statistics, urban planning and local government. Its characteristics are understood to include a high density built environment, high land values, an elevated daytime population and a concentration of regionally, nationally and internationally significant organisations and facilities.

The regional chambers of England were a group of indirectly elected regional bodies that were created by the provisions of the Regional Development Agencies Act 1998. There were eight regional chambers, one for each of the regions of England except Greater London, which had opted for an elected mayor and assembly in 1998. All eight regional chambers had adopted the title "regional assembly" or "assembly" as part of their name, though this was not an official status in law. The chambers were abolished over a two-year period between 31 March 2008 and 31 March 2010 and some of their functions were assumed by newly established local authority leaders' boards.
Strategic health authorities (SHA) were part of the structure of the National Health Service in England between 2002 and 2013. Each SHA was responsible for managing performance, enacting directives and implementing health policy as required by the Department of Health at a regional level.

The Greater Manchester County Council (GMCC) was the top-tier local government administrative body for Greater Manchester from 1974 to 1986. A strategic authority, with responsibilities for roads, public transport, planning, emergency services and waste disposal, it was composed of 106 directly elected members drawn from the ten metropolitan boroughs of Greater Manchester. The Greater Manchester County Council shared power with ten lower-tier district councils, each of which directed local matters. It was also known as the Greater Manchester Council (GMC) and the Greater Manchester Metropolitan County Council (GMMCC).
City region is a term in use since about 1950 by urbanists, economists and urban planners to mean a metropolitan area and hinterland, often having a shared administration. Typically, it denotes a city, conurbation or urban zone with multiple administrative districts, but sharing resources like a central business district, labour market and transport network such that it functions as a single economic unit

The Greater Dublin Area, or simply Greater Dublin, is an informal term that is taken to include the city of Dublin and its hinterland, with varying definitions as to its extent. At the expansive end, it has been defined as including all of the traditional County Dublin and three neighbouring counties, while more commonly it is taken as the contiguous metropolitan area of Dublin plus suburban and commuter towns. The area is defined for strategic planning, and, for example, transport, and it is not a formal administrative or political unit.
Regional spatial strategies (RSS) provided regional level planning frameworks for the regions of England outside London. They were introduced in 2004. Their revocation was announced by the new Conservative/Liberal Democrat government on 6 July 2010.

The London Plan is the statutory spatial development strategy for the Greater London area in the United Kingdom that is written by the Mayor of London and published by the Greater London Authority.

Hackney London Borough Council is the local government authority for the London Borough of Hackney, London, England, one of 32 London borough councils. The council is unusual in the United Kingdom local government system in that its executive function is controlled by a directly elected mayor of Hackney, currently Philip Glanville of the Labour Party. Hackney comprises 19 wards, each electing three councillors. Following the May 2018 election, Hackney London Borough Council consists of 52 Labour Party councillors and 5 Conservative Party councillors. The council was created by the London Government Act 1963 whereby it replaced three local authorities: Hackney Metropolitan Borough Council, Shoreditch Metropolitan Borough Council and Stoke Newington Metropolitan Borough Council.
In England, spatial planning is undertaken at the national level, through the National Planning Policy Framework. The London region is the only one to have a statutory London Plan. Most planning functions are exercised by local authorities, with neighbourhood planning also taking place in some areas.

The regions, formerly known as the government office regions, are the highest tier of sub-national division in England, established in 1994. Between 1994 and 2011, nine regions had officially devolved functions within government. While they no longer fulfil this role, they continue to be used for statistical and some administrative purposes. While the UK was a member of the European Union, they defined areas (constituencies) for the purposes of elections to the European Parliament. Eurostat also used them to demarcate first level Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS) regions within the European Union, which in 2021 were superseded by International Territorial Level (ITL) regions. The regions generally follow the boundaries of the former standard regions, established in the 1940s for statistical purposes.

The Leeds City Region, or informally Greater Leeds, is a local enterprise partnership city region located in West Yorkshire, England. Prior to the West Yorkshire devolution deal, the partnership covered parts of South and North Yorkshire. According to the Office for National Statistics, as of 2017 the city region ranked 2nd behind Greater London for both population and GVA in the United Kingdom. It has a population of 2,320,214 million and a GVA of £69.62 billion.
The Covenant of Mayors is a European co-operation movement involving local and regional authorities. Signatories of the Covenant of Mayors voluntarily commit to increasing energy efficiency and the use of renewable energy sources on their territories. By their commitment, they support the European Union 20% CO2 reduction objective to be reached by 2020.
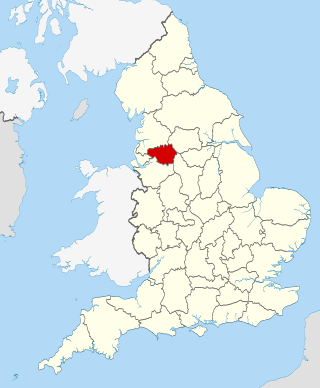
The Greater Manchester Combined Authority (GMCA) is a combined authority for Greater Manchester, England. It was established on 1 April 2011 and consists of 11 members; 10 indirectly elected members, each a directly elected councillor from one of the ten metropolitan boroughs that comprise Greater Manchester, together with the directly elected Mayor of Greater Manchester. The authority derives most of its powers from the Local Government Act 2000 and Local Democracy, Economic Development and Construction Act 2009, and replaced a range of single-purpose joint boards and quangos to provide a formal administrative authority for Greater Manchester for the first time since the abolition of Greater Manchester County Council in 1986.

In the United Kingdom, devolution is the Parliament of the United Kingdom's statutory granting of a greater level of self-government to the Scottish Parliament, the Senedd, the Northern Ireland Assembly and the London Assembly and to their associated executive bodies the Scottish Government, the Welsh Government, the Northern Ireland Executive and in England, the Greater London Authority and combined authorities.

Greater London is an administrative area in England governed by the Greater London Authority. It is organised into 33 local government districts: the 32 London boroughs and the City of London. Greater London is one of the regions of England, also known as the London Region. The Greater London Authority, based in Newham as of the start of 2022, is responsible for strategic local government across the area and consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly.

Councils of governments in Connecticut are organizations that bring together the chief elected officials and/or professional managers from member municipalities in Connecticut. The bodies are meant to aid coordination among neighboring cities and towns, and between the towns and the state government, on issue including land use, zoning, and transportation. They serve some functions analogous to county governments in other states, but have no independent taxing authority. Councils of government also host some intermunicipal services based on the needs and voluntary participation of member or client municipalities. Councils, or COGs, receive funding through membership dues, state grants, and federal grants.