
Assyria, also called the Assyrian Empire, was a Mesopotamian kingdom and empire of the Ancient Near East that existed as a state from perhaps as early as the 25th century BC until its collapse between 612 BC and 609 BC; thereby spanning the periods of the Early to Middle Bronze Age through to the late Iron Age. This vast span of time is divided into the Early Period, Old Assyrian Empire, Middle Assyrian Empire and Neo-Assyrian Empire.

The British Museum, in the Bloomsbury area of London, England, is a public institution dedicated to human history, art and culture. Its permanent collection of some eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence, having been widely collected during the era of the British Empire. It documents the story of human culture from its beginnings to the present. It was the first public national museum in the world. The Museum was established in 1753, largely based on the collections of the Irish physician and scientist Sir Hans Sloane. It first opened to the public in 1759, in Montagu House, on the site of the current building. Its expansion over the following 250 years was largely a result of expanding British colonisation and has resulted in the creation of several branch institutions, the first being the Natural History Museum in 1881.

An emperor is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife, mother, or a woman who rules in her own right. Emperors are generally recognized to be of the highest monarchic honour and rank, surpassing kings. In Europe, the title of Emperor has been used since the Middle Ages, considered in those times equal or almost equal in dignity to that of Pope due to the latter's position as visible head of the Church and spiritual leader of the Catholic part of Western Europe. The Emperor of Japan is the only currently reigning monarch whose title is translated into English as "Emperor", while holding no actual political power.

The Holy Roman Empire was a multi-ethnic complex of territories in Western and Central Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. The largest territory of the empire after 962 was the Kingdom of Germany, though it also included the neighbouring Kingdom of Bohemia and Kingdom of Italy, plus numerous other territories, and soon after the Kingdom of Burgundy was added. However, while by the end of the 15th century the Empire was still in theory composed of three major blocks – Italy, Germany, and Burgundy – in practice only the Kingdom of Germany remained, with the Burgundian territories lost to France and the Italian territories, ignored in the Imperial Reform, although formally part of the Empire, splintered into numerous de facto independent territorial entities. The status of Italy in particular changed throughout the 15th to 19th centuries; some territories like Piedmont-Savoy became increasingly independent, while others like Lombardy and Tuscany became more dependent due to falling directly under the dominions of the Habsburg emperors and their satellite houses. The external borders of the Empire did not change noticeably from the Peace of Westphalia – which acknowledged the exclusion of Switzerland and the Northern Netherlands, and the French protectorate over Alsace – to the dissolution of the Empire. At the conclusion of the Napoleonic Wars in 1815, most of the Holy Roman Empire was included in the German Confederation, with the main exceptions being the Italian states.

The 1st millennium BC was the period of time between from the year 1000 BC to 1 BC . It encompasses the Iron Age in the Old World and sees the transition from the Ancient Near East to classical antiquity.

Ancient history is the aggregate of past events from the beginning of writing and recorded human history and extending as far as post-classical history. The phrase may be used either to refer to the period of time or the academic discipline.

A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, particularly in Commonwealth countries, as an abstract name for the monarchy itself, as distinct from the individual who inhabits it. A specific type of crown is employed in heraldry under strict rules. Indeed, some monarchies never had a physical crown, just a heraldic representation, as in the constitutional kingdom of Belgium, where no coronation ever took place; the royal installation is done by a solemn oath in parliament, wearing a military uniform: the King is not acknowledged as by divine right, but assumes the only hereditary public office in the service of the law; so he in turn will swear in all members of "his" federal government.

This is a timeline of Chinese history, comprising important legal and territorial changes and political events in China and its predecessor states. To read about the background to these events, see History of China. See also the list of Chinese monarchs, Chinese emperors family tree, dynasties in Chinese history and years in China.

Nesebar is an ancient city and one of the major seaside resorts on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast, located in Burgas Province. It is the administrative centre of the homonymous Nesebar Municipality. Often referred to as the "Pearl of the Black Sea", Nesebar is a rich city-museum defined by more than three millennia of ever-changing history. The small city exists in two parts separated by a narrow man-made isthmus with the ancient part of the settlement on the peninsula, and the more modern section on the mainland side. The older part bears evidence of occupation by a variety of different civilisations over the course of its existence.
A classical language is a language with an independent literary tradition and a large and ancient body of written literature. Classical languages are typically dead languages, or show a high degree of diglossia, as the spoken varieties of the language diverge further away from the classical written language over time.

Alinda was an inland city and bishopric in ancient Caria, in Asia Minor (Anatolia). Modern scholars identify Alinda with the Hellenistic foundation of Alexandria ad Latmum noted by Stephanus of Byzantium.
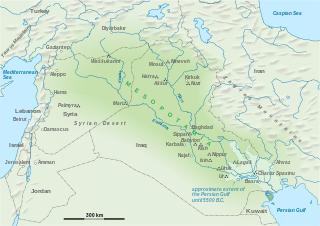
The (pre)history of Mesopotamia ranges from the earliest human occupation in the Paleolithic period up to the Late antiquity. This history is pieced together from evidence retrieved from archaeological excavations and, after the introduction of writing in the late 4th millennium BC, an increasing amount of historical sources. While in the Paleolithic and early Neolithic periods only parts of Upper Mesopotamia were occupied, the southern alluvium was settled during the late Neolithic period. Mesopotamia has been home to many of the oldest major civilizations, entering history from the Early Bronze Age, for which reason it is often dubbed the cradle of civilization.
This is a timeline of Yemeni history, comprising important legal and territorial changes and political events in Yemen and its predecessor states. To understand the context to these events, see History of Yemen. See also the List of rulers of Saba and Himyar, the list of Imams of Yemen and the list of Presidents of Yemen.

The Eurasian Steppe, also called the Great Steppe or the steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome. It stretches through Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova, Ukraine, Western Russia, Siberia, Kazakhstan, Xinjiang, Mongolia, and Manchuria, with one major exclave, the Pannonian steppe or Puszta, located mostly in Hungary.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to ancient history:

The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia, ancient Egypt, ancient Iran, Anatolia/Asia Minor and the Armenian Highlands, the Levant, Cyprus and the Arabian Peninsula. The ancient Near East is studied in the fields of Ancient Near East studies, Near Eastern archaeology and ancient history.

The history of Turkey, understood as the history of the region now forming the territory of the Republic of Turkey, includes the history of both Anatolia and Eastern Thrace. These two previously politically distinct regions came under control of the Roman Empire in the second century BCE, eventually becoming the core of the Roman Byzantine Empire.













