
Project Mercury was the first human spaceflight program of the United States, running from 1958 through 1963. An early highlight of the Space Race, its goal was to put a man into Earth orbit and return him safely, ideally before the Soviet Union. Taken over from the US Air Force by the newly created civilian space agency NASA, it conducted 20 uncrewed developmental flights, and six successful flights by astronauts. The program, which took its name from Roman mythology, cost $2.57 billion. The astronauts were collectively known as the "Mercury Seven", and each spacecraft was given a name ending with a "7" by its pilot.

The Saturn family of American rockets was developed by a team of mostly Nazi rocket engineers and scientists led by Wernher von Braun to launch heavy payloads to Earth orbit and beyond. The Saturn family used liquid hydrogen as fuel in the upper stages. Originally proposed as a military satellite launcher, they were adopted as the launch vehicles for the Apollo Moon program. Three versions were built and flown: the medium-lift Saturn I, the heavy-lift Saturn IB, and the super heavy-lift Saturn V.
The Saturn I was a rocket designed as the United States' first medium lift launch vehicle for up to 20,000-pound (9,100 kg) low Earth orbit payloads. The rocket's first stage was built as a cluster of propellant tanks engineered from older rocket tank designs, leading critics to jokingly refer to it as "Cluster's Last Stand". Its development was taken over from the Advanced Research Projects Agency in 1958 by the newly formed civilian NASA. Its design proved sound and flexible. It was successful in initiating the development of liquid hydrogen-fueled rocket propulsion, launching the Pegasus satellites, and flight verification of the Apollo command and service module launch phase aerodynamics. Ten Saturn I rockets were flown before it was replaced by the heavy lift derivative Saturn IB, which used a larger, higher total impulse second stage and an improved guidance and control system. It also led the way to development of the super-heavy lift Saturn V which carried the first men to landings on the Moon in the Apollo program.

Big Joe 1 (Atlas-10D) launched an uncrewed boilerplate Mercury capsule from Cape Canaveral, Florida on 9 September 1959. The purposes of the Big Joe 1 were to test the Mercury spacecraft ablative heat shield, afterbody heating, reentry dynamics attitude control and recovery capability. It was also the first launch of a spacecraft in Project Mercury.

Mercury-Redstone 1 (MR-1) was the first Mercury-Redstone uncrewed flight test in Project Mercury and the first attempt to launch a Mercury spacecraft with the Mercury-Redstone Launch Vehicle. Intended to be an uncrewed sub-orbital spaceflight, it was launched on November 21, 1960 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. The launch failed in abnormal fashion: immediately after the Mercury-Redstone rocket started to move, it shut itself down and settled back on the pad, after which the capsule jettisoned its escape rocket and deployed its recovery parachutes. The failure has been referred to as the "four-inch flight", for the approximate distance traveled by the launch vehicle.

Mercury-Redstone BD was an uncrewed booster development flight in the U.S. Mercury program. It was launched on March 24, 1961, from Launch Complex 5 at Cape Canaveral, Florida. The mission used a boilerplate Mercury spacecraft and Redstone MRLV-5.

Little Joe 1 (LJ-1) was a failed launch of a Little Joe by NASA, a solid fuel rocket that was designed for a Max Q abort and launch escape system test for the Mercury capsule. The objective was to determine how well the escape rocket would function under the most severe dynamic loading conditions anticipated during a Mercury-Atlas launching.

Little Joe 5 was the November 8, 1960, unmanned atmospheric test flight of the Mercury spacecraft, conducted as part of the U.S. Mercury program. The objective was to test a production Mercury capsule (#3) and the launch escape system during an ascent abort at maximum dynamic pressure. The mission was launched from Wallops Island, Virginia. Sixteen seconds after liftoff, the escape rocket and the tower jettison rocket both fired prematurely. Furthermore, the booster, capsule, and escape tower failed to separate as intended. The entire stack was destroyed on impact with the Atlantic Ocean. The Little Joe 5 flew to an apogee of 10.1 miles (16.2 km) and a range of 13 miles (20.9 km). Some capsule and booster debris was recovered from the ocean floor for post flight analysis.

Little Joe 5A was an uncrewed launch escape system test of the Mercury spacecraft, conducted as part of the U.S. Mercury program. It was an attempted re-test of the failed Little Joe 5 flight. The mission used production Mercury spacecraft #14 atop a Little Joe booster rocket. The mission was launched March 18, 1961, from Wallops Island, Virginia. The LJ-5 failure sequence was repeated when capsule escape rocket again ignited prematurely with the capsule remaining attached to the booster. In this flight however, a ground command was sent to separate the capsule from the booster and escape tower. This allowed the main and reserve parachutes to deploy and the capsule was recovered with only minor damage. It would be used again on the subsequent Little Joe 5B mission, in a third attempt to achieve mission objectives. The Little Joe 5A flew to an apogee of 7.7 miles (12 km) and a range of 18 miles (29 km). The mission lasted 5 minutes 25 seconds. Maximum speed was 1,783 miles per hour (2,869 km/h) and acceleration was 8 G (78 m/s²).

Little Joe II was an American rocket used from 1963 to 1966 for five uncrewed tests of the Apollo spacecraft launch escape system (LES), and to verify the performance of the command module parachute recovery system in abort mode. It was named after a similar rocket designed for the same function in Project Mercury. Launched from White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico, it was the smallest of four launch rockets used in the Apollo program.
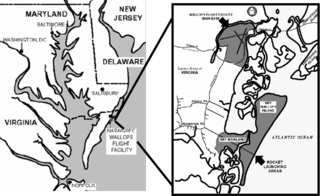
Wallops Flight Facility (WFF) is a rocket launch site on Wallops Island on the Eastern Shore of Virginia, United States, just east of the Delmarva Peninsula and approximately 100 miles (160 km) north-northeast of Norfolk. The facility is operated by the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and primarily serves to support science and exploration missions for NASA and other Federal agencies. WFF includes an extensively instrumented range to support launches of more than a dozen types of sounding rockets; small expendable suborbital and orbital rockets; high-altitude balloon flights carrying scientific instruments for atmospheric and astronomical research; and, using its Research Airport, flight tests of aeronautical research aircraft, including unmanned aerial vehicles.

Project Gemini was NASA's second human spaceflight program. Conducted between projects Mercury and Apollo, Gemini started in 1961 and concluded in 1966. The Gemini spacecraft carried a two-astronaut crew. Ten Gemini crews and 16 individual astronauts flew low Earth orbit (LEO) missions during 1965 and 1966.

A space capsule is a spacecraft designed to transport cargo, scientific experiments, and/or astronauts to and from space. Capsules are distinguished from other spacecraft by the ability to survive reentry and return a payload to the Earth's surface from orbit, and are distinguished from other types of recoverable spacecraft by their blunt shape, not having wings and often containing little fuel other than what is necessary for a safe return. Capsule-based crewed spacecraft such as Soyuz or Orion are often supported by a service or adapter module, and sometimes augmented with an extra module for extended space operations. Capsules make up the majority of crewed spacecraft designs, although one crewed spaceplane, the Space Shuttle, has flown in orbit.

A launch escape system (LES) or launch abort system (LAS) is a crew-safety system connected to a space capsule. It is used in the event of a critical emergency to quickly separate the capsule from its launch vehicle in case of an emergency requiring the abort of the launch, such as an impending explosion. The LES is typically controlled by a combination of automatic rocket failure detection, and a manual activation for the crew commander's use. The LES may be used while the launch vehicle is still on the launch pad, or during its ascent. Such systems are usually of three types:

The Ares V was the planned cargo launch component of the cancelled NASA Constellation program, which was to have replaced the Space Shuttle after its retirement in 2011. Ares V was also planned to carry supplies for a human presence on Mars. Ares V and the smaller Ares I were named after Ares, the Greek god of war.

Ares I was the crew launch vehicle that was being developed by NASA as part of the Constellation program. The name "Ares" refers to the Greek deity Ares, who is identified with the Roman god Mars. Ares I was originally known as the "Crew Launch Vehicle" (CLV).

A boilerplate spacecraft, also known as a mass simulator, is a nonfunctional craft or payload that is used to test various configurations and basic size, load, and handling characteristics of rocket launch vehicles. It is far less expensive to build multiple, full-scale, non-functional boilerplate spacecraft than it is to develop the full system. In this way, boilerplate spacecraft allow components and aspects of cutting-edge aerospace projects to be tested while detailed contracts for the final project are being negotiated. These tests may be used to develop procedures for mating a spacecraft to its launch vehicle, emergency access and egress, maintenance support activities, and various transportation processes.

The Max Launch Abort System (MLAS) was a proposed alternative to the Maxime Faget-invented "tractor" launch escape system (LES) that was planned for use by NASA for its Orion spacecraft in the event an Ares I malfunction during launch required an immediate abort.
The Mercury-Redstone Launch Vehicle, designed for NASA's Project Mercury, was the first American crewed space booster. It was used for six sub-orbital Mercury flights from 1960–1961; culminating with the launch of the first, and 11 weeks later, the second American in space. The four subsequent Mercury human spaceflights used the more powerful Atlas booster to enter low Earth orbit.

The Atlas LV-3B, Atlas D Mercury Launch Vehicle or Mercury-Atlas Launch Vehicle, was a human-rated expendable launch system used as part of the United States Project Mercury to send astronauts into low Earth orbit. Manufactured by Convair, it was derived from the SM-65D Atlas missile, and was a member of the Atlas family of rockets. With the Atlas having been originally designed as a weapon system, testing and design changes were made to the missile to make it a safe and reliable launch vehicle. After the changes were made and approved, the US launched the LV-3B nine times, four of which had crewed Mercury spacecraft.




























