Related Research Articles
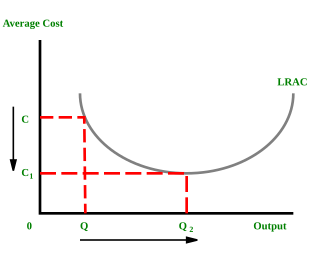
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of output produced per unit of time. A decrease in cost per unit of output enables an increase in scale. At the basis of economies of scale, there may be technical, statistical, organizational or related factors to the degree of market control. This is just a partial description of the concept.

Economic geography is the subfield of human geography that studies economic activity and factors affecting it. It can also be considered a subfield or method in economics. There are four branches of economic geography.

One of the major subfields of urban economics, economies of agglomeration, explains, in broad terms, how urban agglomeration occurs in locations where cost savings can naturally arise. This term is most often discussed in terms of economic firm productivity. However, agglomeration effects also explain some social phenomena, such as large proportions of the population being clustered in cities and major urban centers. Similar to economies of scale, the costs and benefits of agglomerating increase the larger the agglomerated urban cluster becomes. Several prominent examples of where agglomeration has brought together firms of a specific industry are: Silicon Valley and Los Angeles being hubs of technology and entertainment, respectively, in California, United States; and London, United Kingdom, being a hub of finance.

In microeconomics, diseconomies of scale are the cost disadvantages that economic actors accrue due to an increase in organizational size or in output, resulting in production of goods and services at increased per-unit costs. The concept of diseconomies of scale is the opposite of economies of scale. In business, diseconomies of scale are the features that lead to an increase in average costs as a business grows beyond a certain size.
Urban economics is broadly the economic study of urban areas; as such, it involves using the tools of economics to analyze urban issues such as crime, education, public transit, housing, and local government finance. More specifically, it is a branch of microeconomics that studies the urban spatial structure and the location of households and firms.
A business cluster is a geographic concentration of interconnected businesses, suppliers, and associated institutions in a particular field. Clusters are considered to increase the productivity with which companies can compete, nationally and globally. Accounting is a part of the business cluster. In urban studies, the term agglomeration is used. Clusters are also important aspects of strategic management.
Low-cost country sourcing (LCCS) is procurement strategy in which a company sources materials from countries with lower labour and production costs in order to cut operating expenses. LCCS falls under a broad category of procurement efforts called global sourcing.

Deindustrialization is a process of social and economic change caused by the removal or reduction of industrial capacity or activity in a country or region, especially of heavy industry or manufacturing industry.
The urban hierarchy ranks each city based on the size of population residing within the nationally defined statistical urban area. Because urban population depends on how governments define their metropolitan areas, urban hierarchies are conventionally ranked at the national level; however, the ranking can be extended globally to include all cities. Urban hierarchies tell us about the general organization of cities and yield some important insights. First, it tells us that within a system of cities, some cities will grow to be very large, but that number will be small relative to the universe of cities. Second, it refutes the expectation of an optimally sized city. Lastly, it establishes cities as belonging to an inter-related network where one city's growth affects others'.
Spatial inequality refers to the unequal distribution of income and resources across geographical regions. Attributable to local differences in infrastructure, geographical features and economies of agglomeration, such inequality remains central to public policy discussions regarding economic inequality more broadly.

Urbanization in China increased in speed following the initiation of the reform and opening policy. As of 2022, China had an urbanization rate of 64.7% and is expected to reach 75-80% by 2035.
Economic restructuring is used to indicate changes in the constituent parts of an economy in a very general sense. In the western world, it is usually used to refer to the phenomenon of urban areas shifting from a manufacturing to a service sector economic base. It has profound implications for productive capacities and competitiveness of cities and regions. This transformation has affected demographics including income distribution, employment, and social hierarchy; institutional arrangements including the growth of the corporate complex, specialized producer services, capital mobility, informal economy, nonstandard work, and public outlays; as well as geographic spacing including the rise of world cities, spatial mismatch, and metropolitan growth differentials.
Innovation economics is new, and growing field of economic theory and applied/experimental economics that emphasizes innovation and entrepreneurship. It comprises both the application of any type of innovations, especially technological, but not only, into economic use. In classical economics this is the application of customer new technology into economic use; but also it could refer to the field of innovation and experimental economics that refers the new economic science developments that may be considered innovative. In his 1942 book Capitalism, Socialism and Democracy, economist Joseph Schumpeter introduced the notion of an innovation economy. He argued that evolving institutions, entrepreneurs and technological changes were at the heart of economic growth. However, it is only in recent years that "innovation economy," grounded in Schumpeter's ideas, has become a mainstream concept".
Knowledge spillover is an exchange of ideas among individuals. Knowledge spillover is usually replaced by terminations of technology spillover, R&D spillover and/or spillover (economics) when the concept is specific to technology management and innovation economics. In knowledge management economics, knowledge spillovers are non-rival knowledge market costs incurred by a party not agreeing to assume the costs that has a spillover effect of stimulating technological improvements in a neighbor through one's own innovation. Such innovations often come from specialization within an industry.
Cluster theory is a theory of strategy.
A metropolitan economy refers to the cohesive, naturally evolving concentration of industries, commerce, markets, firms, housing, human capital, infrastructure and other economic elements that are comprised in a particular metropolitan area. Rather than the definition of distinct urban and suburban economies that evolve and function independently, a metropolitan economy encompasses all interdependent jurisdictions of particular regional clusters. This type of economy has all its units functioning together in a trans-boundary landscape that often crosses city, county, state, province, and even national lines. Metropolitan economies expand from the parochial view taken in urban economics which focuses entirely on a city's spatial structure, and broadens it into a metropolitan's spatial and social/economic structure.
Overurbanization is a thesis originally developed by scholars of demography, geography, ecology, economics, political science, and sociology in thrergence of International Nongovernmental Organizations Amid Declining States. The term is intentionally comparative and has been used to differentiate between developed and developing countries. Several causes have been suggested, but the most common is rural-push and urban-pull factors in addition to population growth.
Innovation districts are urban geographies of innovation where R&D strong institutions, companies, and other private actors develop integrated strategies and solutions to develop thriving innovation ecosystems–areas that attract entrepreneurs, startups, and business incubators. Unlike science parks, innovation districts are physically compact, leverage density and high levels of accessibility, and provide a “mash up” of activities including housing, office, and neighborhood-serving amenities. Districts signify the collapse back of innovation into cities and is increasingly used as a way to revitalize the economies of cities and their broader regions. As of 2019, there are more than 100 districts worldwide.
Holger Görg is a German economist who currently works as Professor of International Economics at the University of Kiel. Görg also leads the Kiel Center for Globalization and heads the Research Area "Global Division of Labour" at the Kiel Institute for the World Economy. In 2009, he was awarded the Gossen Prize for his contributions to the study of firms' decisions to invest, export and outsource parts of their value chains abroad.
Gianmarco Ireo Paolo Ottaviano is an Italian economist and Professor of Economics at Bocconi University.