
The River Tay is the longest river in Scotland and the seventh-longest in Great Britain. The Tay originates in western Scotland on the slopes of Ben Lui, then flows easterly across the Highlands, through Loch Dochart, Loch Iubhair and Loch Tay, then continues east through Strathtay, in the centre of Scotland, then southeasterly through Perth, where it becomes tidal, to its mouth at the Firth of Tay, south of Dundee. It is the largest river in the United Kingdom by measured discharge. Its catchment is approximately 2,000 square miles, the Tweed's is 1,500 sq mi (3,900 km2) and the Spey's is 1,097 sq mi (2,840 km2).

Loch Maree is a loch in Wester Ross in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland. At 21.7 km (13.46 mi) long and with a maximum width of four kilometres, it is the fourth-largest freshwater loch in Scotland; it is the largest north of Loch Ness. Its surface area is 28.7 km2 (11.08 sq mi).

Loch Morar is a freshwater loch in Lochaber, Highland, Scotland. It is the fifth-largest loch by surface area in Scotland, at 26.7 km2 (10.3 sq mi), and the deepest freshwater body in the British Isles with a maximum depth of 310 m (1,017 ft). The loch was created by glacial action around 10,000 years ago, and has a surface elevation of 9 metres (30 ft) above sea level. It separates the traditional district of North Morar, from Arisaig and Moidart.
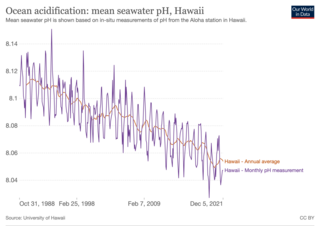
Ocean acidification is the decrease in the pH of the Earth's ocean. Between 1950 and 2020, the average pH of the ocean surface fell from approximately 8.15 to 8.05. Carbon dioxide emissions from human activities are the primary cause of ocean acidification, with atmospheric carbon dioxide levels exceeding 410 ppm. CO2 from the atmosphere is absorbed by the oceans. This produces carbonic acid which dissociates into a bicarbonate ion and a hydrogen ion. The presence of free hydrogen ions lowers the pH of the ocean, increasing acidity. Marine calcifying organisms, such as mollusks and corals, are especially vulnerable because they rely on calcium carbonate to build shells and skeletons.

Apalachicola Bay is an estuary and lagoon located on the northwest coast of the U.S. state of Florida. The Apalachicola Bay system also includes St. George Sound, St. Vincent Sound and East Bay, covering an area of about 208 square miles (540 km2). Four islands, St. Vincent Island to the west, Cape St. George Island and St. George Island to the south, and Dog Island to the east, separate the system from the Gulf of Mexico. Water exchange occurs through Indian Pass, West Pass, East Pass and the Duer Channel. The lagoon has been designated as a National Estuarine Research Reserve and the Apalachicola River is the largest source of freshwater to the estuary. Combined with the Chattahoochee River, Flint River, and Ochlockonee River they drain a watershed of over 20,000 square miles (50,000 km2) at a rate of 19,599 cubic feet per second according to the United States Geological Survey in 2002.

Coregonus vandesius, the vendace, is a freshwater whitefish found in the United Kingdom. Population surveys since the 1960s have revealed a steady decline and the fish is no longer present in some of its previous haunts but is still present in Bassenthwaite Lake and Derwent Water. The main threats it faces are eutrophication and the introduction of alien species of fish which eat its eggs and fry. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as "endangered".

Marine ecosystems are the largest of Earth's aquatic ecosystems and exist in waters that have a high salt content. These systems contrast with freshwater ecosystems, which have a lower salt content. Marine waters cover more than 70% of the surface of the Earth and account for more than 97% of Earth's water supply and 90% of habitable space on Earth. Seawater has an average salinity of 35 parts per thousand of water. Actual salinity varies among different marine ecosystems. Marine ecosystems can be divided into many zones depending upon water depth and shoreline features. The oceanic zone is the vast open part of the ocean where animals such as whales, sharks, and tuna live. The benthic zone consists of substrates below water where many invertebrates live. The intertidal zone is the area between high and low tides. Other near-shore (neritic) zones can include mudflats, seagrass meadows, mangroves, rocky intertidal systems, salt marshes, coral reefs, lagoons. In the deep water, hydrothermal vents may occur where chemosynthetic sulfur bacteria form the base of the food web.

Lough Melvin is a lake in the northwest of the island of Ireland on the border between County Leitrim and County Fermanagh. It is internationally renowned for its unique range of plants and animals.
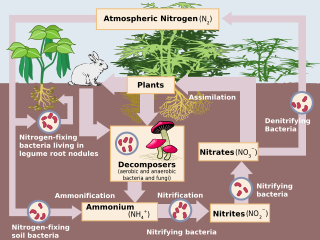
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle is diverse. Agricultural and industrial nitrogen (N) inputs to the environment currently exceed inputs from natural N fixation. As a consequence of anthropogenic inputs, the global nitrogen cycle (Fig. 1) has been significantly altered over the past century. Global atmospheric nitrous oxide (N2O) mole fractions have increased from a pre-industrial value of ~270 nmol/mol to ~319 nmol/mol in 2005. Human activities account for over one-third of N2O emissions, most of which are due to the agricultural sector. This article is intended to give a brief review of the history of anthropogenic N inputs, and reported impacts of nitrogen inputs on selected terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.

A wild fishery is a natural body of water with a sizeable free-ranging fish or other aquatic animal population that can be harvested for its commercial value. Wild fisheries can be marine (saltwater) or lacustrine/riverine (freshwater), and rely heavily on the carrying capacity of the local aquatic ecosystem.

Loch Enoch is a multi-basin freshwater loch in Galloway, to the east of Merrick and south of Mullwharchar. The loch is situated in a granite basin and has several small islands and some beaches on its shore. The sharp granite sand of these beaches was collected and sold for sharpening knives and scythes. The catchment area's vegetation is mainly Purple Moor Grass and Heather.

Loch Neldricken is a loch in Galloway to the south-east of Merrick, south of Craig Neldricken and west of Craignaw. The loch is almost bisected by a long promontory. It drains via the short Mid Burn into Loch Valley and then via Gairland Burn down to Loch Trool.

The Coral Triangle (CT) is a roughly triangular area in the tropical waters around the Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands and Timor-Leste. This area contains at least 500 species of reef-building corals in each ecoregion. The Coral Triangle is located between the Pacific and Indian oceans and encompasses portions of two biogeographic regions: the Indonesian-Philippines Region, and the Far Southwestern Pacific Region. As one of eight major coral reef zones in the world, the Coral Triangle is recognized as a global centre of marine biodiversity and a global priority for conservation. Its biological resources make it a global hotspot of marine biodiversity. Known as the "Amazon of the seas" (by analogy to the Amazon rainforest in South America), it covers 5.7 million square kilometres (2,200,000 sq mi) of ocean waters. It contains more than 76% of the world's shallow-water reef-building coral species, 37% of its reef fish species, 50% of its razor clam species, six out of seven of the world's sea turtle species, and the world's largest mangrove forest. In 2014, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) reported that the gross domestic product of the marine ecosystem in the Coral Triangle is roughly $1.2 trillion per year and provides food to over 120 million people. According to the Coral Triangle Knowledge Network, the region annually brings in about $3 billion in foreign exchange income from fisheries exports, and another $3 billion from coastal tourism revenues.

The Scottish Government's Marine Directorate is responsible for managing Scotland's seas and freshwater fisheries along with delivery partners NatureScot and the Scottish Environment Protection Agency.
Bearskin Lake is an oligotrophic glacial lake near the Boundary Waters Canoe Area (BWCA) in Minnesota, United States. The name Bearskin Lake is an English translation of the Ojibwe-language name Muko-waiani. Bearskin Lake is a source of control sediment for US federal sediment toxicity studies. Bearskin Lake is home to Camp Menogyn, a YMCA camp only accessible by boat.

The Round Loch of Glenhead is a small upland single basin loch in Dumfries and Galloway. It is situated within Galloway Forest Park to the west of the hill Craiglee. It forms a pair with the nearby Long Loch of Glenhead. Both lochs are of similar sizes and each have a small island. The two lochs are separated from Loch Valley and Loch Naroch to the north by the Rig of the Jarkness. The loch is drained to the southwest by Round Loch Burn, which after joining into Glenhead Burn flows into Loch Trool.

Glenade Lough, locally known as Glenade Lake, is a freshwater lake in the northwest of Ireland. It is located in north County Leitrim in the Glenade Valley.

Loch Druidibeag is a freshwater loch situated on the island of South Uist, in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. The loch is near the northern end of the island, to the north-east of Howmore and to the east of the A865 road and south of the B890.

Aquaculture in the United Kingdom is dominated by salmon farming, then by mussel production with trout being the third most important enterprise. Aquaculture in the United Kingdom represents a significant business for the UK, producing over 200,000 tonnes of fish whilst earning over £700 million in 2012 (€793 million).

Human activities affect marine life and marine habitats through overfishing, habitat loss, the introduction of invasive species, ocean pollution, ocean acidification and ocean warming. These impact marine ecosystems and food webs and may result in consequences as yet unrecognised for the biodiversity and continuation of marine life forms.




















