External links
| | This article about a history of philosophy journal is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. See tips for writing articles about academic journals. Further suggestions might be found on the article's talk page. |
| Discipline | Philosophy |
|---|---|
| Language | English, German |
| Standard abbreviations | |
| ISO 4 | Log. Anal. Hist. Philos. |
| Links | |
History of Philosophy & Logical Analysis is a peer-reviewed journal of philosophy. The journal publishes original work, focusing on interpreting classical philosophical texts by drawing on the resources of modern formal logic. Logical analysis is an instrument of interpretation to shift the interpretive focus from the purely exegetical approach towards a given text to the systematic reconstruction of a theory that concerns the issues that are discussed. In this way, novel questions can be presented. New insight with regard to classical texts ensue, so that these are even more fruitful in dealing with the modern philosophy. Articles are published in English and German; the journal is also known as Philosophiegeschichte und logische Analyse.
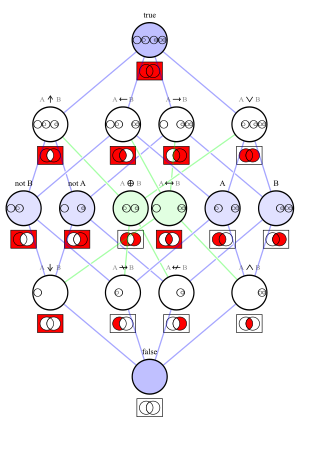
In logic, a logical connective is a logical constant. Connectives can be used to connect logical formulas. For instance in the syntax of propositional logic, the binary connective can be used to join the two atomic formulas and , rendering the complex formula .
Mathematical logic is the study of formal logic within mathematics. Major subareas include model theory, proof theory, set theory, and recursion theory. Research in mathematical logic commonly addresses the mathematical properties of formal systems of logic such as their expressive or deductive power. However, it can also include uses of logic to characterize correct mathematical reasoning or to establish foundations of mathematics.

A genre of arts criticism, literary criticism or literary studies is the study, evaluation, and interpretation of literature. Modern literary criticism is often influenced by literary theory, which is the philosophical analysis of literature's goals and methods. Although the two activities are closely related, literary critics are not always, and have not always been, theorists.
The history of logic deals with the study of the development of the science of valid inference (logic). Formal logics developed in ancient times in India, China, and Greece. Greek methods, particularly Aristotelian logic as found in the Organon, found wide application and acceptance in Western science and mathematics for millennia. The Stoics, especially Chrysippus, began the development of predicate logic.

Hermeneutics is the theory and methodology of interpretation, especially the interpretation of biblical texts, wisdom literature, and philosophical texts. As necessary, hermeneutics may include the art of understanding and communication.
Analytic philosophy is a broad movement or tradition within philosophy focused on analysis, which has been dominant within Western philosophy and especially anglophone philosophy since the latter half of the 20th century. The proliferation of analysis in philosophy began around the turn of the 20th century in the contemporary era in Germany, Austria, the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and Scandinavia.
The Mūlamadhyamakakārikā, abbreviated as MMK, is the foundational text of the Madhyamaka school of Mahāyāna Buddhist philosophy. It was composed by the Indian philosopher Nāgārjuna.
In quantum mechanics, the consistent histories or simply "consistent quantum theory" interpretation generalizes the complementarity aspect of the conventional Copenhagen interpretation. The approach is sometimes called decoherent histories and in other work decoherent histories are more specialized.
Early modern philosophy The early modern era of philosophy was a progressive movement of Western thought, exploring through theories and discourse such topics as mind and matter, is a period in the history of philosophy that overlaps with the beginning of the period known as modern philosophy. It succeeded in the medieval era of philosophy. Early modern philosophy is usually thought to have occurred between the 16th and 18th centuries, though some philosophers and historians may put this period slightly earlier. During this time, influential philosophers included Descartes, Locke, Hume, and Kant, all of whom contributed to the current understanding of philosophy.
The development of Indian logic dates back to the anviksiki of Medhatithi Gautama ; the Sanskrit grammar rules of Pāṇini ; the Vaisheshika school's analysis of atomism ; the analysis of inference by Gotama, founder of the Nyaya school of Hindu philosophy; and the tetralemma of Nagarjuna.

Positivism is a philosophical school that holds that all genuine knowledge is either true by definition or positive—meaning a posteriori facts derived by reason and logic from sensory experience. Other ways of knowing, such as intuition, introspection, or religious faith, are rejected or considered meaningless.
Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems concerning matters such as existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. It is distinguished from other ways of addressing fundamental questions by being critical and generally systematic and by its reliance on rational argument. It involves logical analysis of language and clarification of the meaning of words and concepts.
The Navya-Nyāya or Neo-Logicaldarśana of Indian logic and Indian philosophy was founded in the 13th century CE by the philosopher Gangeśa Upādhyāya of Mithila and continued by Raghunatha Siromani of Nabadwipa in Bengal. It was a development of the classical Nyāya darśana. Other influences on Navya-Nyāya were the work of earlier philosophers Vācaspati Miśra and Udayana. It remained active in India through to the 18th century.
Logic is the formal science of using reason and is considered a branch of both philosophy and mathematics and to a lesser extent computer science. Logic investigates and classifies the structure of statements and arguments, both through the study of formal systems of inference and the study of arguments in natural language. The scope of logic can therefore be very large, ranging from core topics such as the study of fallacies and paradoxes, to specialized analyses of reasoning such as probability, correct reasoning, and arguments involving causality. One of the aims of logic is to identify the correct and incorrect inferences. Logicians study the criteria for the evaluation of arguments.
Jorge J. E. Gracia was a Cuban-born American philosopher who was the Samuel P. Capen Chair, SUNY Distinguished Professor in the Department of Philosophy and Department of Comparative Literature in the State University of New York at Buffalo. Gracia was educated in Cuba, the United States, Canada, and Spain, and received his Ph.D. in Medieval Philosophy from the University of Toronto.

Buddhist logico-epistemology is a term used in Western scholarship to describe Buddhist systems of pramāṇa and hetu-vidya. While the term may refer to various Buddhist systems and views on reasoning and epistemology, it is most often used to refer to the work of the "Epistemological school", i.e. the school of Dignaga and Dharmakirti which developed from the 5th through 7th centuries and remained the main system of Buddhist reasoning until the decline of Buddhism in India.

Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the science of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It studies how conclusions follow from premises due to the structure of arguments alone, independent of their topic and content. Informal logic is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. It examines arguments expressed in natural language while formal logic uses formal language. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Logic plays a central role in many fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics.

Bruno Baron von Freytag-Löringhoff was a German philosopher, mathematician and epistemologist. He was also a university lecturer at the University of Tübingen. During World War II, Freytag-Löringhoff worked as a mathematician in the In 7/VI, that was the signals intelligence agency of the Wehrmacht and worked with Fritz Menzer on the testing of cryptographic devices and procedures. Freytag-Löringhoff worked specifically on the testing of the m-40 cipher machine. His most important contributions to the history of logic and mathematics was his studies and descriptions from 1957, of the calculating machine, built by Wilhelm Schickard.