| | |
| Industry | Electricity |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1948 |
| Defunct | 1998 |
| Fate | Acquired |
| Successor | EDF Energy |
| Headquarters | London, UK |
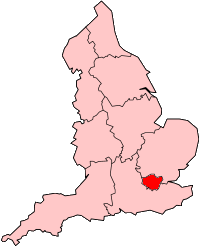
The London Electricity Board was the public sector utility company responsible for the supply and distribution of electricity to domestic, commercial and industrial consumers in London prior to 1990. It also sold and made available for hire and hire-purchase domestic electrical appliances through local showrooms where electricity bills could also be paid. It was shortened to LEB in its green and blue logo, consisting of the three letters. As London Electricity plc it was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.