Related Research Articles
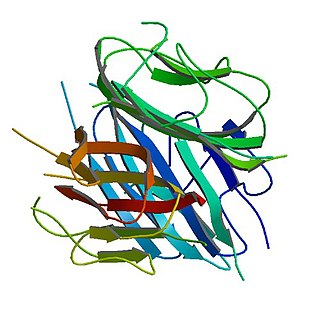
Adiponectin is a protein hormone and adipokine, which is involved in regulating glucose levels and fatty acid breakdown. In humans, it is encoded by the ADIPOQ gene and is produced primarily in adipose tissue, but also in muscle and even in the brain.

Plasmin is an important enzyme present in blood that degrades many blood plasma proteins, including fibrin clots. The degradation of fibrin is termed fibrinolysis. In humans, the plasmin protein is encoded by the PLG gene.
High-molecular-weight kininogen is a circulating plasma protein which participates in the initiation of blood coagulation, and in the generation of the vasodilator bradykinin via the kallikrein-kinin system. HMWK is inactive until it either adheres to binding proteins beneath an endothelium disrupted by injury, thereby initiating coagulation; or it binds to intact endothelial cells or platelets for functions other than coagulation.
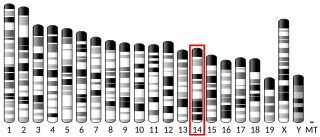
L-Gulonolactone oxidase is an enzyme that produces vitamin C, but is non-functional in Haplorrhini, in some bats, and in guinea pigs. It catalyzes the reaction of L-gulono-1,4-lactone with oxygen to form L-xylo-hex-3-gulonolactone (2-keto-gulono-γ-lactone) and hydrogen peroxide. It uses FAD as a cofactor. The L-xylo-hex-3-gulonolactone then converts to ascorbic acid spontaneously, without enzymatic action.

Plasma kallikrein is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Kininogens are precursor proteins for kinins, biologically active polypeptides involved in blood coagulation, vasodilation, smooth muscle contraction, inflammatory regulation, and the regulation of the cardiovascular and renal systems.

Batroxobin, also known as reptilase, is a snake venom enzyme with Venombin A activity produced by Bothrops atrox and Bothrops moojeni, venomous species of pit viper found east of the Andes in South America. It is a hemotoxin which acts as a serine protease similarly to thrombin, and has been the subject of many medical studies as a replacement of thrombin. Different enzymes, isolated from different species of Bothrops, have been called batroxobin, but unless stated otherwise, this article covers the batroxobin produced by B. moojeni, as this is the most studied variety.

8-Oxoguanine glycosylase, also known as OGG1, is a DNA glycosylase enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the OGG1 gene. It is involved in base excision repair. It is found in bacterial, archaeal and eukaryotic species.
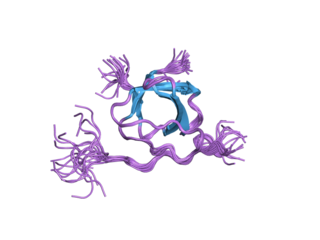
Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LYN gene.

Kallikrein-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLK1 gene. KLK1 is a member of the peptidase S1 family.

Kininogen-1 (KNG1), also known as alpha-2-thiol proteinase inhibitor, Williams-Fitzgerald-Flaujeac factor or the HMWK-kallikrein factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KNG1 gene. Kininogen-1 is the precursor protein to high-molecular-weight kininogen (HMWK), low-molecular-weight kininogen (LMWK), and bradykinin.

5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) 1E receptor (5-HT1E) is a highly expressed human G-protein coupled receptor that belongs to the 5-HT1 receptor family. The human gene is denoted as HTR1E.

5-Hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 5A, also known as HTR5A, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR5A gene. Agonists and antagonists for 5-HT receptors, as well as serotonin uptake inhibitors, present promnesic (memory-promoting) and/or anti-amnesic effects under different conditions, and 5-HT receptors are also associated with neural changes.

Calpain-1 catalytic subunit(CANP 1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPN1 gene.

40S ribosomal protein S19 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPS19 gene.
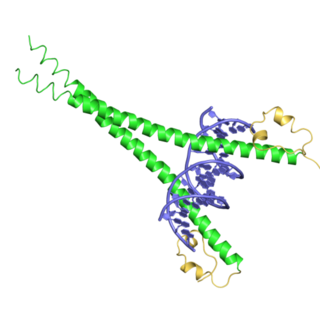
Transcription factor MafG is a bZip Maf transcription factor protein that in humans is encoded by the MAFG gene.

Transcription factor MafK is a bZip Maf transcription factor protein that in humans is encoded by the MAFK gene.

Transcription factor MafF is a bZip Maf transcription factor protein that in humans is encoded by the MAFF gene.

Alazocine, also known more commonly as N-allylnormetazocine (NANM), is a synthetic opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan family related to metazocine, which was never marketed. In addition to its opioid activity, the drug is a sigma receptor agonist, and has been used widely in scientific research in studies of this receptor. Alazocine is described as a potent analgesic, psychotomimetic or hallucinogen, and opioid antagonist. Moreover, one of its enantiomers was the first compound that was found to selectively label the σ1 receptor, and led to the discovery and characterization of the receptor.

Organisms can live at high altitude, either on land, in water, or while flying. Decreased oxygen availability and decreased temperature make life at such altitudes challenging, though many species have been successfully adapted via considerable physiological changes. As opposed to short-term acclimatisation, high-altitude adaptation means irreversible, evolved physiological responses to high-altitude environments, associated with heritable behavioural and genetic changes. Among vertebrates, only few mammals and certain birds are known to have completely adapted to high-altitude environments.
References
- ↑ Shesely E, Hu C, Alhenc-Gelas F, Meneton P, Carretero O (2006). "A second expressed kininogen gene in mice". Physiol Genomics. 26 (2): 152–7. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00244.2005. PMID 16837654.
- ↑ Semba U, Umeda Y, Shibuya Y, Okabe H, Tanase S, Yamamoto T (2004). "Primary structures of guinea pig high- and low-molecular-weight kininogens". Int Immunopharmacol. 4 (10–11): 1391–400. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2004.06.003. PMID 15313436.
- ↑ Semba U, Shibuya Y, Okabe H, Hayashi I, Yamamoto T (2000). "Whale high-molecular-weight and low-molecular-weight kininogens". Thromb Res. 97 (6): 481–90. doi:10.1016/S0049-3848(99)00199-1. PMID 10704658.
- ↑ Stefan Offermanns; Walter Rosenthal (2008). Encyclopedia of Molecular Pharmacology. Springer. pp. 673–. ISBN 978-3-540-38916-3 . Retrieved 11 December 2010.