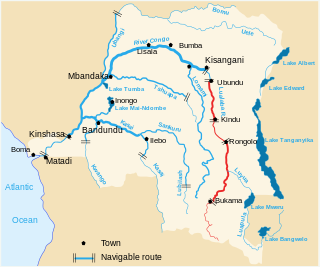
The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third-largest river in the world by discharge volume, following the Amazon and Ganges rivers. It is the world's deepest recorded river, with measured depths of around 220 m (720 ft). The Congo-Lualaba-Chambeshi River system has an overall length of 4,700 km (2,900 mi), which makes it the world's ninth-longest river. The Chambeshi is a tributary of the Lualaba River, and Lualaba is the name of the Congo River upstream of Boyoma Falls, extending for 1,800 km (1,100 mi).

The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued by King George III on 7 October 1763. It followed the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally ended the Seven Years' War and transferred French territory in North America to Great Britain. The Proclamation forbade all settlements west of a line drawn along the Appalachian Mountains, which was delineated as an Indian Reserve. Exclusion from the vast region of Trans-Appalachia created discontent between Britain and colonial land speculators and potential settlers. The proclamation and access to western lands was one of the first significant areas of dispute between Britain and the colonies and would become a contributing factor leading to the American Revolution. The 1763 proclamation line is more or less similar to the Eastern Continental Divide, extending from Georgia in the south to the divide's northern terminus near the middle of the northern border of Pennsylvania, where it intersects the northeasterly St. Lawrence Divide, and extends further through New England.
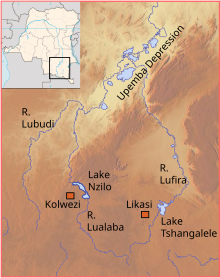
The Lualaba River flows entirely within the eastern part of Democratic Republic of the Congo. It provides the greatest streamflow to the Congo River, while the source of the Congo is recognized as the Chambeshi. The Lualaba is 1,800 kilometres (1,100 mi) long. Its headwaters are in the country's far southeastern corner near Musofi and Lubumbashi in Katanga Province, next to the Zambian Copperbelt.
The pre-colonial history of the modern-day Democratic Republic of the Congo encompasses the history of the Congo Basin region up to the establishment of European colonial rule in the era of New Imperialism and particularly the creation of the Congo Free State and its expansion into the interior after 1885. As the modern territorial boundaries of the Democratic Republic of the Congo did not exist in this period, it is inseparable from the wider pre-colonial histories of Central Africa, the Great Lakes and Rift Valley as well as the Atlantic World and Swahili coast.

Kolwezi or Kolwesi is the capital city of Lualaba Province in the south of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, west of Likasi. It has an airport and a railway to Lubumbashi. Just outside of Kolwezi there is the static inverter plant of the HVDC Inga-Shaba. The population is approximately 573,000.

The Lukuga River is a tributary of the Lualaba River in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) that drains Lake Tanganyika. It is unusual in that its flow varies not just seasonally but also due to longer term climate fluctuations.

The Luba people or Baluba are an Bantu ethno-linguistic group indigenous to the south-central region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The majority of them live in this country, residing mainly in Katanga, Kasaï, Kasaï-Oriental, Kasaï-Central, Lomami and Maniema. The Baluba consist of many sub-groups or clans.
The Dosso Kingdom is a precolonial state in what is now southwest Niger which has survived in a ceremonial role to the modern day.

The Kingdom of Luba or Luba Empire (1585–1889) was a pre-colonial Central African state that arose in the marshy grasslands of the Upemba Depression in what is now southern Democratic Republic of Congo.

The Musonoi mine is a set of open-cut pits near Kolwezi from which copper and other metals have been extracted since the 1940s. The mining complex is located in the Lualaba Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Kolwezi is about 320 kilometres (200 mi) northwest from Lubumbashi, the provincial capital.

Lualaba District was a district of the pre-2015 Katanga Province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The district dates back to the days of the Congo Free State and the Belgian Congo. The original Lualaba District was merged into Katanga in 1910, but in 1933 a new Lualaba District was formed within Katanga. After various significant boundary changes, in 2015 the district became the western part of the present Lualaba Province.

The Holoholo also known as Kalanga are a Bantu ethnic group that inhabit the shores of central lake Tanganyika. The majority of them live near Kalemie city on Lake Tanganyika in Tanganyika Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and on the opposite shore of the lake in Uvinza District of Kigoma Region in Tanzania.
Katende, or Sungu-Katende, was a royal sacred village of the Kingdom of Luba. It was adjacent to the village of Kabondo. Katende is on the upper Lomami in the Lualaba region in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Ilunga Sungu was a ruler (Mulopwe) of the Kingdom of Luba in what is now the Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, said to have reigned from about 1780 to his death.
The Hemba people are a Bantu ethnic group in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).

The Lukushi River is a tributary of the Luvua River. It runs from south to north through the Malemba-Nkulu Territory of Haut-Lomami Province and the Manono Territory of Tanganyika Province, passing the twin tin-mining towns of Kitotolo and Manono shortly before entering the Luvua.

Haut-Lomami District was a district of the pre-2015 Katanga Province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The district dates back to the days of the Belgian Congo. At its greatest extent it roughly corresponded to the northern part of the current Lualaba Province and to the present Haut-Lomami Province.

The Sultanate of Utetera (1860–1887), also referred as Tippu Tip's state, was one of the Arab sultanates established in eastern Africa. It was a 19th century short-lived state ruled by the infamous Swahili slave trader Tippu Tip and his son Sefu. The capital of the state was the town of Kasongo, located in modern Maniema Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Tippu Tip's controlled territory reached as far to eastern Kasai and to Aruwimi Basin in the west.

Tanganyika Concessions Limited was a British mining and railway company founded by the Scottish engineer and entrepreneur Robert Williams in 1899. The purpose was to exploit minerals in Northern Rhodesia and in the Congo Free State. Partly-owned subsidiaries included the Union Minière du Haut-Katanga (UMHK), which undertook mining in the Katanga portion of the copperbelt, and the Benguela railway, which provided a rail link across Angola to the Atlantic Ocean. Belgian banks eventually took over control of the company. The Angolan railway concession was returned to the state of Angola in 2001.

Kamatanda is a region just north of Likasi in the Haut-Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It gives its name to an open-pit copper mine, a railway junction, an abandoned airport and a residential area of Likasi.