
The Sierra Madre Occidental pine–oak forests are a Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion of the Sierra Madre Occidental range from the southwest USA region to the western part of Mexico. They are home to a large number of endemic plants and important habitat for wildlife.

The Sierra Madre sparrow, also known as Bailey's sparrow, is an endangered, range-restricted, enigmatic American sparrow. It is endemic to Mexico and is threatened with extinction through habitat loss.

Abies guatemalensis, the Guatemalan fir or pinabete, is an evergreen tree native to Central America and is the southernmost member of the genus Abies being spread to the south lower than 14° N. Its range is from southern Mexico in the north to Honduras and El Salvador in the south. It is a warm-loving and moisture-loving tree of the tropical mountain coniferous and mixed cloud forests of these countries. The Guatemalan fir is an almost completely non-frost-resistant tree. Due to logging and loss of habitat, the tree is considered threatened and is protected in CITES Appendix I.
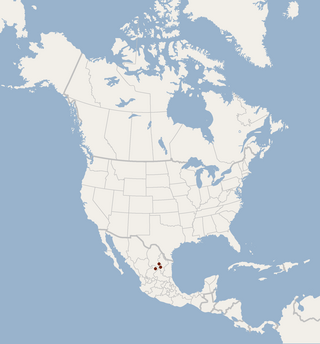
The flat-headed myotis is a species of vesper bat. It is endemic to Mexico where it is found in certain montane forests in the Sierra Madre Oriental in the northeast of the country. Once thought to be extinct, this bat was rediscovered in 2004 by Joaquín Arroyo-Cabrales and colleagues. The species is now classified as endangered by the IUCN.
Magnolia iltisiana is a species of plant in the family Magnoliaceae. It is endemic to Mexico. Common names include ahuatoso and yoloxochitl.
Magnolia schiedeana is a species of flowering plant in the family Magnoliaceae. It is endemic to Mexico, where it occurs along the slopes of the Gulf of Mexico.

Quercus conzattii is an oak endemic to Mexico. It is placed in Quercus section Lobatae.

The Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt pine–oak forests is a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt of central Mexico.

Quercus iltisii is a species of oak tree native to western Mexico, where it is found in a small portion of Jalisco and Colima states.
Quercus hirtifolia is a rare Mexican species of oak. It has been found only in a small region of the southern Sierra Madre Oriental in northern Puebla and eastern Hidalgo states in east-central Mexico.

Magnolia pacifica is a species of Magnolia from Jalisco and Nayarit states in western Mexico.

Magnolia sharpii is a tree species of Magnolia from Chiapas, Mexico. It grows in wet tropical habitats.

The Sierra de San Juan Biosphere Reserve is a protected area in Nayarit state of western Mexico. It was established in 2003, and has an area of 198.01 km2. It lies just southwest of the city of Tepic. It protects a portion of the Sierra de San Juan, a mountain range which lies between Tepic and the Pacific Ocean.

Magnolia vallartensis is a species of Magnolia from Jalisco state in western Mexico.
Magnolia krusei is a species of plant in the family Magnoliaceae. It is endemic to Mexico.
Magnolia nuevoleonensis is a species of flowering plant in the family Magnoliaceae. It is native to the Sierra Madre Oriental of Nuevo León state in northeastern Mexico.
Magnolia rzedowskiana is a species of flowering plant in the family Magnoliaceae. It is native to the Sierra Madre Oriental of San Luis Potosí, Querétaro, and Hidalgo states in eastern Mexico.
Magnolia pedrazae is a species of flowering plant in the family Magnoliaceae. It is endemic to the Sierra Madre Oriental of eastern Mexico.
Magnolia vazquezii is a species of flowering plant in the family Magnoliaceae. It is endemic to the Sierra Madre del Sur of Guerrero state in southern Mexico.
Magnolia oaxacensis is a species of flowering plant in the family Magnoliaceae. It is endemic to the Sierra Madre de Oaxaca of Oaxaca state in southern Mexico.











