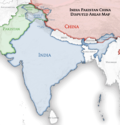
India's international borders in Kashmir (left) and Northeast India (right), outside of mainland India, are disputed by Pakistan and China (centre).
Mainland India is a geo-political term sometimes used to refer to India excluding the region of Northeast India and Kashmir, [a] [3] [4] [5] with the north-east connected by the Siliguri Corridor. [6] [7] [8] [9] [10]
Contents
In a geographical context, Mainland India includes the entirety of India (including Northeast India) in continental Asia, excluding islands such as the union territories of Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep.