Lieutenant Commander is a commissioned officer rank in many navies. The rank is superior to a lieutenant and subordinate to a commander. The corresponding rank in most armies and air forces is major, and in the Royal Air Force and other Commonwealth air forces is squadron leader. It is roughly equivalent to the Corvette Captain rank in central European countries and the Captain 3rd rank rank in eastern European/CIS countries.
Brigadier general or brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed to a field command, a brigadier general is typically in command of a brigade consisting of around 4,000 troops or.

An aide-de-camp is a personal assistant or secretary to a person of high rank, usually a senior military, police or government officer, or to a member of a royal family or a head of state.
The United States Air Force officer rank insignia in use today.
Pilot officer is a junior officer rank used by some air forces, with origins from the Royal Air Force. The rank is used by air forces of many countries that have historical British influence.
Officer Cadet is a rank held by military cadets during their training to become commissioned officers. In the United Kingdom, the rank is also used by members of University Royal Naval Units, University Officer Training Corps and University Air Squadron; however, these are not trainee officers with many not choosing a career in the armed forces.

A gorget, from the French gorge meaning throat, was a band of linen wrapped around a woman's neck and head in the medieval period or the lower part of a simple chaperon hood. The term later described a steel or leather collar to protect the throat, a set of pieces of plate armour, or a single piece of plate armour hanging from the neck and covering the throat and chest. Later, particularly from the 18th century, the gorget became primarily ornamental, serving as a symbolic accessory on military uniforms, a use which has survived in some armies.

Mess dress uniform is the most formal type of evening-wear uniform used by military personnel, police personnel, and other uniformed services members. It frequently consists of a mess jacket, trousers, white dress shirt and a black bow tie, along with orders and medals insignia. Design may depend on regiment or service branch, e.g. army, navy, air force, marines, etc. In modern Western dress codes, mess dress uniform is the supplementary alternative equivalent to the civilian black tie for evening wear. Mess dress uniforms are typically less formal than full dress uniform, but more formal than service dress uniform.

These are the official Royal Navy Officer ranks ordered by rank. These ranks are now part of the NATO/United Kingdom ranks, including modern and past.

Gorget patches are an insignia in the form of paired patches of cloth or metal on the collar of a uniform (gorget), used in the military and civil service in some countries. Collar tabs sign the military rank, the rank of civil service, the military unit, the office (department) or the branch of the armed forces and the arm of service.
The following tables present the ranks and insignia of the Sri Lanka Navy. These ranks are similar to Royal Naval officer ranks and the ratings ranks. Sri Lanka does have an Admiral rank, but it is usually only awarded to the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) or as an honorary rank; Admiral Wasantha Karannagoda was the only Sri Lankan naval officer to hold a full admiral rank while in active service.

General is the highest attainable and full general rank of the Sri Lankan Army and was created as a direct equivalent of the British military rank of general; it is also considered a four-star rank.
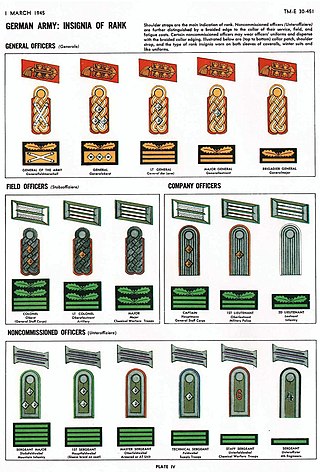
The Heer as the German army and part of the Wehrmacht inherited its uniforms and rank structure from the Reichsheer of the Weimar Republic (1921–1935). There were few alterations and adjustments made as the army grew from a limited peacetime defense force of 100,000 men to a war-fighting force of several million men.
The rank insignia of the federal armed forces of the Federal Republic of Germany indicate rank and branch of service in the German Army, German Air Force, or the German Navy.

Lieutenant general is the second-highest rank of the Sri Lanka Army and generally it is the highest active rank as the Sri Lanka army do not have any appointment in the rank of full general but in the case of the appointment of Chief of Defence Staff, the rank of full general is given. It was created as a direct equivalent of the British military rank of lieutenant general, and is considered a three-star rank.
This article deals with the rank insignia of the Austro-Hungarian Army, as worn by the Austro-Hungarian Army after the reorganisation in 1867 until 1918.

Field marshal (FM) is the five-star rank of the Sri Lanka Army and ranks immediately above general. the rank has been awarded only once, to Sarath Fonseka as an honorary rank. It is equivalent to admiral of the fleet and marshal of the Sri Lanka Air Force.

The ranks and rank insignia of the Red Army and Red Navy between 1940 and 1943 were characterised by continuing reforms to the Soviet armed forces in the period immediately before Operation Barbarossa and the war of national survival following it. The Soviet suspicion of rank and rank badges as a bourgeois institution remained, but the increasing experience of Soviet forces, and the massive increase in manpower all played their part, including the creation of a number of new general officer ranks and the reintroduction of permanent enlisted ranks and ratings.

The uniforms of the Sri Lanka Army currently exist in several categories ranging from ceremonial uniforms to combat dress.
Star Insignia of Army officer vehicles differ from each other starting from one star up until five stars. The first four stars should be granted to an officer in active duty while the fifth Star insignia can be wore by a retired officer. The only retired officer who is permitted to wear the five star insignia in Sri Lanka is Field Marshal Sarath Fonseka.










