Related Research Articles

Bugzilla is a web-based general-purpose bug tracking system and testing tool originally developed and used by the Mozilla project, and licensed under the Mozilla Public License.
Berkeley DB (BDB) is an embedded database software library for key/value data, historically significant in open-source software. Berkeley DB is written in C with API bindings for many other programming languages. BDB stores arbitrary key/data pairs as byte arrays and supports multiple data items for a single key. Berkeley DB is not a relational database, although it has database features including database transactions, multiversion concurrency control and write-ahead logging. BDB runs on a wide variety of operating systems, including most Unix-like and Windows systems, and real-time operating systems.

Debian, also known as Debian GNU/Linux, is a free and open source Linux distribution, developed by the Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock in August 1993. Debian is the basis for many other distributions, such as Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Tails, Proxmox, Kali Linux, Pardus, TrueNAS SCALE, and Astra Linux.

Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, and distribute it and any adapted versions. Free software is a matter of liberty, not price; all users are legally free to do what they want with their copies of a free software regardless of how much is paid to obtain the program. Computer programs are deemed "free" if they give end-users ultimate control over the software and, subsequently, over their devices.
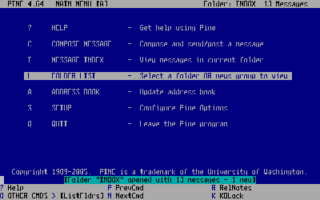
Pine is a freeware, text-based email client which was developed at the University of Washington. The first version was written in 1989, and announced to the public in March 1992. Source code was available for only the Unix version under a license written by the University of Washington. Pine is no longer under development, and has been replaced by the Alpine client, which is available under the Apache License.

GNU Mailman is a computer software application from the GNU Project for managing electronic mailing lists. Mailman is coded primarily in Python and currently maintained by Abhilash Raj. Mailman is free software, licensed under the GNU General Public License.
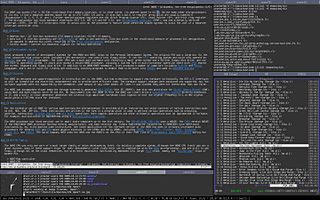
In Unix computing, Ion is a tiling and tabbing window manager for the X Window System. It is designed such that it is possible to manage windows using only a keyboard, without needing a mouse. It is the successor of PWM and is written by the same author, Tuomo Valkonen. Since the first release of Ion in the summer 2000, similar alternative window management ideas have begun to show in other new window managers: Larswm, ratpoison, StumpWM, wmii, xmonad and dwm.
The term Listserv has been used to refer to electronic mailing list software applications in general, but is more properly applied to a few early instances of such software, which allows a sender to send one email to a list, which then transparently sends it on to the addresses of the subscribers to the list.

ClamAV (antivirus) is a free software, cross-platform antimalware toolkit able to detect many types of malware, including viruses. It was developed for Unix and has third party versions available for AIX, BSD, HP-UX, Linux, macOS, OpenVMS, OSF (Tru64), Solaris and Haiku. As of version 0.97.5, ClamAV builds and runs on Microsoft Windows. Both ClamAV and its updates are made available free of charge. One of its main uses is on mail servers as a server-side email virus scanner.

Webmin is a web-based server management control panel for Unix-like systems. Webmin allows the user to configure operating system internals, such as users, disk quotas, services and configuration files, as well as modify and control open-source apps, such as BIND, Apache HTTP Server, PHP, and MySQL.

Zimbra Collaboration, formerly known as the Zimbra Collaboration Suite (ZCS) before 2019, is a collaborative software suite that includes an email server and a web client.

Linux is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries—many of which are provided by the GNU Project—to create a complete operating system, designed as a clone of Unix and released under the copyleft GPL license.
GNATS is the GNU project's issue-tracking software.

FreeBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) which currently runs on IA-32, x86-64, ARM, PowerPC and RISC-V based computers. The first version was released in 1993 developed from 386BSD — the first free Unix system — and has since continously been the most commonly used BSD-derived operating system.

Claws Mail is a free and open-source, C/GTK-based e-mail client, which is both lightweight and highly configurable. Claws Mail runs on both Windows and Unix-like systems such as Linux, BSD, and Solaris. It stores mail in the MH mailbox format. Plugins allow to read HTML mail, but there is none to compose HTML messages.

Dada Mail is a web-based electronic mailing list management system that can be used for announcement lists. It can also be used to create and manage discussion lists by the use of an included plug-in called Dada Bridge, which requires a cron task.

NetBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). It was the first open-source BSD descendant officially released after 386BSD was forked. It continues to be actively developed and is available for many platforms, including servers, desktops, handheld devices, and embedded systems.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Perl programming language:

Octopussy, also known as 8Pussy, is a free and open-source computer-software which monitors systems, by constantly analyzing the syslog data they generate and transmit to such a central Octopussy server. Therefore, software like Octopussy plays an important role in maintaining an information security management system within ISO/IEC 27001-compliant environments.
References
- 1 2 "Mailing Lists -- Majordomo History". Living Internet. Retrieved 20 February 2013.
The first version took him [Brent Chapman] about 20 hours, consisted of about 600 lines of code in the Perl language, and was deployed in June, 1992.
- ↑ Majordomo License Agreement
- ↑ Wilson, Chan. "Majordomo 1.94.5 released -- security and bugfix release". Majordomo-Announce. Great Circle. Retrieved 19 February 2013.
- ↑ "What is Majordomo?". Majordomo Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ). Great Circle. Retrieved 19 February 2013.
Majordomo is written in Perl. It will work with Perl 4.036 or Perl 5.002 or greater
- ↑ "Majordomo". Linux Links - The Linux Portal Site. Retrieved 20 February 2013.
It is written in Perl and has a long history, coming into popular use since 1992
- ↑ Houle, Bill. "MajorCool: A Web Interface To Majordomo". SILICONexus. Retrieved 19 February 2013.
- ↑ "Index of /Pub/Mj2/Snapshots".
- ↑ "Majordomo 2". Steven Pritchard. Retrieved 19 February 2013.
- ↑ OpenBSD Mailing List Server
- ↑ "Majordomo License Agreement". Great Circle Associates. p. 2.b. Retrieved 19 February 2013.
No part of Majordomo may be incorporated into any program or other product that is sold, or for which any revenue is received without written permission of Great Circle Associates, with the following exceptions