
Mindanao is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of the same name that also includes its adjacent islands, notably the Sulu Archipelago. According to the 2020 census, Mindanao has a population of 26,252,442 people, while the entire island group has an estimated population of 27,021,036 according to the 2021 census.

Misamis Oriental, officially the Province of Misamis Oriental, is a province located in the region of Northern Mindanao in the Philippines. Its capital, largest city and provincial center is the city of Cagayan de Oro, which is governed independently from the province.

Bukidnon, officially the Province of Bukidnon, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Northern Mindanao region. Its capital is the city of Malaybalay. The province borders, clockwise from the north, Misamis Oriental, Agusan del Sur, Davao del Norte, Cotabato, Lanao del Sur, and Lanao del Norte. According to the 2020 census, the province is inhabited by 1,541,308 residents. The province is composed of 2 component cities and 20 municipalities. It is the third largest province in the country in terms of total area of jurisdiction behind Palawan and Isabela respectively.

Davao del Sur, officially the Province of Davao del Sur, is a province in the Philippines located in the Davao Region in Mindanao. Its capital is Digos. Davao City is the largest city in terms of area and population within the province's jurisdiction, yet it is administratively independent from the province; as such, Davao City is only grouped for geographical and statistical purposes.

Agusan del Sur, officially the Province of Agusan del Sur, is a province in Caraga region, Mindanao, Philippines. Its capital is the municipality of Prosperidad. It is bordered on the northwest by Agusan del Norte and Misamis Oriental; east by Surigao del Sur; southeast by Davao Oriental; mid-south by Davao de Oro; southwest by Davao del Norte and, mid-west by Bukidnon. It is the fourth largest province in the country in terms of area, with the size of 3,856 sq miles.

Cotabato or North Cotabato, officially the Province of Cotabato, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Soccsksargen region in Mindanao. Its capital is the city of Kidapawan. Some of its barangays are under the jurisdiction of the nearby Bangsamoro Autonomous Region.

Malaybalay, officially the City of Malaybalay, is a 1st class component city and capital of the province of Bukidnon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 190,712 people.

Kibawe, officially the Municipality of Kibawe, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Bukidnon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 41,897 people.

Manolo Fortich, officially the Municipality of Manolo Fortich, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Bukidnon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 113,200 people.

Claveria, officially the Municipality of Claveria, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Misamis Oriental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 52,478 people.

Tagoloan, officially the Municipality of Tagoloan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Misamis Oriental, Philippines. It is located to the east of Cagayan de Oro and located south-east of Macajalar Bay. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 80,319 people.
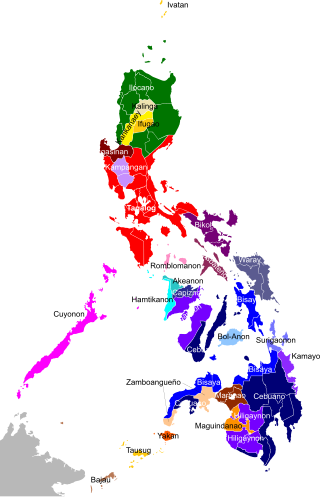
The Philippines is inhabited by more than 182 ethnolinguistic groups, many of which are classified as "Indigenous Peoples" under the country's Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act of 1997. Traditionally-Muslim peoples from the southernmost island group of Mindanao are usually categorized together as Moro peoples, whether they are classified as Indigenous peoples or not. About 142 are classified as non-Muslim Indigenous people groups, and about 19 ethnolinguistic groups are classified as neither Indigenous nor Moro. Various migrant groups have also had a significant presence throughout the country's history.

The Lumad are a group of Austronesian indigenous peoples in the southern Philippines. It is a Cebuano term meaning "native" or "indigenous". The term is short for Katawhang Lumad, the autonym officially adopted by the delegates of the Lumad Mindanao Peoples Federation (LMPF) founding assembly on 26 June 1986 at the Guadalupe Formation Center, Balindog, Kidapawan, Cotabato, Philippines. Usage of the term was accepted in Philippine jurisprudence when President Corazon Aquino signed into law Republic Act 6734, where the word was used in Art. XIII sec. 8(2) to distinguish Lumad ethnic communities from the islands of Mindanao.

The Christian And Missionary Alliance Churches of the Philippines (CAMACOP) is a Christian evangelical group in the Philippines that originated from The Christian and Missionary Alliance (C&MA). It is one of the largest evangelical groups in the Philippines.

The Pulangi River ;, also spelled Pulangui, is one of the major tributaries of the Rio Grande de Mindanao, an extensive river system in Mindanao, Philippines. With a length of 320 kilometres (199 mi), it is the longest river in Bukidnon and the 5th longest river in the Philippines. It traverses through majority of the cities and municipalities of Bukidnon from its source in Barangay Kalabugao, Impasugong, Bukidnon.

The Manobo languages are a group of languages spoken in the Philippines. Their speakers are primarily located around Northern Mindanao, Central Mindanao and Caraga regions where they are natively spoken. Some outlying groups make Manobo geographically discontiguous as other speakers can be located as far as the southern peninsula of Davao Oriental, most of Davao Occidental and coastal areas of Sultan Kudarat. The Kagayanen speakers are the most extremely remote and can be found in certain portions of Palawan.
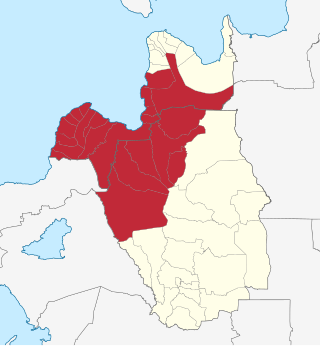
Metropolitan Cagayan de Oro, also known as Metro Cagayan de Oro, is the fourth largest metropolitan area in the Philippines. It is located on the northern coast of Mindanao, and comprises the two chartered cities of Cagayan de Oro and El Salvador and the fourteen municipalities of Misamis Oriental which are Alubijid, Balingasag, Claveria, Gitagum, Initao, Jasaan, Laguindingan, Libertad, Lugait, Manticao, Naawan, Opol, Tagoloan, and Villanueva and the six municipalities of Bukidnon which are Manolo Fortich, Baungon, Libona, Malitbog, Sumilao and Talakag. According to the 2015 Philippine census, Metro Cagayan de Oro has a population of 1,687,159 people.
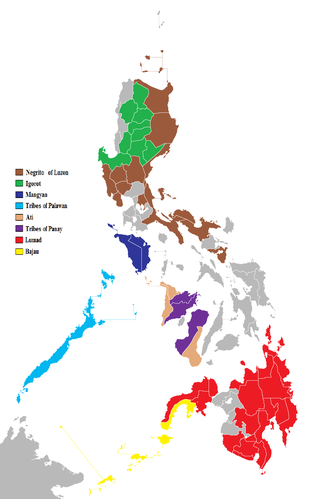
The indigenous peoples of the Philippines are ethnolinguistic groups or subgroups that maintain partial isolation or independence throughout the colonial era, and have retained much of their traditional pre-colonial culture and practices.
Higaonon is a Manobo language spoken on the island of Mindanao in the Philippines. It is partially (80%) intelligible with Binukid.

Pantaron Mountain Range, also called the Central Cordillera of Mindanao, Philippines is a mountain range straddling across the provinces of Misamis Oriental, Bukidnon, Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur, Davao del Norte and Davao del Sur. The range contains one of the last remaining old growth or primary forest blocks in Mindanao. Major rivers on the island also have their headwaters on the mountain range, including Mindanao River, Pulangi River, Davao River, Tagoloan River and major tributaries of Agusan River.




















