The inex is an eclipse cycle of 10,571.95 days. The cycle was first described in modern times by Crommelin in 1901, but was named by George van den Bergh who studied it in detail half a century later. It has been suggested that the cycle was known to Hipparchos. One inex after an eclipse of a particular saros series there will be an eclipse in the next saros series, unless the latter saros series has come to an end.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on May 26, 2040. The northern limb of the moon will pass through the center of the Earth's shadow. This is the second central lunar eclipse of Saros series 131.

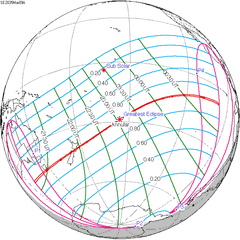
A total lunar eclipse will take place between Monday and Tuesday, June 25-26, 2029. A central total eclipse lasting 1 hour and 41 minutes 53 seconds will plunge the full Moon into deep darkness, as it passes right through the centre of the Earth's umbral shadow. While the visual effect of a total eclipse is variable, the Moon may be stained a deep orange or red color at maximum eclipse. It will be able to be seen from most of the Americas, Western Europe and Africa. The partial eclipse will last for 3 hours and 39 minutes 32 seconds in total.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Friday, August 6, 1971, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 1971. A dramatic total eclipse lasting 1 hour, 39 minutes and 24.8 seconds plunged the full Moon into deep darkness, as it passed right through the centre of the Earth's umbral shadow. While the visual effect of a total eclipse is variable, the Moon may have been stained a deep orange or red colour at maximum eclipse. This was a great spectacle for everyone who saw it. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 35 minutes and 31.9 seconds in total. Occurring only 2.2 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was 3.6% larger than average and the moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow.

A total lunar eclipse will take place between Sunday, September 7 and Monday, September 8, 2025. The Moon will barely miss the center of the Earth's shadow. It will be the second of two total lunar eclipses. Occurring roughly 3 days before perigee, the Moon will appear larger than usual.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, April 13, 1968, the first of two total eclipses in 1968, the second being on October 6, 1968.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on June 6, 2058. The moon will pass through the center of the Earth's shadow.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Sunday, July 26, 1953.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on May 6, 2069. The eclipse will be a dark one with the southern tip of the moon passing through the center of the Earth's shadow. This is the first central eclipse of Saros series 132.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the ascending node of the Moon's orbit on Tuesday, July 2, 2019, with an eclipse magnitude of 1.0459. Totality was visible from the southern Pacific Ocean east of New Zealand to the Coquimbo Region in Chile and Central Argentina at sunset, with the maximum of 4 minutes 33 seconds visible from the Pacific Ocean. The Moon was only 2.4 days before perigee, making it fairly large.

An annular solar eclipse took place on February 26, 2017. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring only 4.7 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. The moon's apparent diameter was just over 0.7% smaller than the Sun's.

A total solar eclipse occurred on July 22, 1990. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in southern Finland, the Soviet Union, and eastern Andreanof Islands and Amukta of Alaska.
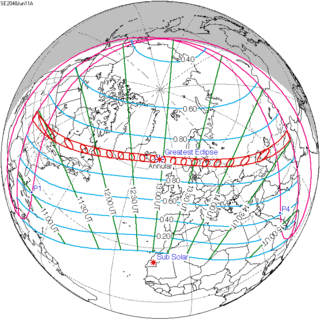
An annular solar eclipse will occur on Thursday, June 11, 2048 with a magnitude of 0.9441. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse occurred on June 30, 1992. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in southeastern Uruguay and southern tip of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on August 11, 1961. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. A small annular eclipse covered only 94% of the Sun in a very broad path, 499 km wide at maximum, and lasted 6 minutes and 35 seconds.
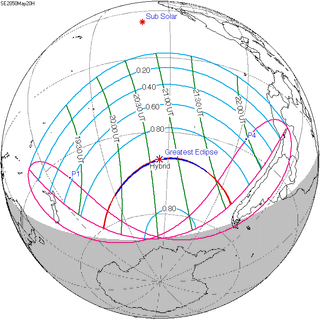
A total solar eclipse will occur on May 20, 2050. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. This eclipse is a hybrid eclipse, starting and ending as an annular solar eclipse.

A total solar eclipse will occur on Saturday, May 22, 2077. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on August 10, 1934, with an eclipse magnitude of 0.9436. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse occurred on September 21, 1903. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse occurred on August 31, 1932. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from Northwest Territories and Quebec in Canada, and northeastern Vermont, New Hampshire, southwestern Maine, northeastern tip of Massachusetts and northeastern Cape Cod in the United States.