
Organ donation is the process when a person allows an organ of their own to be removed and transplanted to another person, legally, either by consent while the donor is alive or dead with the assent of the next of kin.
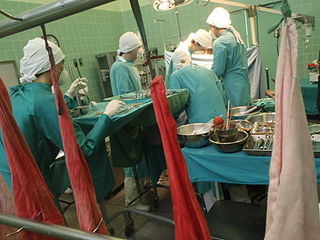
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transported from a donor site to another location. Organs and/or tissues that are transplanted within the same person's body are called autografts. Transplants that are recently performed between two subjects of the same species are called allografts. Allografts can either be from a living or cadaveric source.

United Way is an international network of over 1,800 local nonprofit fundraising affiliates. United Way was the largest nonprofit organization in the United States by donations from the public, prior to 2016.
FreeWill Co is a company whose website, FreeWill.com, has online software which helps people write wills for free and make charitable contributions, and it reports each person's planned bequests to charities which pay subscription fees. It also helps people write advance healthcare directives and living trusts in California.

A donation is a gift for charity, humanitarian aid, or to benefit a cause. A donation may take various forms, including money, alms, services, or goods such as clothing, toys, food, or vehicles. A donation may satisfy medical needs such as blood or organs for transplant.
Gen Con is the largest tabletop game convention in North America by both attendance and number of events. It features traditional pen-and-paper, board, and card games, including role-playing games, miniatures wargames, live action role-playing games, collectible card games, and strategy games. Gen Con also features computer games. Attendees engage in a variety of tournament and interactive game sessions. In 2019, Gen Con had nearly 70,000 unique attendees.

A blood donation occurs when a person voluntarily has blood drawn and used for transfusions and/or made into biopharmaceutical medications by a process called fractionation. Donation may be of whole blood, or of specific components directly (apheresis). Blood banks often participate in the collection process as well as the procedures that follow it.

A gift card also known as gift certificate in North America, or gift voucher or gift token in the UK is a prepaid stored-value money card, usually issued by a retailer or bank, to be used as an alternative to cash for purchases within a particular store or related businesses. Gift cards are also given out by employers or organizations as rewards or gifts. They may also be distributed by retailers and marketers as part of a promotion strategy, to entice the recipient to come in or return to the store, and at times such cards are called cash cards. Gift cards are generally redeemable only for purchases at the relevant retail premises and cannot be cashed out, and in some situations may be subject to an expiry date or fees. American Express, MasterCard, and Visa offer generic gift cards which need not be redeemed at particular stores, and which are widely used for cashback marketing strategies. A feature of these cards is that they are generally anonymous and are disposed of when the stored value on a card is exhausted.
Oblation, meaning "the act of offering; an instance of offering" and by extension "the thing offered", is a term used, particularly in ecclesiastical use, for a solemn offering, sacrifice or presentation to God, to the Church for use in God's service, or to the faithful, such as giving alms to the poor.

Body donation, anatomical donation, or body bequest is the donation of a whole body after death for research and education. Donated bodies are mostly used for medical education and research. They are used for gross anatomy, surgical anatomy and for furthering medical education. For years, only medical schools accepted bodies for donation, but now private programs also accept donors. Depending on the program's need for body donation, some programs accept donors with different specifications.
ActBlue is an American nonprofit technology organization established in June 2004 that enables left-leaning nonprofits, Democratic candidates, and progressive groups to raise money from individual donors on the Internet by providing them with online fundraising software. Its stated mission is to "empower small-dollar donors".
A Catholic funeral is carried out in accordance with the prescribed rites of the Catholic Church. Such funerals are referred to in Catholic canon law as "ecclesiastical funerals" and are dealt with in canons 1176–1185 of the 1983 Code of Canon Law, and in canons 874–879 of the Code of Canons of the Eastern Churches. In Catholic funerals, the Church "seeks spiritual support for the deceased, honors their bodies, and at the same time brings the solace of hope to the living." The Second Vatican Council in its Constitution on the Liturgy decreed: "The rite for the burial of the dead should express more clearly the paschal character of Christian death, and should correspond more closely to the circumstances and traditions found in various regions."
Organ trade is the trading of human organs, tissues, or other body products, usually for transplantation. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), organ trade is a commercial transplantation where there is a profit, or transplantations that occur outside of national medical systems. There is a global need or demand for healthy body parts for transplantation, which exceeds the numbers available.
Organ transplantation in Israel has historically been low compared to other Western countries due to a common belief that organ donation is prohibited under Jewish law. This changed with the passage of new organ donation laws in 2008. If two patients have the same medical need, priority will now go to the patient who has signed an organ donor card, or whose family members have donated an organ. This policy was nicknamed don't give, don't get. The law also defines "brain death" as an indication of death for all legal purposes, including organ donation. Additionally the law provides financial reimbursement to living donors for medical expenses due to donation and lost time at work. Organ trafficking is explicitly banned. Health insurance plans can no longer reimburse patients who go abroad to receive transplants.
A charity gift card allows a gift giver to make a charitable donation that the gift recipient may direct to the charity of their choice. Although a charity gift card has many similarities to a store gift card, a charity gift card functions quite differently. A charity gift card is an indicator of control over a small donor advised fund. The purchaser of the charity gift card creates the donor advised fund with the charity gift card purchase money. When the charity gift card recipient “spends” the gift card, the recipient is in actuality advising the holder of the associated donor advised fund to send the money to the charity that the charity gift card recipient selects.
A charitable organization in Canada is regulated under the Canadian Income Tax Act through the Charities Directorate of the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA).
In the Catholic Church, a Mass stipend is a donation given by the laity to a priest for praying a Mass. Despite the name, it is considered as a gift or offering freely given rather than a payment as such.

MOHAN Foundation is a not-for-profit, registered non-government charity organisation in India that works in the field of deceased organ donation and transplantation. MOHAN is an acronym for Multi Organ Harvesting Aid Network. It has offices in Chennai, Hyderabad, Bengaluru, Delhi, Mumbai, Chandigarh, Nagpur, Jaipur and information centers at Kerala and Imphal.

Carding is a term describing the trafficking and unauthorized use of credit cards. The stolen credit cards or credit card numbers are then used to buy prepaid gift cards to cover up the tracks. Activities also encompass exploitation of personal data, and money laundering techniques. Modern carding sites have been described as full-service commercial entities.
Organ donation in India is regulated by the Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues Act, 1994. The law allows both deceased and living donors to donate their organs. It also identifies brain death as a form of death. The National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO) functions as the apex body for activities of relating to procurement, allotment and distribution of organs in the country.








