In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic; their odor is usually faint, and may be similar to that of gasoline or lighter fluid. They occur in a diverse range of molecular structures and phases: they can be gases, liquids, low melting solids or polymers.

Oil shale is an organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rock containing kerogen from which liquid hydrocarbons can be produced. In addition to kerogen, general composition of oil shales constitutes inorganic substance and bitumens. Based on their deposition environment, oil shales are classified as marine, lacustrine and terrestrial oil shales. Oil shales differ from oil-bearing shales, shale deposits that contain petroleum that is sometimes produced from drilled wells. Examples of oil-bearing shales are the Bakken Formation, Pierre Shale, Niobrara Formation, and Eagle Ford Formation. Accordingly, shale oil produced from oil shale should not be confused with tight oil, which is also frequently called shale oil.
Petroleum geology is the study of the origins, occurrence, movement, accumulation, and exploration of hydrocarbon fuels. It refers to the specific set of geological disciplines that are applied to the search for hydrocarbons.
Basin modelling is the term broadly applied to a group of geological disciplines that can be used to analyse the formation and evolution of sedimentary basins, often but not exclusively to aid evaluation of potential hydrocarbon reserves.

Kerogen is solid, insoluble organic matter in sedimentary rocks. It consists of a variety of organic materials, including dead plants, algae, and other microorganisms, that have been compressed and heated by geological processes. All the kerogen on earth is estimated to contain 1016 tons of carbon. This makes it the most abundant source of organic compounds on earth, exceeding the total organic content of living matter 10,000-fold.
Vitrinite is one of the primary components of coals and most sedimentary kerogens. Vitrinite is a type of maceral, where "macerals" are organic components of coal analogous to the "minerals" of rocks. Vitrinite has a shiny appearance resembling glass (vitreous). It is derived from the cell-wall material or woody tissue of the plants from which coal was formed. Chemically, it is composed of polymers, cellulose and lignin.

Hydrocarbon exploration is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for deposits of hydrocarbons, particularly petroleum and natural gas, in the Earth's crust using petroleum geology.

Organic-rich sedimentary rocks are a specific type of sedimentary rock that contains significant amounts (>3%) of organic carbon. The most common types include coal, lignite, oil shale, or black shale. The organic material may be disseminated throughout the rock giving it a uniform dark color, and/or it may be present as discrete occurrences of tar, bitumen, asphalt, petroleum, coal or carbonaceous material. Organic-rich sedimentary rocks may act as source rocks which generate hydrocarbons that accumulate in other sedimentary "reservoir" rocks. Potential source rocks are any type of sedimentary rock that the ability to dispel available carbon from within it. Good reservoir rocks are any sedimentary rock that has high pore-space availability. This allows the hydrocarbons to accumulate within the rock and be stored for long periods of time. Highly permeable reservoir rocks are also of interest to industry professionals, as they allow for the easy extraction of the hydrocarbons within. The hydrocarbon reservoir system is not complete however without a "cap rock". Cap rocks are rock units which have very low porosity and permeability, which trap the hydrocarbons within the units below as they try to migrate upwards.

The geology of the Falkland Islands is described in several publications. The Falkland Islands are located on a projection of the Patagonian continental shelf. In ancient geological time this shelf was part of Gondwana, which around 400 million years ago broke from what is now Africa and drifted westwards relative to Africa. Studies of the seabed surrounding the islands indicated the possibility of oil. Intensive exploration began in 1996, although there had been some earlier seismic surveys in the region.

The Bend Arch–Fort Worth Basin Province is a major petroleum producing geological system which is primarily located in North Central Texas and southwestern Oklahoma. It is officially designated by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) as Province 045 and classified as the Barnett-Paleozoic Total Petroleum System (TPS).
In petroleum geology, source rock is rock which has generated hydrocarbons or which could generate hydrocarbons. Source rocks are one of the necessary elements of a working petroleum system. They are organic-rich sediments that may have been deposited in a variety of environments including deep water marine, lacustrine and deltaic. Oil shale can be regarded as an organic-rich but immature source rock from which little or no oil has been generated and expelled. Subsurface source rock mapping methodologies make it possible to identify likely zones of petroleum occurrence in sedimentary basins as well as shale gas plays.

Van Krevelen diagrams are graphical plots developed by Dirk Willem van Krevelen and used to assess the origin and maturity of kerogen and petroleum. The diagram cross-plots the hydrogen:carbon atomic ratio as a function of the oxygen:carbon atomic ratio.
Safaniya Oil Field, operated and owned by Saudi Aramco, is the largest offshore oil field in the world. It is located about 265 kilometres (165 mi) north of the company headquarters in Dhahran on the coast of the Persian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Measuring 50 by 15 kilometres, the field has a producing capability of more than 1.2 million barrels per day.

Pyrobitumen is a type of solid, amorphous organic matter. Pyrobitumen is mostly insoluble in carbon disulfide and other organic solvents as a result of molecular cross-linking, which renders previously soluble organic matter insoluble. Not all solid bitumens are pyrobitumens, in that some solid bitumens are soluble in common organic solvents, including CS
2, dichloromethane, and benzene-methanol mixtures.
The Halibut Field is an oil field, within the Gippsland Basin offshore of the Australian state of Victoria. The oil field is located approximately 64 km offshore of southeastern Australia. The total area of this field is 26.9 km2 and is composed of 10 mappable units.
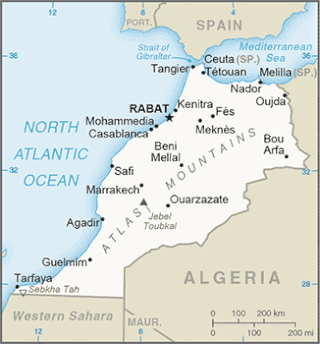
The Tarfaya Basin is a structural basin located in southern Morocco that extends westward into the Moroccan territorial waters in the Atlantic Ocean. The basin is named for the city of Tarfaya located near the border of Western Sahara, a region governed by the Kingdom of Morocco. The Canary Islands form the western edge of the basin and lie approximately 100 km to the west.

The Bolivar Coastal Fields (BCF), also known as the Bolivar Coastal Complex, is located on the eastern margin of Lake Maracaibo, Venezuela. Bolivar Coastal Field is the largest oil field in South America with its 6,000-7,000 wells and forest of related derricks, stretches thirty-five miles along the north-east coast of Lake Maracaibo. They form the largest oil field outside of the Middle East and contain mostly heavy oil with a gravity less than 22 degrees API. Also known as the Eastern Coast Fields, Bolivar Coastal Oil Field consists of Tía Juana, Lagunillas, Bachaquero, Ceuta, Motatán, Barua and Ambrosio. The Bolivar Coast field lies in the Maracaibo dry forests ecoregion, which has been severely damaged by farming and ranching as well as oil exploitation. The oil field still plays an important role in production from the nation with approximately 2.6 million barrels of oil a day. It is important to note that the oil and gas industry refers to the Bolivar Coastal Complex as a single oilfield, in spite of the fact that the oilfield consists of many sub-fields as stated above.
Bituminite is an autochthonous maceral that is a part of the liptinite group in lignite, that occurs in petroleum source rocks originating from organic matter such as algae which has undergone alteration or degradation from natural processes such as burial. It occurs as fine-grained groundmass, laminae or elongated structures that appear as veinlets within horizontal sections of lignite and bituminous coals, and also occurs in sedimentary rocks. Its occurrence in sedimentary rocks is typically found surrounding alginite, and parallel along bedding planes. Bituminite is not considered to be bitumen because its properties are different from most bitumens. It is described to have no definite shape or form when present in bedding and can be identified using different kinds of visible and fluorescent lights. There are three types of bituminite: type I, type II and type III, of which type I is the most common. The presence of bituminite in oil shales, other oil source rocks and some coals plays an important factor when determining potential petroleum-source rocks.
The Officer Basin is an intracratonic sedimentary basin that covers roughly 320,000 km2 along the border between southern and western Australia. Exploration for hydrocarbons in this basin has been sparse, but the geology has been examined for its potential as a hydrocarbon reservoir. This basin's extensive depositional history, with sedimentary thicknesses exceeding 6 km and spanning roughly 350 Ma during the Neoproterozoic, make it an ideal candidate for hydrocarbon production.

The Arkoma Basin is a peripheral foreland basin that extends from central west Arkansas to south eastern Oklahoma. The basin lies in between the Ozark Uplift and Oklahoma Platform to the north and Ouachita Mountains to the south and with an area of approximately 33,800 mi2. Along the southern edge of the basin, the Choctaw Fault is the boundary that separates the mountains from the basin itself. This basin is one of seven that lie along the front of the Ouachita and Appalachian mountain systems. This basin is Oklahoma's fourth largest in terms of natural gas production. Oil has been extracted locally, but not on a commercial scale. Coal was the first natural resource used commercially within the basin. Surface mapping of coal seams in the early part of the 20th century lead to the discovery of sub-surface features that indicated the presence of natural gas. Mansfield, Arkansas was the site of the first natural gas discovery in 1902.











