Related Research Articles
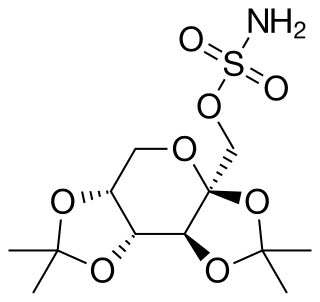
Topiramate, sold under the brand name Topamax among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy and prevent migraines. It has also been used in alcohol dependence and essential tremor. For epilepsy this includes treatment for generalized or focal seizures. It is taken orally.
An anorectic or anorexic is a drug which reduces appetite, resulting in lower food consumption, leading to weight loss. By contrast, an appetite stimulant is referred to as orexigenic.

Dantrolene sodium, sold under the brand name Dantrium among others, is a postsynaptic muscle relaxant that lessens excitation-contraction coupling in muscle cells. It achieves this by inhibiting Ca2+ ions release from sarcoplasmic reticulum stores by antagonizing ryanodine receptors. It is the primary drug used for the treatment and prevention of malignant hyperthermia, a rare, life-threatening disorder triggered by general anesthesia or drugs. It is also used in the management of neuroleptic malignant syndrome, muscle spasticity (e.g. after strokes, in paraplegia, cerebral palsy, or patients with multiple sclerosis), and poisoning by 2,4-dinitrophenol or by the related compounds dinoseb and dinoterb.

2,4-Dinitrophenol (2,4-DNP or simply DNP) is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H3(NO2)2. It has been used in explosives manufacturing and as a pesticide and herbicide.
Anti-obesity medication or weight loss medications are pharmacological agents that reduce or control weight. These medications alter one of the fundamental processes of the human body, weight regulation, by altering either appetite, or absorption of calories. The main treatment modalities for overweight and individuals with obesity remain dieting and physical exercise.
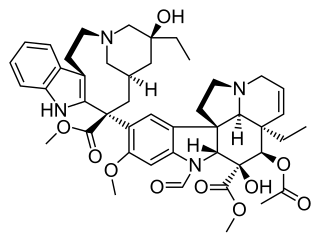
Vincristine, also known as leurocristine and marketed under the brand name Oncovin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, Hodgkin's disease, neuroblastoma, and small cell lung cancer among others. It is given intravenously.

Phentermine (phenyl-tertiary-butylamine), with several brand names including Ionamin and Sentis, is a medication used together with diet and exercise to treat obesity. It is taken by mouth for up to a few weeks at a time, after which the benefits subside. It is also available as the combination phentermine/topiramate.

Sibutramine, formerly sold under the brand name Meridia among others, is an appetite suppressant which has been discontinued in many countries. It works as a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor similar to a tricyclic antidepressant. Until 2010, it was widely marketed and prescribed as an adjunct in the treatment of obesity along with diet and exercise. It has been associated with increased cardiovascular diseases and strokes and has been withdrawn from the market in 2010 in several countries and regions including Australia, Canada, China, the European Union, Hong Kong, India, Mexico, New Zealand, the Philippines, Thailand, the United Kingdom, and the United States. However, the drug remains available in some countries.
Thermogenic means tending to produce heat, and the term is commonly applied to drugs which increase heat through metabolic stimulation, or to microorganisms which create heat within organic waste. Approximately all enzymatic reaction in the human body is thermogenic, which gives rise to the basal metabolic rate.

Oxandrolone, sold under the brand names Oxandrin and Anavar, among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used to help promote weight gain in various situations, to help offset protein catabolism caused by long-term corticosteroid therapy, to support recovery from severe burns, to treat bone pain associated with osteoporosis, to aid in the development of girls with Turner syndrome, and for other indications. It is taken by mouth.

Amfepramone, also known as diethylpropion, is a stimulant drug of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and cathinone classes that is used as an appetite suppressant. It is used in the short-term management of obesity, along with dietary and lifestyle changes. Amfepramone has a similar chemical structure to the antidepressant and smoking cessation aid bupropion, which has also been developed as a weight-loss medicine when in a combination product with naltrexone.
Benfluorex, sold under the brand name Mediator, is an anorectic and hypolipidemic agent that is structurally related to fenfluramine. It may improve glycemic control and decrease insulin resistance in people with poorly controlled type-2 diabetes.

Caroverine is a muscle-relaxing drug used in Austria and Switzerland to relieve spasms in smooth muscles, and the use in those countries was extended to aid with cerebrovascular diseases there, and eventually to treat tinnitus. It is also used to treat tinnitus in India.

Suritozole is an investigational cognition enhancer. It acts as a partial inverse agonist at the benzodiazepine receptor site on the GABAA ion channel complex, but does not have either anxiogenic or convulsant effects, unlike other BZD inverse agonists such as DMCM. It was investigated for the treatment of depression and Alzheimer's disease, but clinical development seems to have been discontinued.
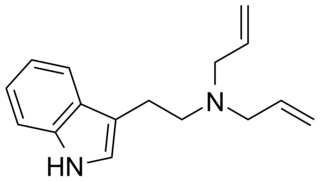
N,N-Diallyltryptamine (DALT) is a tryptamine derivative which has been identified as a new psychoactive substance. It has been used as an intermediate in the preparation of radiolabeled diethyltryptamine.
An uncoupler or uncoupling agent is a molecule that disrupts oxidative phosphorylation in prokaryotes and mitochondria or photophosphorylation in chloroplasts and cyanobacteria by dissociating the reactions of ATP synthesis from the electron transport chain. The result is that the cell or mitochondrion expends energy to generate a proton-motive force, but the proton-motive force is dissipated before the ATP synthase can recapture this energy and use it to make ATP. Uncouplers are capable of transporting protons through mitochondrial and lipid membranes.
A calorie deficit is any shortage in the number of calories consumed relative to the number of calories needed for maintenance of current body weight.
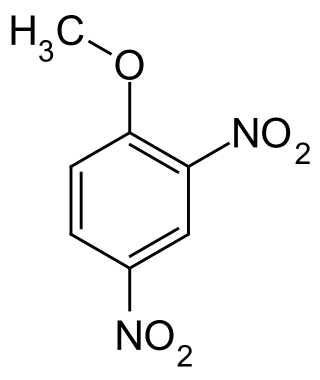
2,4-Dinitroanisole (DNAN) is a low sensitivity organic compound. It has an anisole (methoxybenzene) core, with two nitro groups (–NO2) attached.

Setmelanotide, sold under the brand name Imcivree, is a medication used for the treatment of genetic obesity caused by a rare single-gene mutation.
Nicholas Bachynsky is a Russian-born American former doctor and convicted fraudster. In the 1980s, he ran a weight loss clinic in Texas where he provided the unlicensed drug 2,4-Dinitrophenol (DNP) to patients under the name "Mitcal"; court filings reported that he had treated 14,000 people with the drug. Many reported adverse effects. After one patient died of an overdose in 1984, Bachynsky was convicted and fined for violating drug laws. Despite this, he continued to dispense DNP. In 2008, he was convicted of fraud for his role in a scheme to sell DNP.
References
- 1 2 "Medical News". Journal of the American Medical Association. 122 (4): 243. 22 May 1943. doi:10.1001/jama.1943.02840210035014.
- ↑ Swann, John P. (2010). "Reducing with dinitrophenol : self-medication, and the challenge of regulating a dangerous pharmaceutical before the US Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act". Perspectives on Twentieth-century Pharmaceuticals. Peter Lang. p. 286. ISBN 978-3-03910-920-3.
- ↑ Sousa, Daniela; Carmo, Helena; Roque Bravo, Rita; Carvalho, Félix; Bastos, Maria de Lourdes; Guedes de Pinho, Paula; Dias da Silva, Diana (April 2020). "Diet aid or aid to die: an update on 2,4-dinitrophenol (2,4-DNP) use as a weight-loss product". Archives of Toxicology. 94 (4): 1071–1083. doi:10.1007/s00204-020-02675-9.
- ↑ "Maurice L. Tainter". BioScience. 16 (10): 687. 1 October 1966. doi:10.1093/bioscience/16.10.687.