
The Islamic State (IS), also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) and by its Arabic acronym Daesh, is a transnational Salafi jihadist group and a former unrecognised quasi-state. Its origins were in the Jai'sh al-Taifa al-Mansurah organization founded by Abu Omar al-Baghdadi in 2004, which fought alongside al-Qaeda during the Iraqi insurgency. The group gained global prominence in 2014, when its militants successfully captured large territories in northwestern Iraq and eastern Syria, taking advantage of the ongoing Syrian civil war. By the end of 2015, it ruled an area with an estimated population of twelve million people, where it enforced its extremist interpretation of Islamic law, managed an annual budget exceeding US$1 billion, and commanded more than 30,000 fighters.
The following is a timeline of the Syrian civil war from August to December 2014. Information about aggregated casualty counts is found at Casualties of the Syrian Civil War.

Many states began to intervene against the Islamic State, in both the Syrian Civil War and the War in Iraq (2013–2017), in response to its rapid territorial gains from its 2014 Northern Iraq offensives, universally condemned executions, human rights abuses and the fear of further spillovers of the Syrian Civil War. These efforts are called the War against the Islamic State, or the War against ISIS. In later years, there were also minor interventions by some states against IS-affiliated groups in Nigeria and Libya. All these efforts significantly degraded the Islamic State's capabilities by around 2019–2020. While moderate fighting continues in Syria, as of 2024, ISIS has been contained to a manageably small area and force capability.

On 22 September 2014, the United States officially intervened in the Syrian civil war with the stated aim of fighting the Islamic State as part of Operation Inherent Resolve in the international war against the Islamic State. The U.S. also supports the Syrian rebels and the Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces opposed to both the Islamic State and Syrian president Bashar al-Assad.

Operation Shader is the operational code name given to the contribution of the United Kingdom in the ongoing military intervention against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant. The operation involves the British Army providing ground support and training to allied forces fighting against ISIL, the Royal Air Force providing humanitarian aid airdrops, reconnaissance and airstrikes, and the Royal Navy providing reconnaissance and airstrikes from the UK Carrier Strike group and escort to allied carrier battle groups.

On 15 June 2014, U.S. President Barack Obama ordered United States forces to be dispatched in response to the Northern Iraq offensive of the Islamic State (IS) as part of Operation Inherent Resolve. At the invitation of the Iraqi government, American troops went to assess Iraqi forces and the threat posed by ISIL.

Operation Inherent Resolve (OIR) is the United States military's operational name for the international war against the Islamic State (IS), including both a campaign in Iraq and a campaign in Syria, with a closely related campaign in Libya. Through 18 September 2018, the U.S. Army's III Armored Corps was responsible for Combined Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve (CJTF—OIR) and were replaced by the XVIII Airborne Corps. The campaign is primarily waged by American and British forces in support of local allies, most prominently the Iraqi security forces and Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF). Combat ground troops, mostly special forces, infantry, and artillery have also been deployed, especially in Iraq. Of the airstrikes, 70% have been conducted by the military of the United States, 20% by the United Kingdom and the remaining 10% being carried out by France, Turkey, Canada, the Netherlands, Denmark, Belgium, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Australia and Jordan.
Abu Sayyaf was the nom de guerre of a senior leader of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) who was described as overseeing gas and oil operations. United States authorities identified Abu Sayyaf's real name as Fathi Ben Awn Ben Jildi Murad al-Tunisi. Abu Sayyaf was killed on the night of May 15–16, 2015 while resisting capture during a United States Army Delta Force operation in eastern Syria.

The Mosul offensive (2015) was an offensive launched by Kurdish Peshmerga forces on 21 January 2015, with the objective of severing key ISIL supply routes to Mosul, Iraq, and to recapture neighboring areas around Mosul. The effort was supported by US-led coalition airstrikes. The Iraqi Army was widely expected to launch the planned operation to retake the actual city of Mosul in the Spring of 2015, but the offensive was postponed to October 2016, after Ramadi fell to ISIL in May 2015.
Nasrin As'ad Ibrahim, better known by the nom de guerreUmm Sayyaf, is the widow of Abu Sayyaf. She was captured in May 2015 by US Delta Force soldiers on the mission where they killed her husband, a suspected leader of the Islamic State.
The following is a timeline of the Syrian Civil War from January to July 2015. Information about aggregated casualty counts is found at Casualties of the Syrian Civil War.
Oil production and smuggling was the largest source of revenue for the finances of the Islamic State in Syria and Iraq until the complete loss of its territory in 2019. Most oil extracted was distributed for use within the Islamic State, but some was also smuggled to surrounding states at below market price.

Operation Tidal Wave II was a US-led coalition military operation beginning on or about 21 October 2015 against oil transport, refining and distribution facilities and infrastructure under the control of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant. Targets included transport trucks, operated by middlemen, which previously were not usually targeted.
In early 2014, the jihadist group Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant captured extensive territory in Western Iraq in the Anbar campaign, while counter-offensives against it were mounted in Syria. Raqqa in Syria became its headquarters. The Wall Street Journal estimated that eight million people lived under its control in the two countries.
This article contains a timeline of events from January 2015 to December 2015 related to the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL/ISIS). This article contains information about events committed by or on behalf of the Islamic State, as well as events performed by groups who oppose them.
Collaboration with the Islamic State refers to the cooperation and assistance given by governments, non-state actors, and private individuals to the Islamic State (IS) during the Syrian Civil War, Iraqi Civil War, and Libyan Civil War.
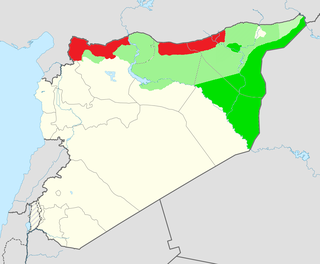
The Eastern Syria insurgency is an armed insurgency being waged by remnants of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) and both pro and anti-Syrian government Arab nationalist insurgents, against the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (AANES), its military, and their allies in the US-led Combined Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve (CJTF–OIR) coalition.

The US intervention in the Syrian civil war is the United States-led support of Syrian opposition and the Federation of Northern Syria during the course of the Syrian Civil War and active military involvement led by the United States and its allies — the militaries of the United Kingdom, France, Jordan, Turkey, Canada, Australia and more — against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) and al-Nusra Front since 2014. Since early 2017, the U.S. and other Coalition partners have also targeted the Syrian government and its allies via airstrikes and aircraft shoot-downs.








