Related Research Articles

Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to hedge against the risk of a contingent or uncertain loss.

Medicare is a government national health insurance program in the United States, begun in 1965 under the Social Security Administration (SSA) and now administered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). It primarily provides health insurance for Americans aged 65 and older, but also for some younger people with disability status as determined by the SSA, including people with end stage renal disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Health insurance or medical insurance is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among many individuals. By estimating the overall risk of health risk and health system expenses over the risk pool, an insurer can develop a routine finance structure, such as a monthly premium or payroll tax, to provide the money to pay for the health care benefits specified in the insurance agreement. The benefit is administered by a central organization, such as a government agency, private business, or not-for-profit entity.
In an insurance policy, the deductible is the amount paid out of pocket by the policy holder before an insurance provider will pay any expenses. In general usage, the term deductible may be used to describe one of several types of clauses that are used by insurance companies as a threshold for policy payments.
A health savings account (HSA) is a tax-advantaged medical savings account available to taxpayers in the United States who are enrolled in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP). The funds contributed to an account are not subject to federal income tax at the time of deposit. Unlike a flexible spending account (FSA), HSA funds roll over and accumulate year to year if they are not spent. HSAs are owned by the individual, which differentiates them from company-owned Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRA) that are an alternate tax-deductible source of funds paired with either high-deductible health plans or standard health plans.

In business and accounting, net income is an entity's income minus cost of goods sold, expenses, depreciation and amortization, interest, and taxes for an accounting period.
Long-term care insurance is an insurance product, sold in the United States, United Kingdom and Canada that helps pay for the costs associated with long-term care. Long-term care insurance covers care generally not covered by health insurance, Medicare, or Medicaid.
The healthcare in Switzerland is universal and is regulated by the Swiss Federal Law on Health Insurance. There are no free state-provided health services, but private health insurance is compulsory for all persons residing in Switzerland.
In the United States, a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) is a health insurance plan with lower premiums and higher deductibles than a traditional health plan. It is intended to incentivize consumer-driven healthcare. Being covered by an HDHP is also a requirement for having a health savings account. Some HDHP plans also offer additional "wellness" benefits, provided before a deductible is paid. High-deductible health plans are a form of catastrophic coverage, intended to cover for catastrophic illnesses. Adoption rates of HDHPs have been growing since their inception in 2004, not only with increasing employer options, but also increasing government options. As of 2016, HDHPs represented 29% of the total covered workers in the United States; however, the impact of such benefit design is not widely understood.
Health care in Australia operates under a shared public-private model underpinned by the Medicare system, the national single-payer funding model. State and territory governments operate public health facilities where eligible patients receive care free-of-charge. Primary health services, such as GP clinics, are privately owned in most situations, but attract Medicare rebates. Australian citizens, permanent residents, and some visitors and visa holders are eligible for health services under the Medicare system. Individuals are encouraged through tax surcharges to purchase health insurance to cover services offered in the private sector, and further fund health care.
Health insurance in the United States is any program that helps pay for medical expenses, whether through privately purchased insurance, social insurance, or a social welfare program funded by the government. Synonyms for this usage include "health coverage", "health care coverage", and "health benefits". In a more technical sense, the term "health insurance" is used to describe any form of insurance providing protection against the costs of medical services. This usage includes both private insurance programs and social insurance programs such as Medicare, which pools resources and spreads the financial risk associated with major medical expenses across the entire population to protect everyone, as well as social welfare programs like Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program, which both provide assistance to people who cannot afford health coverage.

Health insurance coverage in the United States is provided by several public and private sources. During 2019, the U.S. population overall was approximately 330 million, with 59 million people 65 years of age and over covered by the federal Medicare program. The 273 million non-institutionalized persons under age 65 either obtained their coverage from employer-based or non-employer based sources, or were uninsured. During the year 2019, 89% of the non-institutionalized population had health insurance coverage. Separately, approximately 12 million military personnel received coverage through the Veteran's Administration and Military Health System.
A loss ratio is a ratio of losses to gains, used normally in a financial context. It is the opposite of the gross profit ratio.
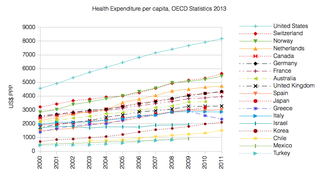
The French health care system is one of universal health care largely financed by government national health insurance. In its 2000 assessment of world health care systems, the World Health Organization found that France provided the "best overall health care" in the world. In 2017, France spent 11.3% of GDP on health care, or US$5,370 per capita, a figure higher than the average spent by rich countries, though similar to Germany (10.6%) and Canada (10%), but much less than in the US. Approximately 77% of health expenditures are covered by government funded agencies.
The healthcare reform debate in the United States has been a political issue focusing upon increasing medical coverage, decreasing costs, insurance reform, and the philosophy of its provision, funding, and government involvement.
Capitation is a payment arrangement for health care service providers. It pays a set amount for each enrolled person assigned to them, per period of time, whether or not that person seeks care. The amount of remuneration is based on the average expected health care utilization of that patient, with payment for patients generally varying by age and health status.
There were a number of different health care reforms proposed during the Obama administration. Key reforms address cost and coverage and include obesity, prevention and treatment of chronic conditions, defensive medicine or tort reform, incentives that reward more care instead of better care, redundant payment systems, tax policy, rationing, a shortage of doctors and nurses, intervention vs. hospice, fraud, and use of imaging technology, among others.
Health insurance costs in the United States are a major factor in access to health coverage. The rising cost of health insurance leads more consumers to go without coverage and increase in insurance cost and accompanying rise in the cost of health care expenses has led health insurers to provide more policies with higher deductibles and other limitations that require the consumer to pay a greater share of the cost themselves.
Healthcare in the United States is far outspent than any other nation, measured both in per capita spending and as a percentage of GDP. Despite this, the country has significantly worse healthcare outcomes when compared to peer nations. The US is the only developed nation without a system of universal healthcare, with a large proportion of its population not carrying health insurance, a substantial factor in the country's excess mortality.
Health care finance in the United States discusses how Americans obtain and pay for their healthcare, and why U.S. healthcare costs are the highest in the world based on various measures.
References
- ↑ Slee, Vergil N. and H. Joachim Schmidt. (2007) Slee's Health Care Terms. Boston: Jones & Bartlett Publishers p. 344. ISBN 0-7637-4615-0