
Asphalt, also known as bitumen, is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term asphaltum was also used. The word is derived from the Ancient Greek ἄσφαλτος ásphaltos. The largest natural deposit of asphalt in the world, estimated to contain 10 million tons, is the Pitch Lake located in La Brea in southwest Trinidad, within the Siparia Regional Corporation.

Oil sands, tar sands, crude bitumen, or bituminous sands, are a type of unconventional petroleum deposit. Oil sands are either loose sands or partially consolidated sandstone containing a naturally occurring mixture of sand, clay, and water, soaked with bitumen, a dense and extremely viscous form of petroleum.

The Athabasca oil sands, also known as the Athabasca tar sands, are large deposits of bitumen or extremely heavy crude oil, located in northeastern Alberta, Canada – roughly centred on the boomtown of Fort McMurray. These oil sands, hosted primarily in the McMurray Formation, consist of a mixture of crude bitumen, silica sand, clay minerals, and water. The Athabasca deposit is the largest known reservoir of crude bitumen in the world and the largest of three major oil sands deposits in Alberta, along with the nearby Peace River and Cold Lake deposits.

Melville Island is an uninhabited island of the Arctic Archipelago with an area of 42,149 km2 (16,274 sq mi). It is the 33rd largest island in the world and Canada's eighth largest island.
Unconventional oil is petroleum produced or extracted using techniques other than the conventional method. Industry and governments across the globe are investing in unconventional oil sources due to the increasing scarcity of conventional oil reserves. Unconventional oil and gas have already made a dent in international energy linkages by reducing US energy import dependency.

Petroleum production in Canada is a major industry which is important to the economy of North America. Canada has the third largest oil reserves in the world and is the world's fourth largest oil producer and fourth largest oil exporter. In 2019 it produced an average of 750,000 cubic metres per day (4.7 Mbbl/d) of crude oil and equivalent. Of that amount, 64% was upgraded and non-upgraded bitumen from oil sands, and the remainder light crude oil, heavy crude oil and natural-gas condensate. Most of Canadian petroleum production is exported, approximately 600,000 cubic metres per day (3.8 Mbbl/d) in 2019, with 98% of the exports going to the United States. Canada is by far the largest single source of oil imports to the United States, providing 43% of US crude oil imports in 2015.
Steam-assisted gravity drainage is an enhanced oil recovery technology for producing heavy crude oil and bitumen. It is an advanced form of steam stimulation in which a pair of horizontal wells is drilled into the oil reservoir, one a few metres above the other. High pressure steam is continuously injected into the upper wellbore to heat the oil and reduce its viscosity, causing the heated oil to drain into the lower wellbore, where it is pumped out. Dr. Roger Butler, engineer at Imperial Oil from 1955 to 1982, invented the steam assisted gravity drainage (SAGD) process in the 1970s. Butler "developed the concept of using horizontal pairs of wells and injected steam to develop certain deposits of bitumen considered too deep for mining". In 1983 Butler became director of technical programs for the Alberta Oil Sands Technology and Research Authority (AOSTRA), a crown corporation created by Alberta Premier Lougheed to promote new technologies for oil sands and heavy crude oil production. AOSTRA quickly supported SAGD as a promising innovation in oil sands extraction technology.

Wabasca is an oil field in a remote area of northern Alberta, Canada. It is the fourth largest deposit of oil sands located in Alberta, located southwest of the larger Athabasca oil sands deposit. It is also known as the Pelican Lake Oilfield.
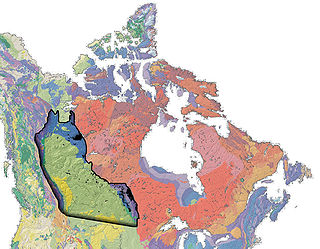
The Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin (WCSB) underlies 1.4 million square kilometres (540,000 sq mi) of Western Canada including southwestern Manitoba, southern Saskatchewan, Alberta, northeastern British Columbia and the southwest corner of the Northwest Territories. This vast sedimentary basin consists of a massive wedge of sedimentary rock extending from the Rocky Mountains in the west to the Canadian Shield in the east. This wedge is about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) thick under the Rocky Mountains, but thins to zero at its eastern margins. The WCSB contains one of the world's largest reserves of petroleum and natural gas and supplies much of the North American market, producing more than 450 million cubic metres per day of gas in 2000. It also has huge reserves of coal. Of the provinces and territories within the WCSB, Alberta has most of the oil and gas reserves and almost all of the oil sands.

Canada's oil sands and heavy oil resources are among the world's great petroleum deposits. They include the vast oil sands of northern Alberta, and the heavy oil reservoirs that surround the small city of Lloydminster, which sits on the border between Alberta and Saskatchewan. The extent of these resources is well known, but better technologies to produce oil from them are still being developed.

Oil reserves in Canada were estimated at 172 billion barrels as of the start of 2015 . This figure includes the oil sands reserves that are estimated by government regulators to be economically producible at current prices using current technology. According to this figure, Canada's reserves are third only to Venezuela and Saudi Arabia. Over 95% of these reserves are in the oil sands deposits in the province of Alberta. Alberta contains nearly all of Canada's oil sands and much of its conventional oil reserves. The balance is concentrated in several other provinces and territories. Saskatchewan and offshore areas of Newfoundland in particular have substantial oil production and reserves. Alberta has 39% of Canada's remaining conventional oil reserves, offshore Newfoundland 28% and Saskatchewan 27%, but if oil sands are included, Alberta's share is over 98%.
The Clearwater Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Early Cretaceous (Albian) age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in northeastern Alberta, Canada. It was first defined by R.G. McConnell in 1893 and takes its name from the Clearwater River near Fort McMurray.

The McMurray Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Early Cretaceous age of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in northeastern Alberta. It takes the name from Fort McMurray and was first described from outcrops along the banks of the Athabasca River 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) north of Fort McMurray by F.H. McLearn in 1917. It is a well-studied example of fluvial to estuarine sedimentation, and it is economically important because it hosts most of the vast bitumen resources of the Athabasca Oil Sands region.
The Duvernay Formation is a stratigraphical unit of Frasnian age in the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin.

The Cold Lake oil sands are a large deposit of oil sands located near Cold Lake, Alberta. Cold Lake is east of Alberta's capital, Edmonton, near Alberta's border with Saskatchewan, and a small portion of the Cold Lake field lies in Saskatchewan.
Marie Bay is a fjord on the Northwest tip of Melville Island. Marie Bay lies on the part of Melville Island that is in the Northwest Territories. The Eastern part of the Island is in Nunavut.
The Bjorne Formation is a formation of sandstones and shales in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The southern edge of the formation includes petroleum reserves in Melville Island. The basin also includes Mackenzie King Island, Lougheed Island and portions of Prince Patrick Island, Borden Island, Ellef Ringnes Island, Amund Ringnes Island, and Cornwall Island.

The Beaver Lake Cree Nation is a First Nations band government located 105 kilometres (65 mi) northeast of Edmonton, Alberta, representing people of the Cree ethno-linguistic group in the area around Lac La Biche, Alberta, where the band office is currently located. Their treaty area is Treaty 6. The Intergovernmental Affairs office consults with persons on the Government treaty contacts list. There are two parcels of land reserved for the band by the Canadian Crown, Beaver Lake Indian Reserve No. 131 and Blue Quills First Nation Indian Reserve. The latter reserve is shared by six bands; Beaver Lake Cree Nations, Cold Lake First Nations, Frog Lake First Nation, Heart Lake First Nation, Kehewin Cree Nation, Saddle Lake Cree Nation.

Located in northwest-central Alberta, the Peace River oil sands deposit is the smallest of four large deposits of oil sands of the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin formation.






